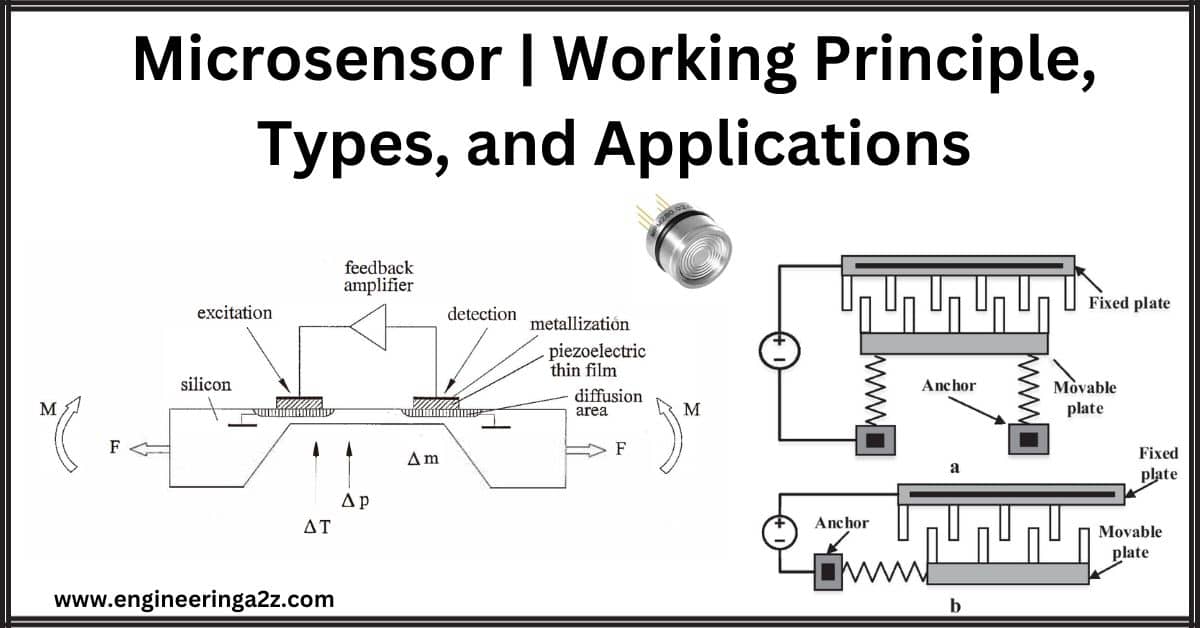
Microsensor | Working Principle, Types, and Applications
Introduction A microsensor is a minuscule device built to sense and measure specific physical properties…
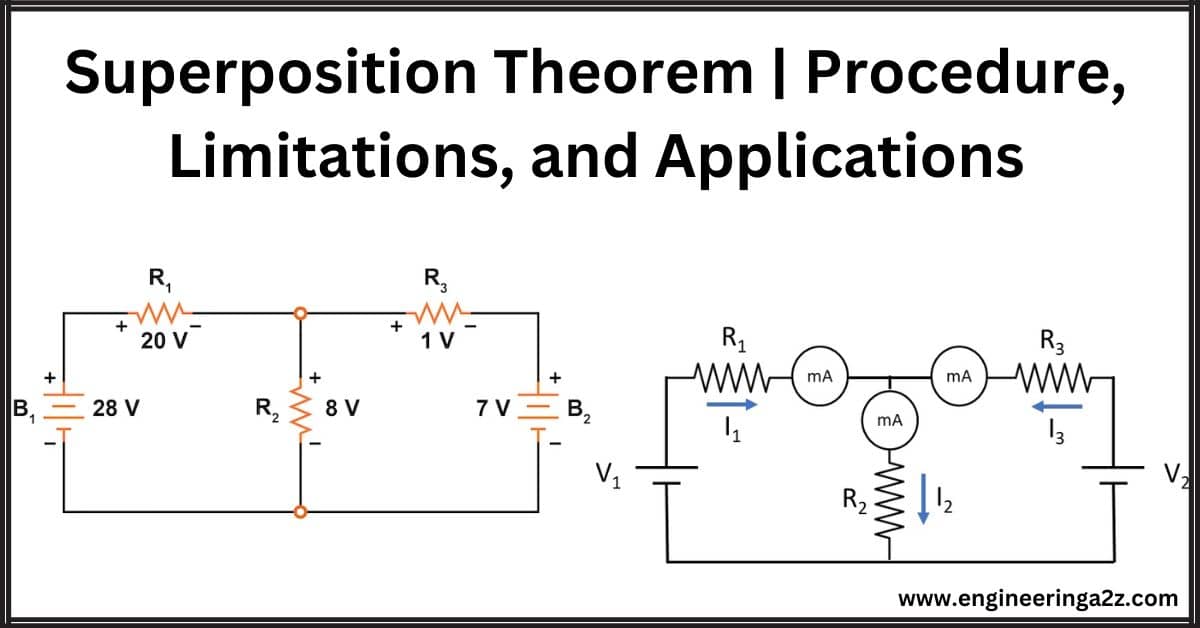
Superposition Theorem | Procedure, Limitations, and Applications
