Table of Contents
DC Motor
A DC motor is a machine which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy is known as DC motor.

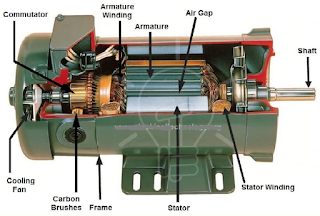
Construction of DC Motor
The construction of DC motor have following main parts :
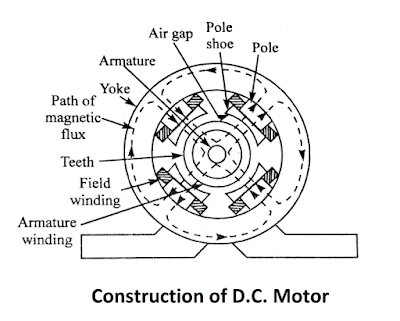
1. Yoke :- It is made of cast iron for small machines & cast steel or rolled steel for large machines. Yoke provides space for providing poles for magnetic flux & it carries the magnetic flux produced by the poles.
2. Pole Core :- The pole core is made of cast iron of solid piece or cast steel. The pole core may be made of thin cast steel laminations riveted together. This type of pole is held in position with frame by means of bolts.
3. Pole Shoe :- The pole shoe is laminated & is screwed to the pole face means of counter sunk screws. Its main purpose is to spread the magnetic flux in air gap more uniformly.
4. Field Coil :- Enamelled copper wire is used for the construction of field coils. The coil is wound on the former & then placed around the pole core.
5. Armature :- Armature is the rotating part of DC machine. Active winding is placed on the armature. The core of the armature is made of steel laminations, which are circular in shape. Slots are provided on the armature to house conductor or armature winding.
6. Armature Winding :- The insulated conductors housed in the armature slots are suitable connected. This is known as armature winding. The armature winding is the heart of DC machines. In DC machines two types of winding are used :
- Lap Winding
- Wave Winding
7. Commutators :- It supplies d.c. current from supply to the armature windings. It is mounted on the shaft of the DC machine. It has wedge shaped copper segments. These segments are insulated from each other by mica. Every segments of commutator is connected to armature coil by using a copper lugs. Number of commutator segments is equals to the number of armature coils.
8. Brushes :- It collects the current from DC source & supply it to the armature through commutator. The carbon brushes are used. These are held in their position with the help of brush holder. They have a continues contact with the rotating commutator. These need regular adjustment of contact pressure which can be adjusted with the help of an adjustable spring.
9. Shaft & Bearings :- All the rotating parts such as armature & commutator are mounted on mild steel shaft. The shaft is supported on bearing at both ends. The function of the bearing is to reduce friction between the rotating & stationary parts of the machine.
10. Terminal Box :- Terminal box is mounted on the yoke of machine. Connecting leads are brought from brushes to the terminals box to be connected to the DC supply.
Working Principle of DC Motor
The working of a DC motor is based on the principle that when a current is passed through a conductor which lies in a magnetic field, it experiences a force whose direction is given by Fleming’s Left Hand Rule & its magnitude is given by the relation, F = BIL newtons
where,
B = Magnetic flux density in weber/sq. meter
I = Current in conductor in amperes
L = Length of conductor in meters
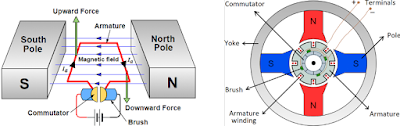
When its field magnets are excited & armature conductors are supplied current from a separate source, they experience a force tending to rotate the armature. Armature conductors under north-pole are assumed to carry current downwards (crosses) & those under south-pole to carry current upward (dots). The direction of this force is given by Fleming’s Left Hand Rule (also known as motor rule). It is seen that each conductor experiences a force F which tends to rotate the armature in anti-clockwise direction . These forces combine & produce driving torque to keep the armature rotating.
Read Also :
- Single Phase Induction Motor | Double Revolving Field Theory
- Three Phase Induction Motor || Construction & Working Principle
- B.Tech – MDU Previous Year Question Papers Download











Comments (1)
It’s going to be finish of mine day, however before end I am reading this great post to increase my experience.