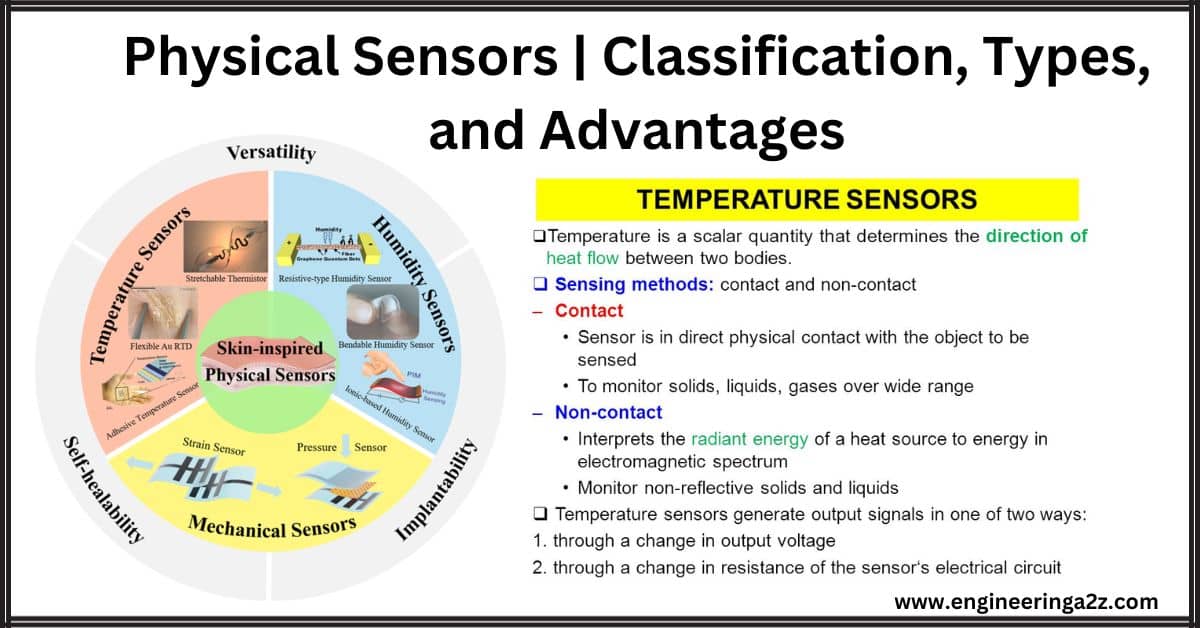
Physical Sensors | Classification, Types, and Advantages
Introduction Physical sensors are devices that detect and respond to physical input from the environment.…
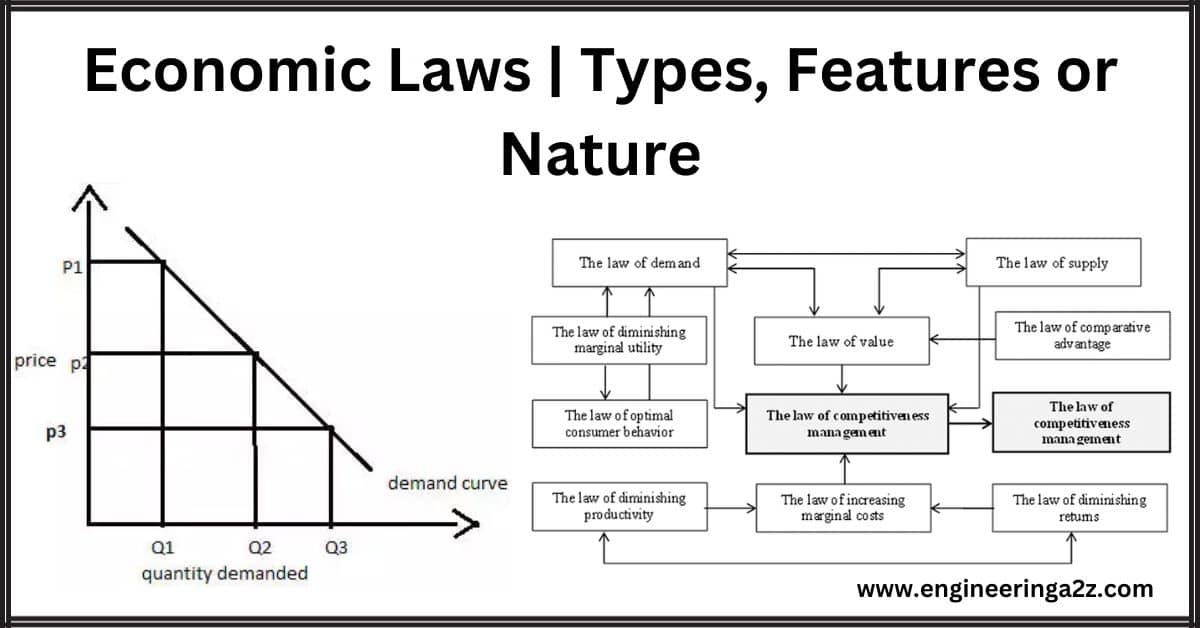
Economic Laws | Types, Features or Nature
