Pyrolysis | Basic Principles, Types and Uses
Introduction Pyrolysis is a process that breaks down organic material at temperatures between 400 °C…
Radar | Block Diagram, Working Principle and it’s Applications
Radar RADAR stands for "Radio Detection and Ranging System". Radar is a detection system that…
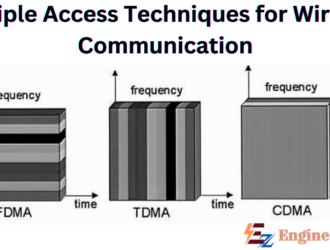
Multiple Access Techniques for Wireless Communication
Multiple Access Techniques Multiple Accessing is also called Multiple Destinations because the transmission from each…
OSI Model | Seven Layers Of OSI Model and Working
OSI Model OSI stands for open system interconnection. A computer network establishes a connection between…
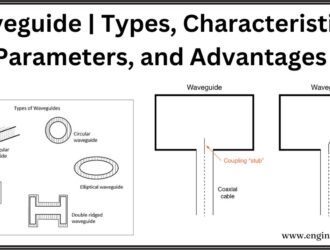
Waveguide | Types, Characteristics, Parameters, and Advantages
Introduction A hollow metallic tube of uniform cross-section for transmitting electromagnetic waves by successive reflection…
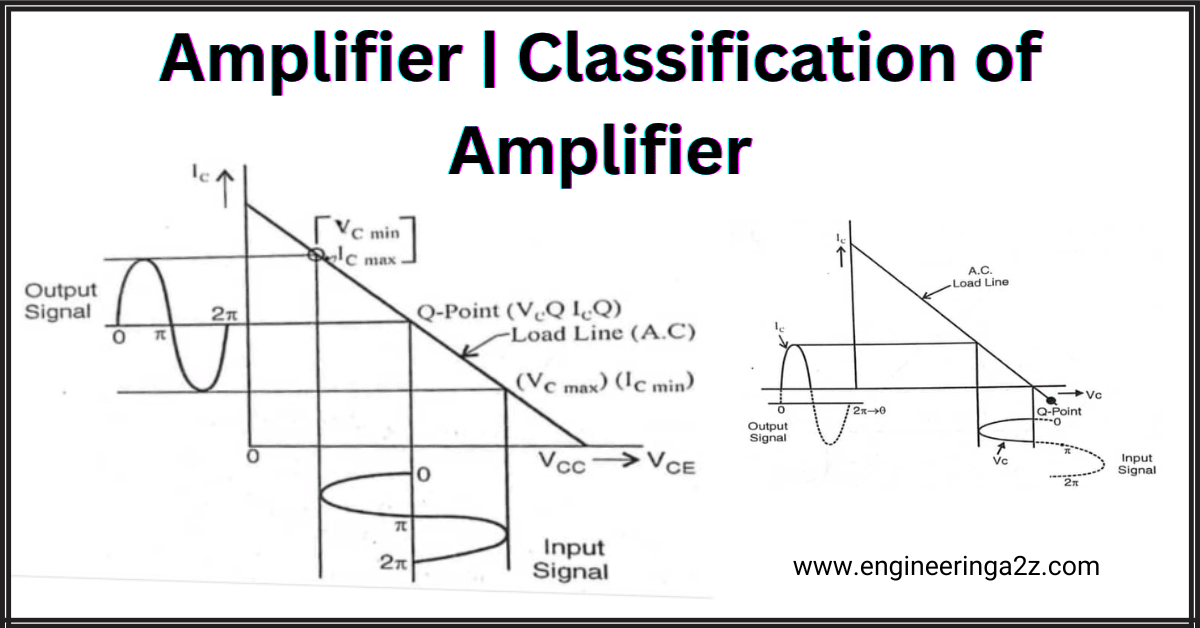
Amplifier | Classification of Amplifier
Amplifier A power amplifier may be defined as a device that converts DC power into…
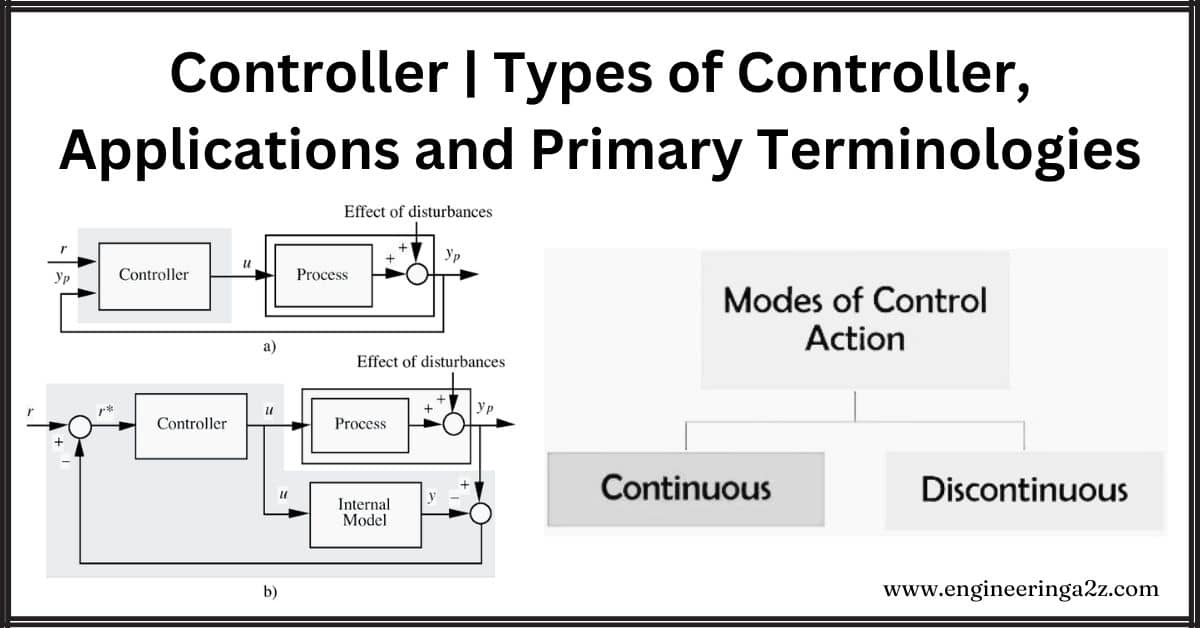
Controller | Types of Controller, Applications, and Primary Terminologies
