Elementary Concepts | VAT, GATT, WTO, and TRIPS
Value Added Tax (VAT) An added tax is such an indirect tax that is imposed…
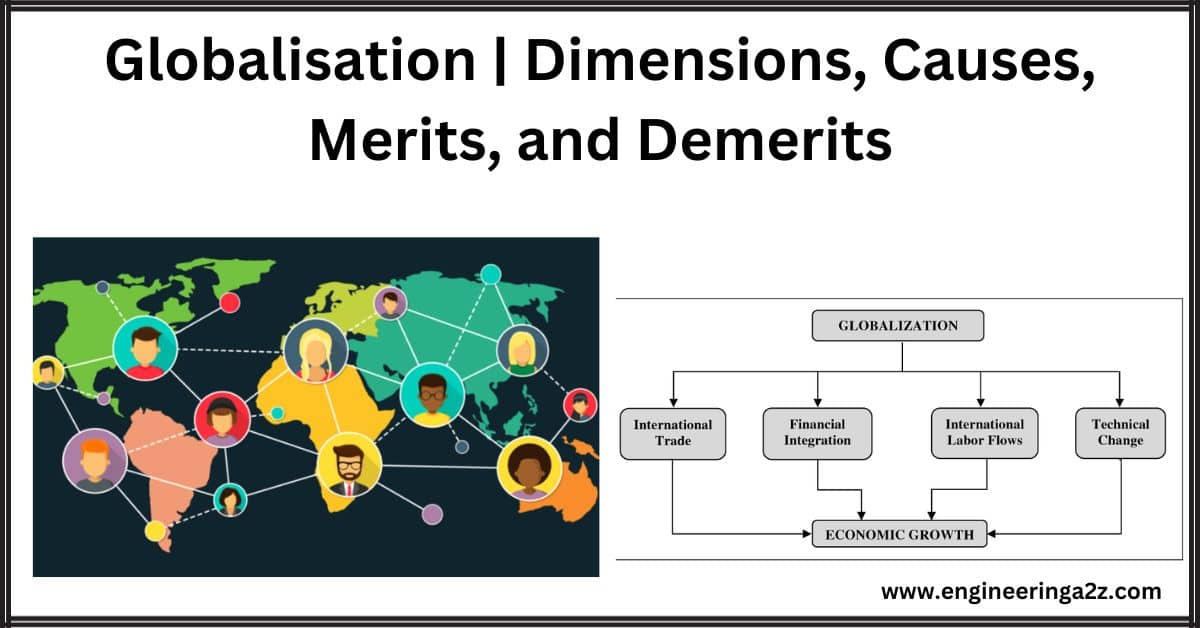
Globalisation | Dimensions, Causes, Merits, and Demerits
Introduction Globalization means that countries are becoming more connected to the global economy. In the…
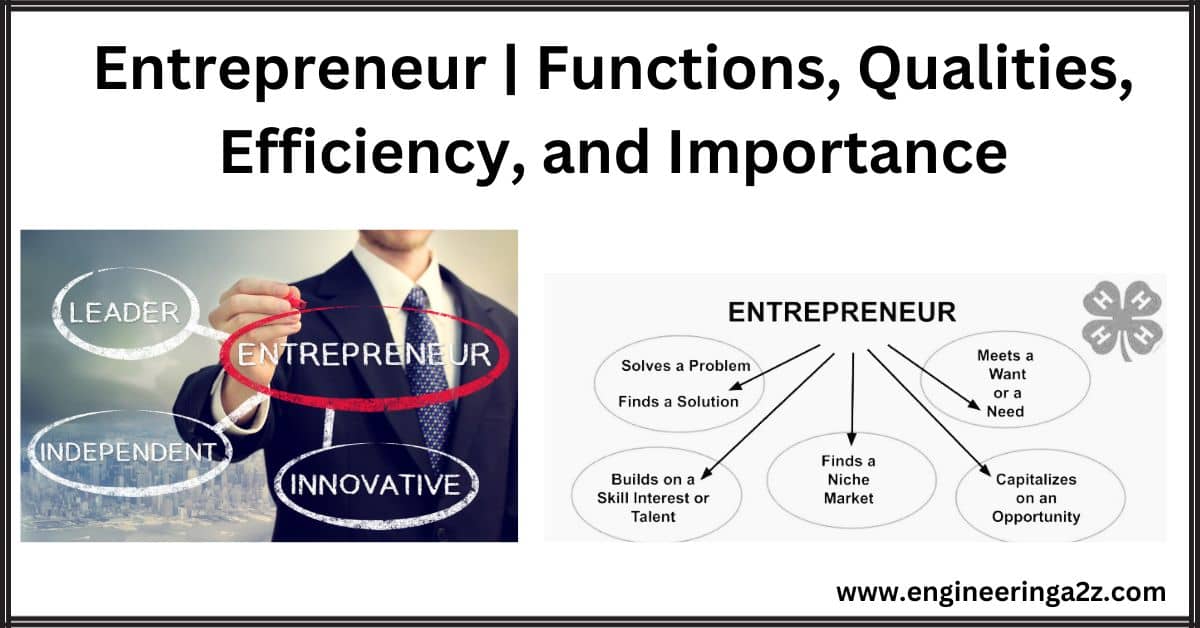
Entrepreneur | Functions, Qualities, Efficiency, and Importance