Introduction Like all other sciences, economics collects facts and undertakes systematic study. The facts are…
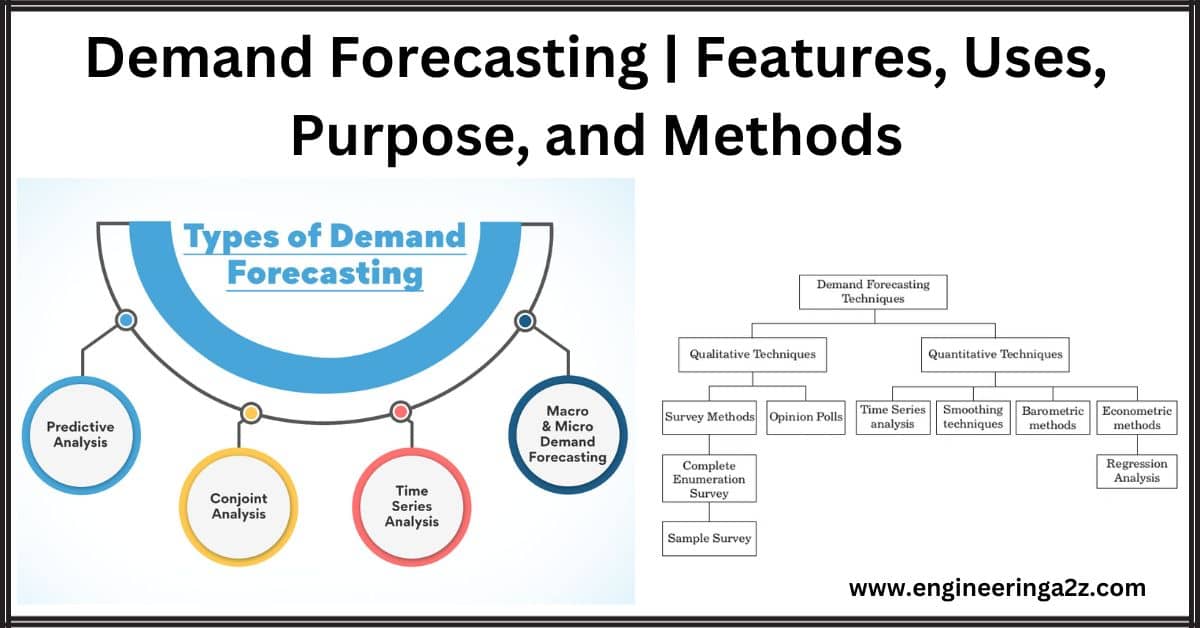
Demand Forecasting | Features, Uses, Purpose, and Methods
A forecast, particularly in the context of demand forecasting, is a prediction or estimation of…
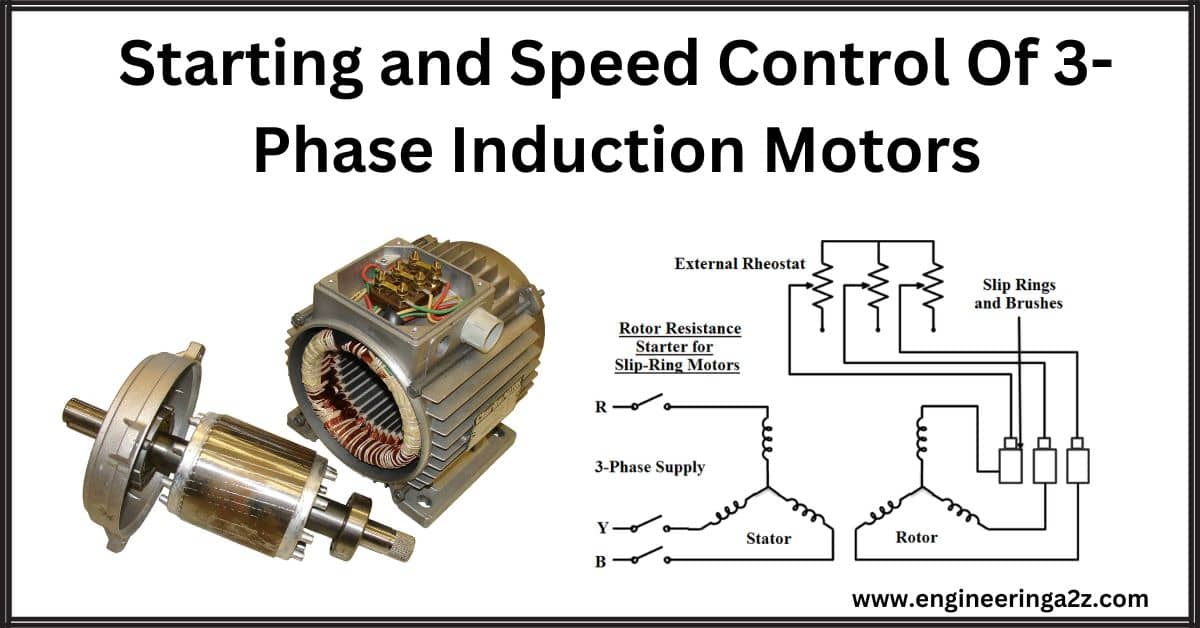