Introduction The superposition theorem states that the voltage or current in any part of a linear…
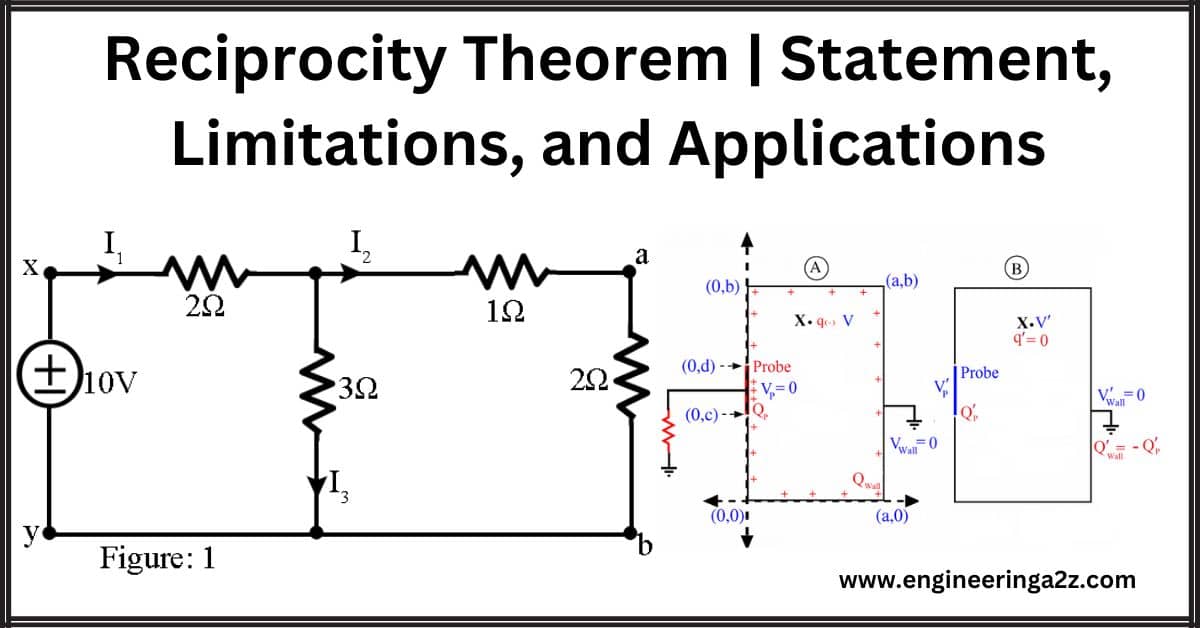
Reciprocity Theorem | Statement, Limitations, and Applications
Introduction The reciprocity theorem in electrical networks says that if you have a bunch of…
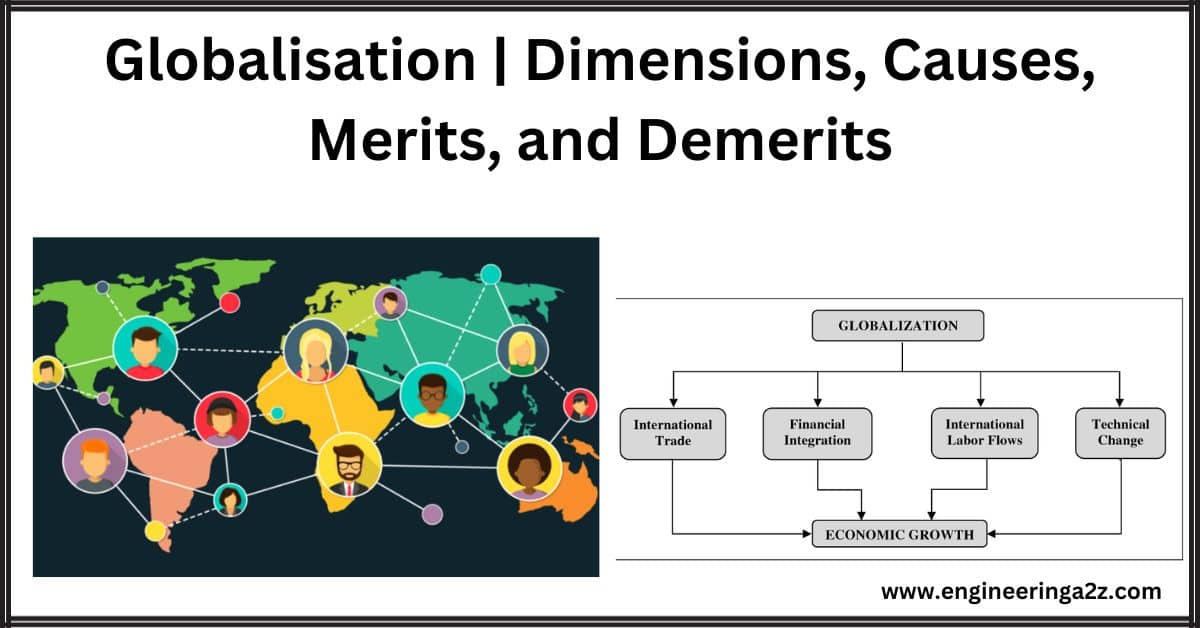
