Table of Contents
Thermal Power Plant
The thermal power plant is main source of electric power generation in our country. In this power plant, the heat energy is converted into electric energy. The heat energy generated by burning of fuel mostly coal is used to heat water and generate steam. This generated steam runs the turbine and this turbine works as a prime mover, gives mechanical power to the alternator. Thermal power generation requires coal and enough quantity of water for cooling purpose.
Thermal Power Plant Working
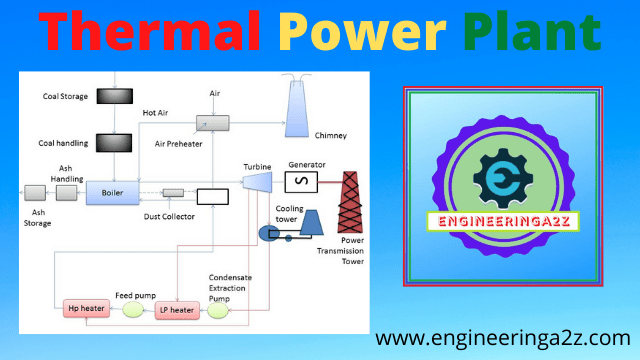
The working of thermal power plant starts with the arrival of coal. Coal stored in a coal storage passes to the furnace through the coal handling plant for the generation of heat energy, and the ash resulting from combustion of coal collected at the back of boiler and is removed to the ash storage yard through ash handling equipment. The heat energy generated by the burning of coal is used to heat the water in the boiler and converts it into a wet steam.
This wet steam passes to superheater, where the wet steam changes to superheated steam. When the high pressure and temperature, superheated steam passes through the turbine, it gets expanded and moves the prime mover or turbine. With the turbine, a generator is attached by a shaft, which rotates to generate electricity.
Thermal Power Plant Diagram
Components of Thermal Power Plant
1. Boiler
Boiler is used for producing steam under pressure. Water tube boilers are generally used for this purpose.
2. Super heater
It convert wet steam into superheated steam .Steam is superheated in it before passing from the boiler to the prime movers to attain an increased efficiency.
3. Economiser
In economiser, heat in flue gases is partially used to heat incoming feed water. It makes use of remaining heat of the gases in heating the feed water.
4. Turbine
The function of the turbine is to convert the heat energy of steam into mechanical energy of the shaft. Turbine works as a prime mover for the generator.
5. Condenser
In the condenser, low pressure steam is condensed into water. It condenses steam used by the steam turbine. The condensed steam known as condensate is used as a feed water.
6. Evaporator
Make up water in the raw form is passed through evaporator which hears it to steam and is then condensed back to water, which then enters the feed water system.
7. Alternator
The Alternator is coupled to the turbine The function of the Alternator is to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. After passing through transformer, the electrical output from the alternator is delivered to the Bus-bars.
8. Feed Water Pump
It pumps water in the water tubes of boiler against boiler steam pressure.
9. Air Preheater
In air preheater, heat in flue gases is partially used to heat incoming air.
10. Cooling Tower
It cools the condenser circulating water. Condenser cooling water absorbs heat from steam. This heat is discharged to atmosphere in cooling water.
Salient Features Of Steam Power Plant
The thermal efficiency of power plant is as low as 30%. Overall efficiency of the power station which is the product of Generator efficiency. Turbine efficiency and Boiler efficiency, is 18% to 29%. This low efficiency of the power station is due to
- Heat lost in condenser.
- Heat losses at various stages.
The steam power plant for generation of electric power is preferred, where large amount of power is required to be generated (normally in the form of AC at about 11.000 volts) and financial, climatic and geographical conditions do not permit the installation hydroelectric power plant whereas coal is available in plenty.
The Vindhyachal Thermal Power Station in the Singrauli district of Madhya Pradesh, with an installed capacity of 4760 MW , is currently the biggest thermal power plant in India and Mejia Thermal Power Station has an installed capacity of 2430 MW which is at durlabhpur, Bankura inn West Bengal.
Advantages of Thermal Power Plant
- Less space is required as compared to hydro-electric power station
- Cheaper in initial cost as compared to other power stations. Its cost varies from Rs. 1200 to Rs. 1400 per kW of installed capacity.
- The fuel used is cheaper.
- It is possible to install these plants near the load centres.
- In comparison to diesel power station, the cost of generation is low.
Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plant
- Higher running cost as compared to hydro electric plants.
- It creates pollution.
- Large area is required for disposing off ash.
Selection of Site For Thermal Power Station
- The steam power stations should be installed at a site preferably near large number of consumers or load centre.
- Adequate cooling water must be available at the site.
- The transport cost of the fuel should be less as possible.
- These must be an proper arrangement for disposing off the ash.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why super heated steam is used in thermal power plant?
The super heated steam is used in thermal power plant because it increases the overall efficiency of plant and too much condensation in the last stages of turbine is avoided. The heated steam from the super heater is fed to steam turbine through the main valve.
What is NTPC full form?
NTPC stands for National Thermal Power Corporation Private limited. The total installed capacity of the company is 66,900 MW (including JVs) own stations include 24 coal based, 7 gas based, 1 Hydro, 1 Wind, 13 Solar and 1 Small hydro plant. NTPC has 9 coal based, 4 gas based and 13 renewable energy projects.
Which is the biggest thermal power plant in India?
The Vindhyachal Thermal Power Plant in the Singrauli district of Madhya Pradesh, with an installed capacity of 4760 MW , is currently the biggest thermal power plant in India.
What is economiser in thermal power plant?
Economiser is a mechanical device which is used in saving of coal consumption and higher boiler efficiency. In economiser, heat in flue gases is partially used to heat incoming feed water. It makes use of remaining heat of the gases in heating the feed water.






Comments (6)
Great content.
Thanks for your lovely comment
Do you mіnd if I quote a few of your posts aѕ
long as I provide credit and sources back to your webpage?
My wеƅsite is in the very same area of interest as yours and my users would certainly
benefit from some of the information you provide here.
Pleaѕe lеt me know if this alright with you. Appreciate it!
Please send the URL of your website in our contact form and you can use it by giving credit to us.
constantly i used to read smaller articles or reviews that also clear their motive, and that is also happening with this article which I am reading here.
This article provides a clear and concise explanation of the principles and working of thermal power plants! The breakdown of the functions of various components is particularly well done, making it an excellent resource for learners and professionals alike.