Starting and Speed Control Methods of 3-Phase Induction Motors
Introduction A three-phase induction motor has a kind of electrical "resistance" when it starts, which…
Energy Conservation | Principle, Importance and Its Benefits
Introduction Energy conservation means using less energy by being smarter with how we use it.…
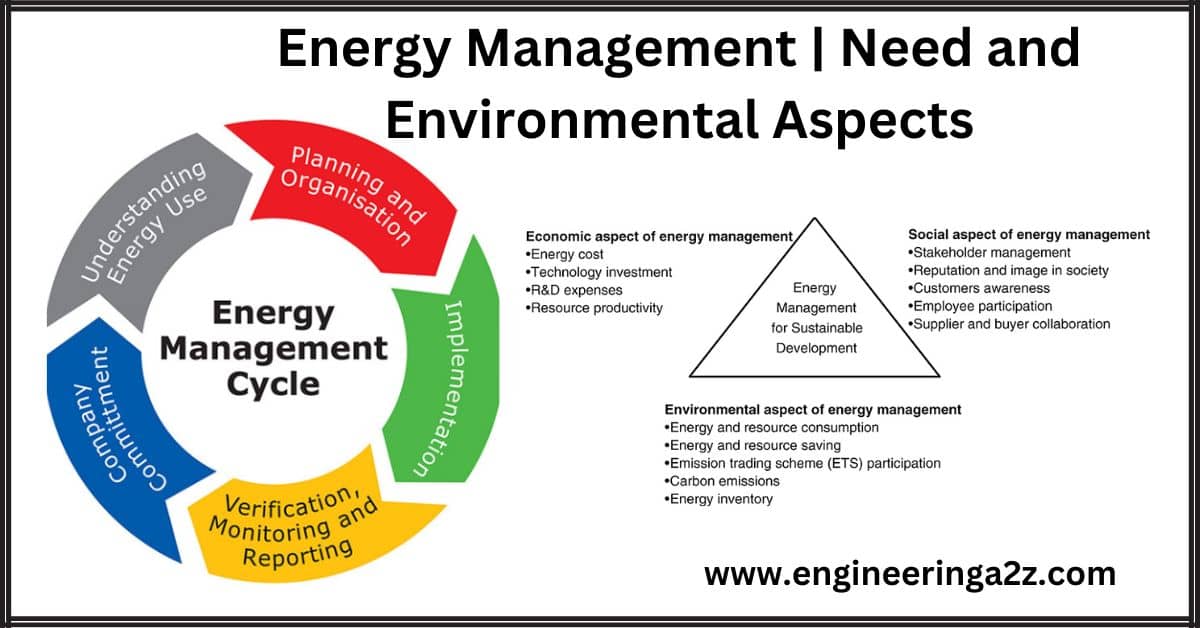
Energy Management | Need and Environmental Aspects
Energy Management The term energy management refers to the saving of energy. This notably means…
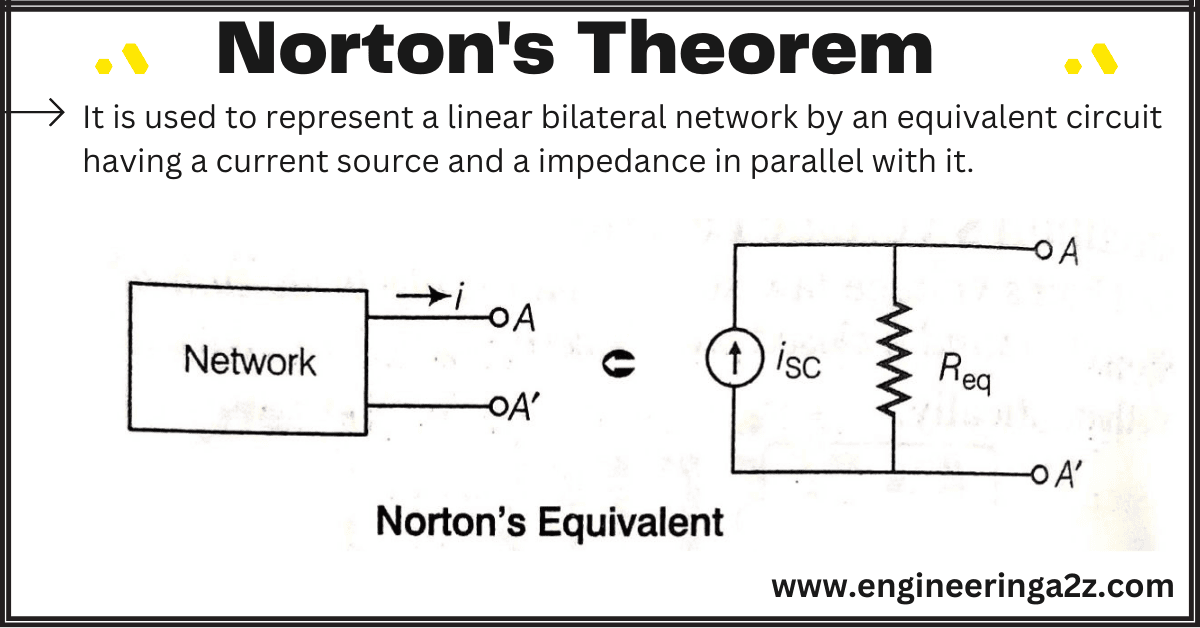
Norton’s Theorem
Circuit Theorem Circuit theorems are fundamental principles