Globalisation | Dimensions, Causes, Merits, and Demerits
Introduction Globalization means that countries are becoming more connected to the global economy. In the…
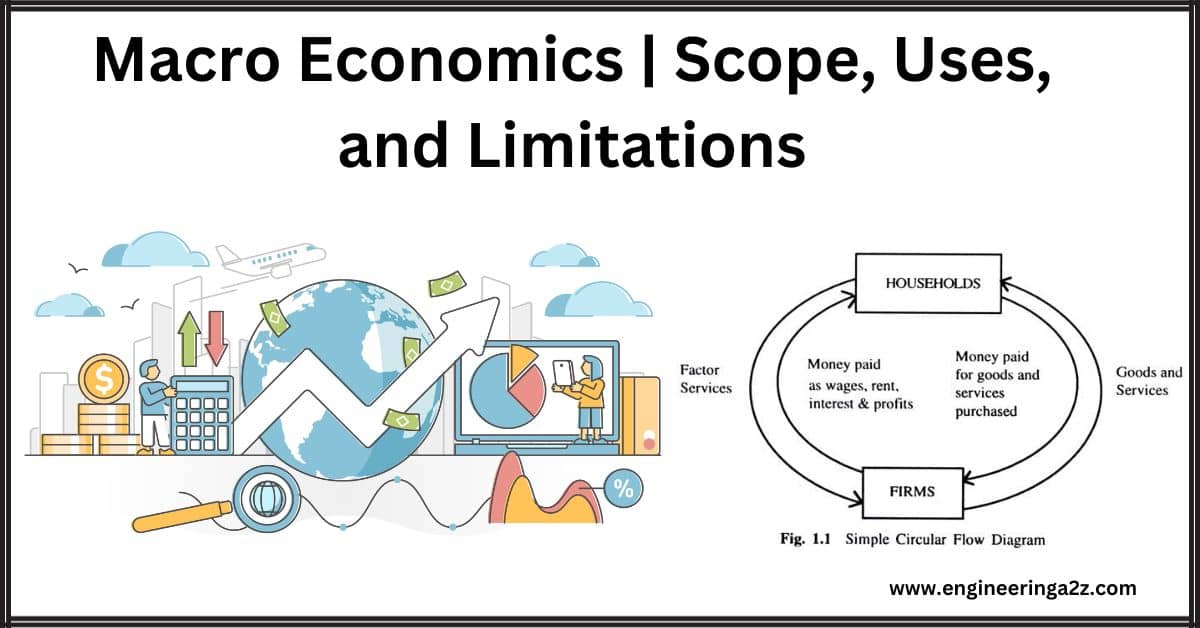
Macro Economics | Scope, Uses, and Limitations
'Macro' as used in the English language originates in the Greek word Makros, meaning large.…
