Table of Contents
MOSFET
The MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) transistor is a semiconductor device that is widely used for switching purposes and for the amplification of electronic signals in electronic devices.
MOSFET is a voltage-controlled device, meaning by applying a rated voltage to the gate pin, the MOSFET will start conducting through the Drain and Source.
Symbol of MOSFET
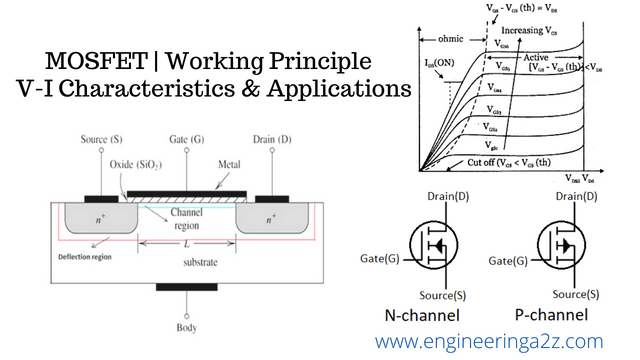
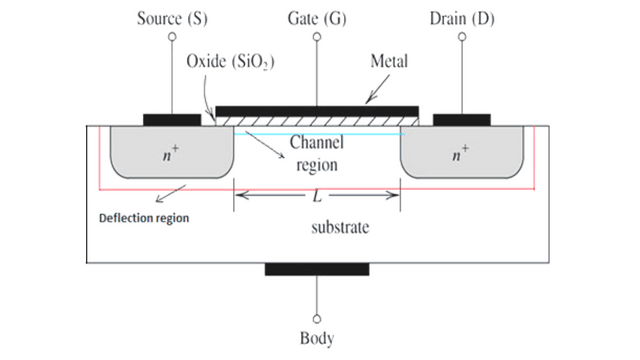
In general, the MOSFET is a four-terminal device with a Drain (D), Source (S), gate (G) and a Body (B) / Substrate terminals. The body terminal will always be connected to the source terminal hence, the MOSFET will operate as a three-terminal device.
Types of MOSFET
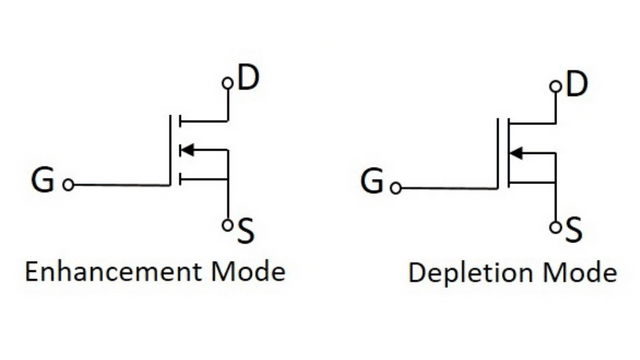
- Enhancement Mode MOSFET (E-MOSFET)
- Depletion Mode MOSFET (D-MOSFET)
Enhancement Mode MOSFET (E-MOSFET)
When there is no voltage across the gate terminal, then the device does not conduct. When there is the maximum voltage across the gate terminal, then the device shows enhanced conductivity.
Depletion Mode MOSFET (D-MOSFET)
When there is no voltage across the gate terminal, the channel shows its maximum conductance. Whereas when the voltage across the gate terminal is either positive or negative , then the channel conductivity decreases.
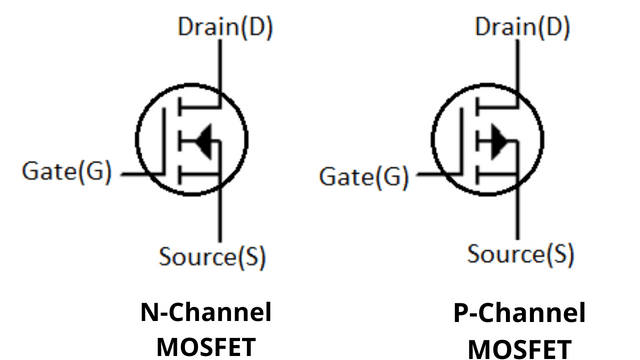
These MOSFETs are further classified based on the material used for construction as n-channel and p-channel. So, in general, there are 4 different types of MOSFETs.
- N-Channel Depletion Mode MOSFET
- P-Channel Depletion Mode MOSFET
- N-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFET
- P-Channel Enhancement Mode MOSFET
According to the internal construction of a MOSFET, the Gate(G), Drain (D), and Source(S) pins are physically connected in a Depletion Mode MOSFET, while they are physically separated in Enhancement Mode, this is the reason why the symbol appears broken for an Enhancement Mode MOSFET.
Working Principle of MOSFET
The main principle of the MOSFET device is to be able to control the voltage & current flow between the source & drain terminals. It works almost like a switch & the functionality of the device is based on the MOS capacitor. The MOS capacitor is the main part of MOSFET.
V-I Characteristics of MOSFET
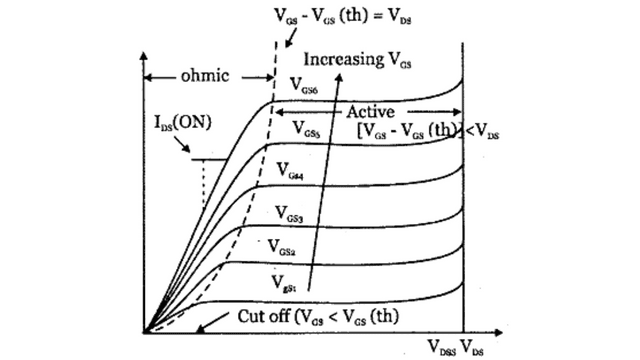
In general, any MOSFET is seen to exhibit three operating regions viz.,
Cut-Off Region :- Cut-off region is a region in which the MOSFET will be OFF as there will be no current flow through it. In this region, MOSFET behaves like an open switch and is thus used when they are required to function as electronic switches.
Ohmic or Linear Region :- Cut-off region is a region in which the MOSFET will be OFF as there will be no current flow through it. In this region, MOSFET behaves like an open switch and is thus used when they are required to function as electronic switches.
Saturation Region :- This is the region in which transistor trends to behave as an open switch. The transistor has the effect of its Collector and Emitter being shorted. The Collector and Emitter currents are maximum in this mode of operation.
Applications of MOSFET
- It is used as an inverter.
- It can be used in digital circuit.
- MOSFET can be used as a high frequency amplifier.
- It can be used in electronics DC relay.
- It can be used in brushless DC motor drive.
- It is used in switch mode power supply (SMPS).
Read Also :
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
- SCR | Silicon Controlled Rectifier
- DIAC | Diode for Alternating Current
- B.Tech – MDU Previous Year Question Papers Download






Comments (1)
I got this website from my buddy who told me
on the topic of this site and now this time I am visiting this website
and reading very informative posts at this place.