and mathematical techniques utilized in the analysis and…
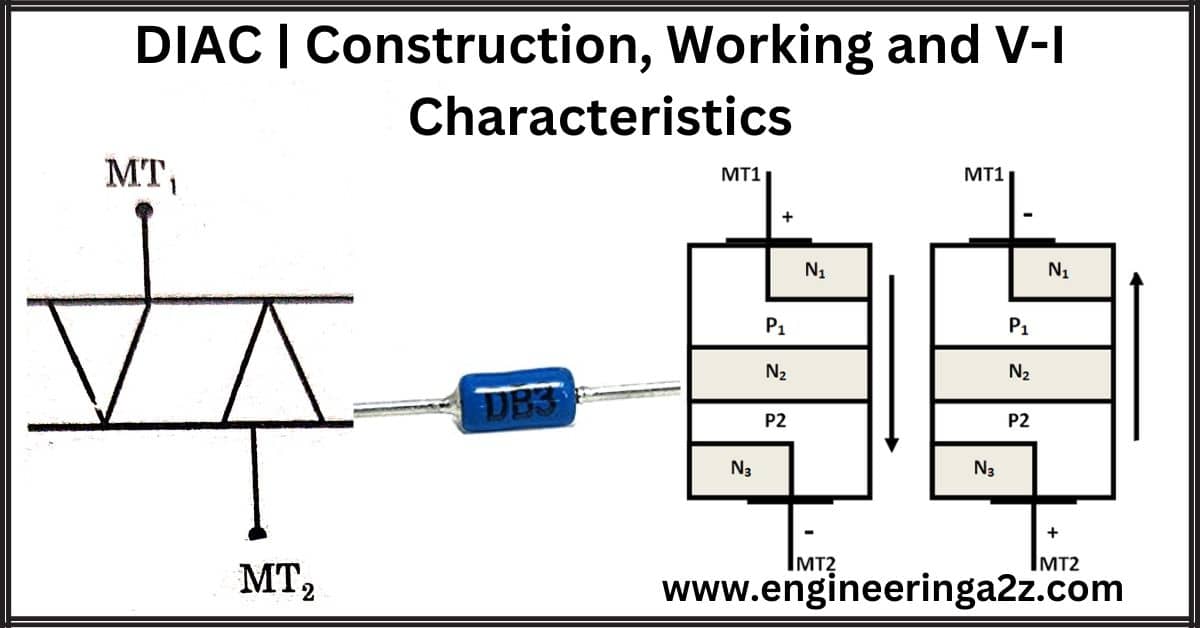
DIAC | Construction | Working and V-I Characteristics
DIAC DIAC can be abbreviated as Diode for alternating current. A DIAC is a bidirectional…
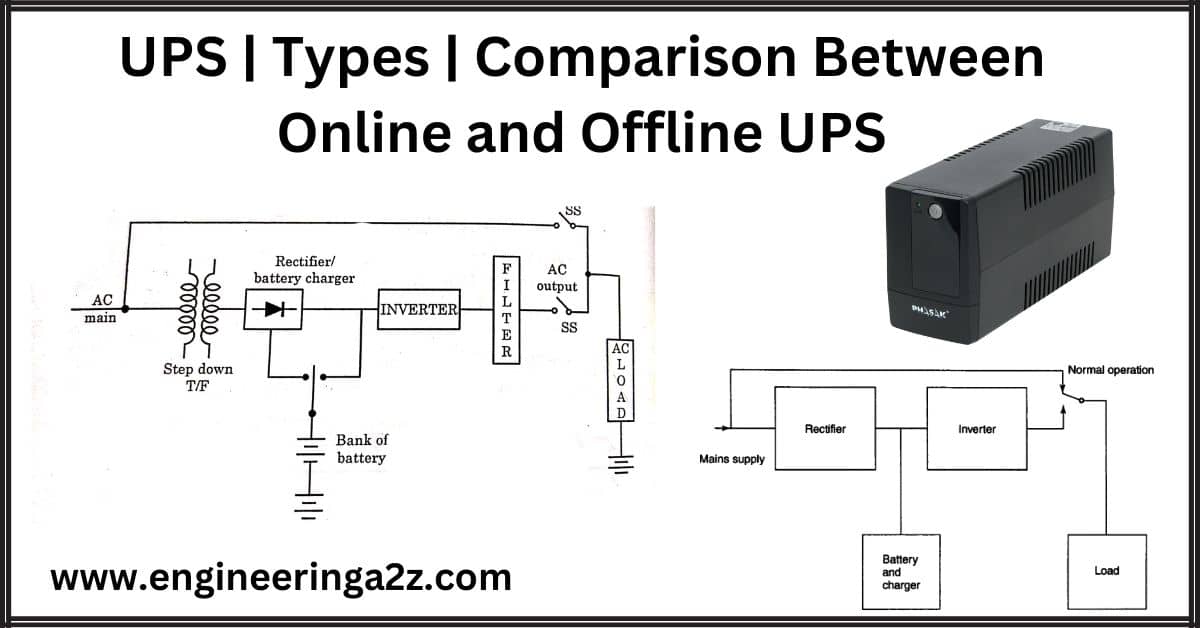
UPS | Types | Comparison Between Online and Offline UPS