What is a Controller? Controllers are like the brains of a control system, working to…
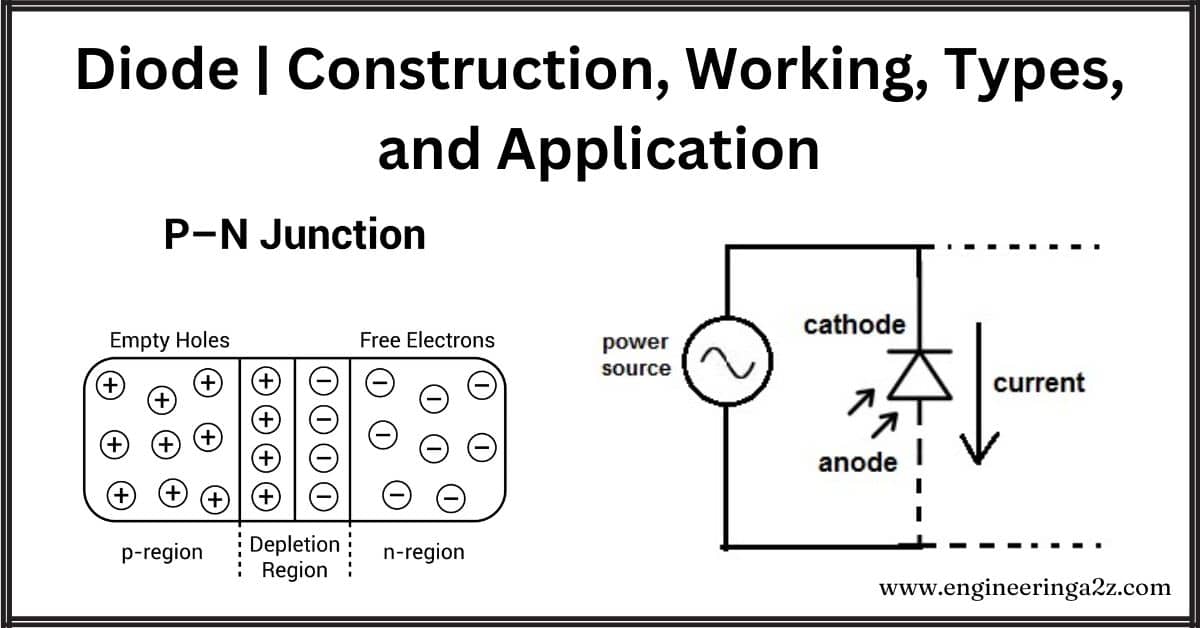
Diode | Construction, Working, Types, and Application
Introduction A diode is a small device with two ends, and it mostly allows electricity…
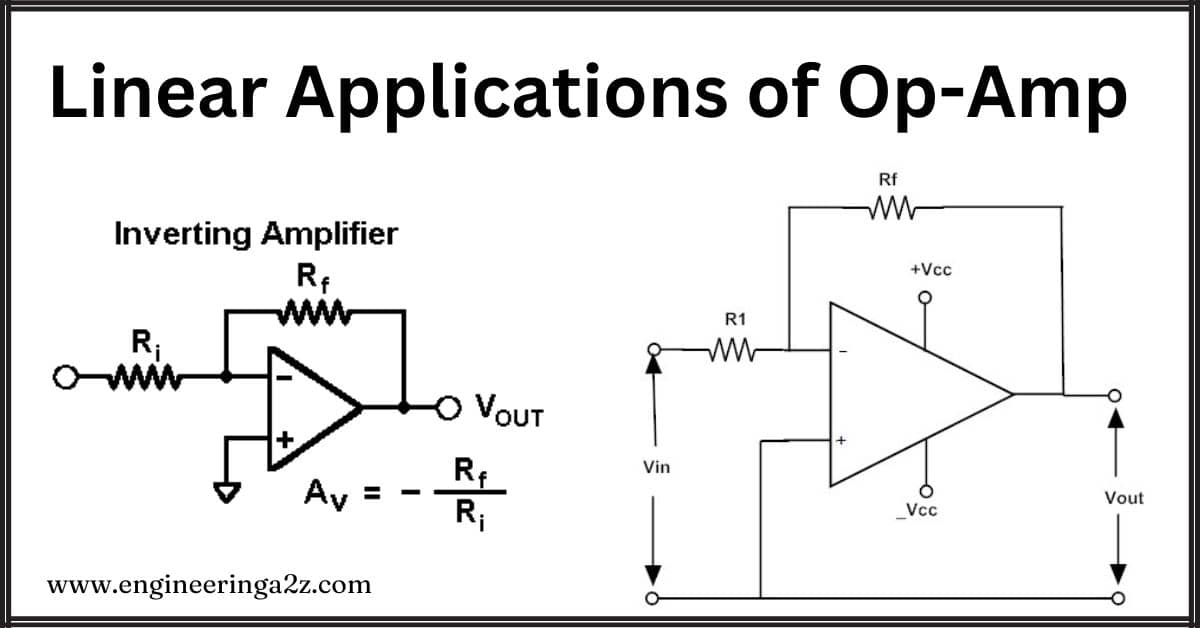
Linear Applications of Op-Amp
A linear amplifier like an op amp has many different applications. It can make weak…
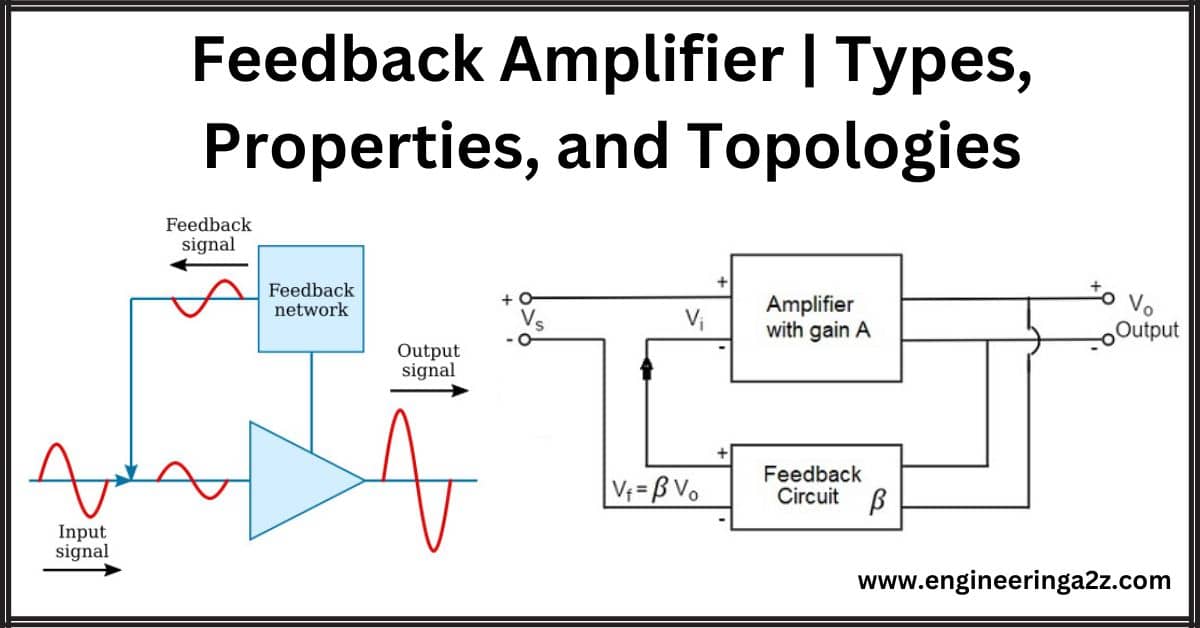
Feedback Amplifier | Types, Properties, and Topologies
Introduction A feedback amplifier is like a loop where the output connects back to the…









Comments