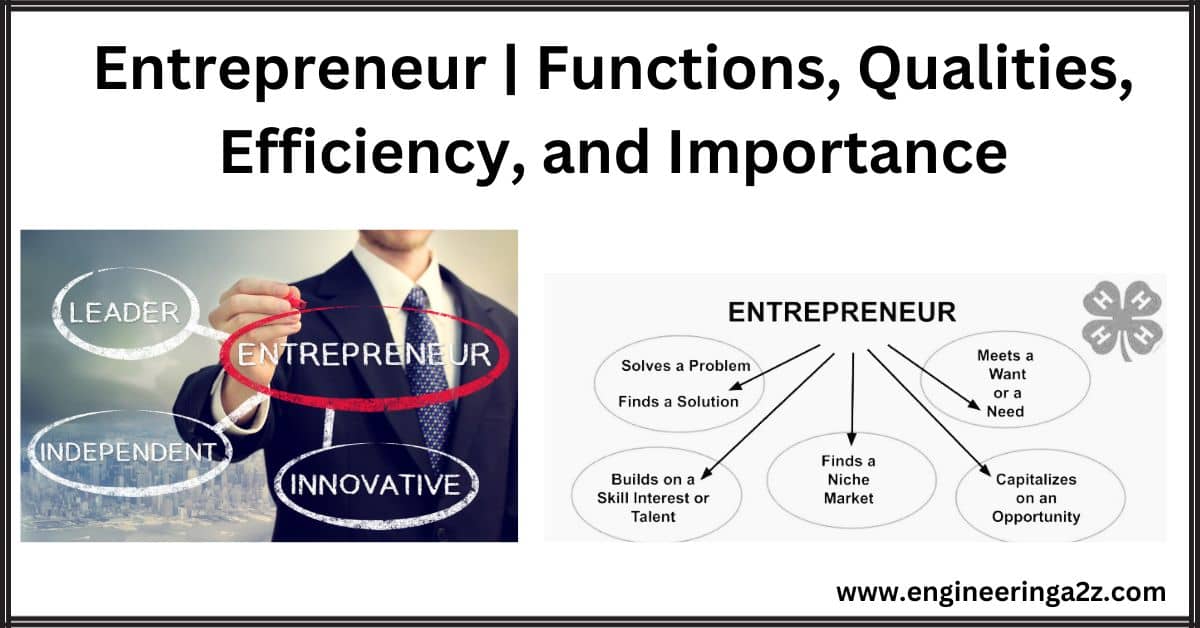
Entrepreneur | Functions, Qualities, Efficiency, and Importance
Entrepreneur In the modern age, the significance of the entrepreneur as a factor of production…
Division of Labour | Main Forms, Advantages, and Favourable Conditions
Introduction Adam Smith came up with the idea that people should do what they're best…