UPS UPS stands for Uninterruptible Power Supply as the name suggests is an arrangement to…
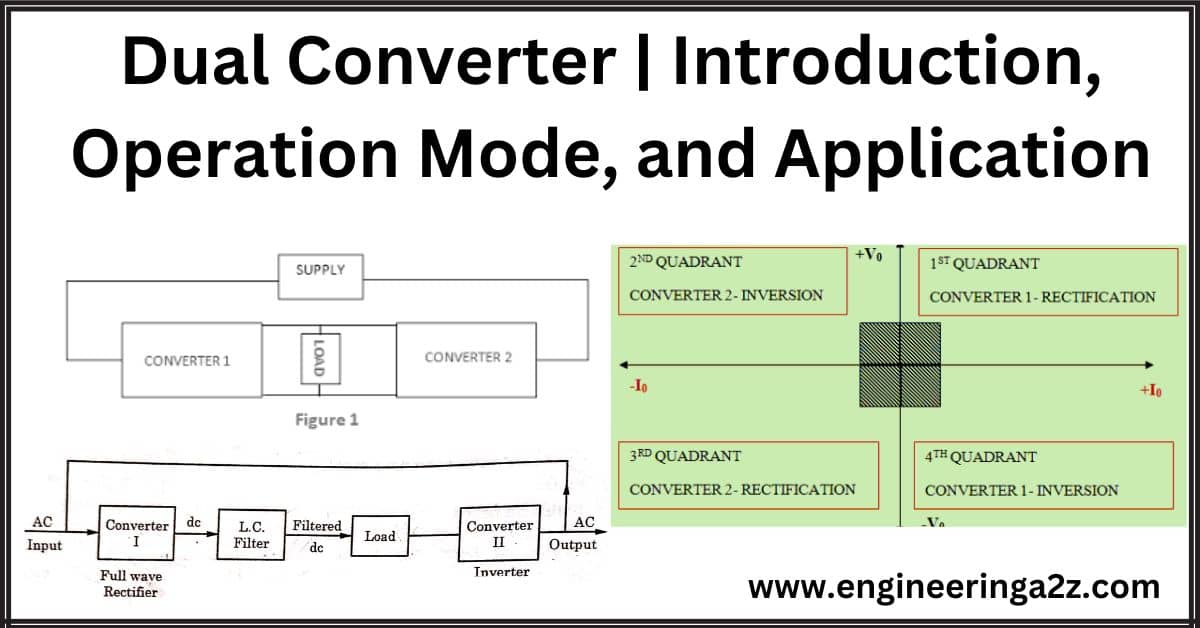
Dual Converter | Introduction, Operation Mode and Application
Dual Converter A dual converter is generally used to get reversible DC for a given…







Comments