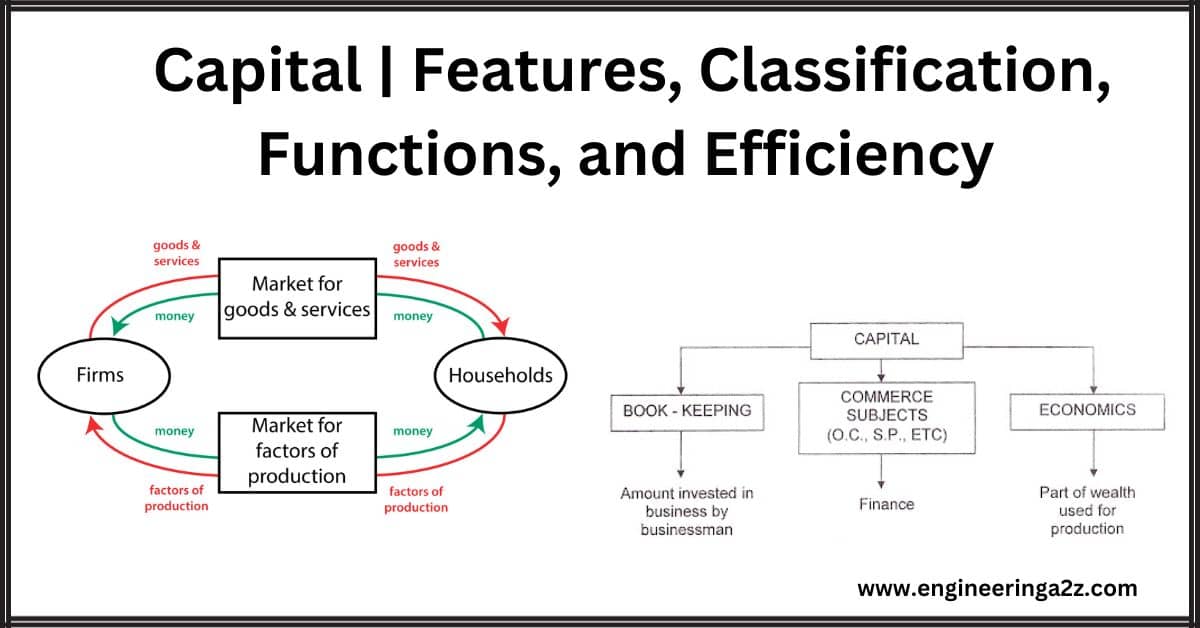
Capital | Features, Classification, Functions, and Efficiency
Capital Capital is a crucial factor in production. In everyday language, we often use terms…
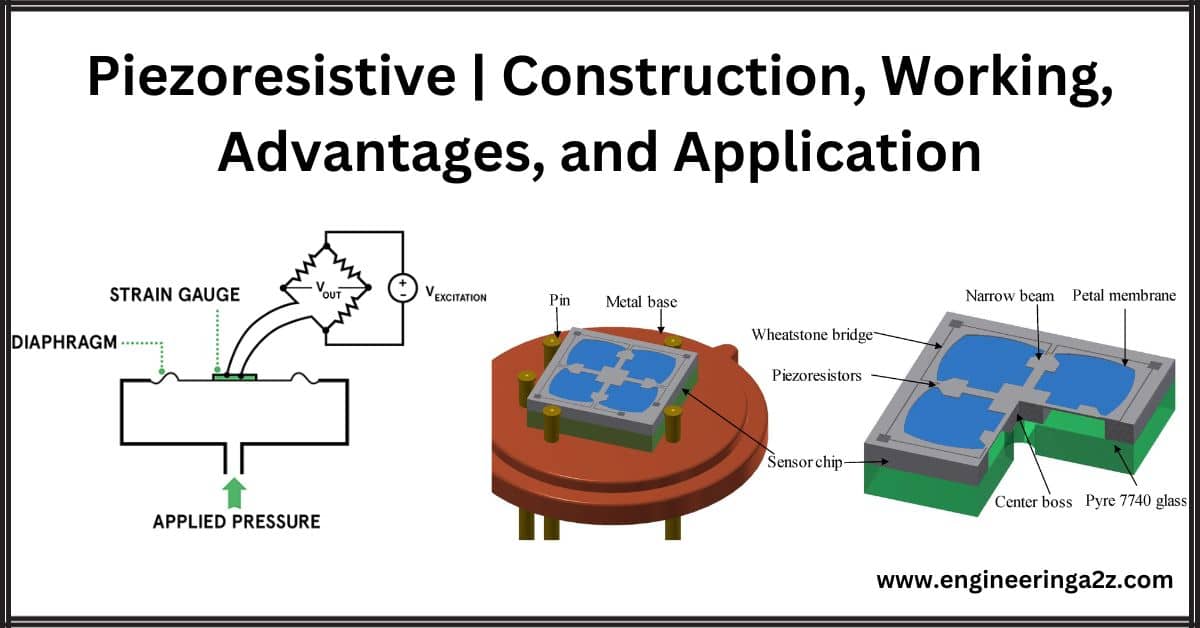
Piezoresistive | Construction, Working, Advantages, and Application
Piezoresistive Piezoresistive materials are substances that exhibit changes in electrical resistance when subjected to mechanical…
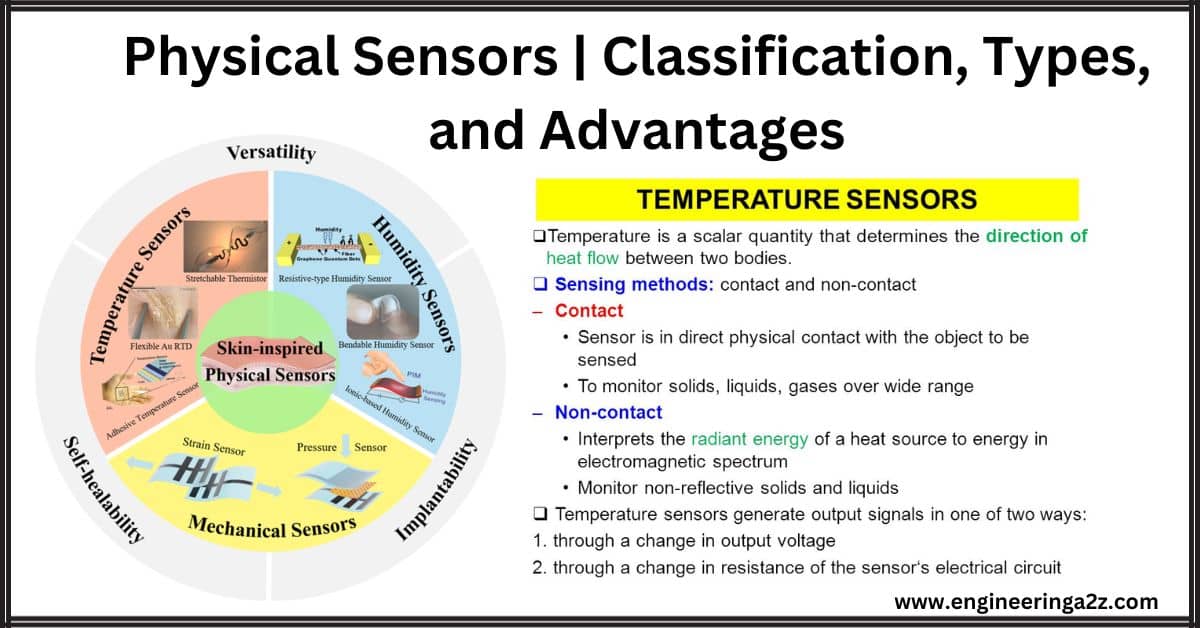
Physical Sensors | Classification, Types, and Advantages
Introduction Physical sensors are devices that detect and respond to physical input from the environment.…










Comments