Entrepreneur In the modern age, the significance of the entrepreneur as a factor of production…
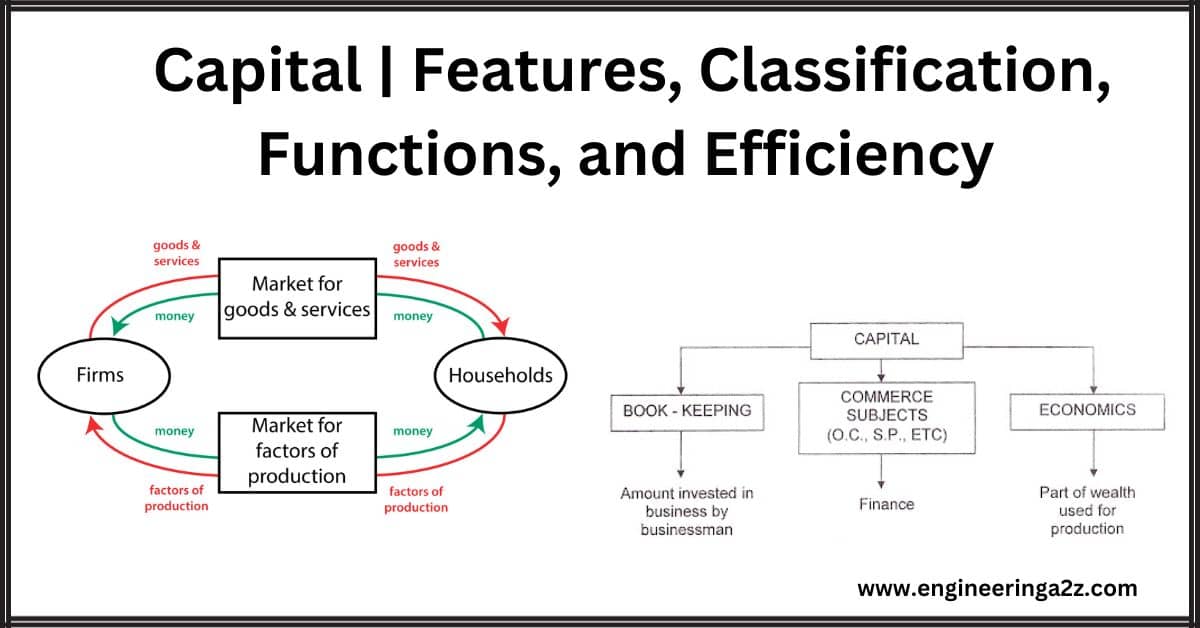
Capital | Features, Classification, Functions, and Efficiency
Capital Capital is a crucial factor in production. In everyday language, we often use terms…
Land | Characteristics, Productivity, and Importance
Introduction The soil we cultivate, the river water with which we irrigate our fields, the…
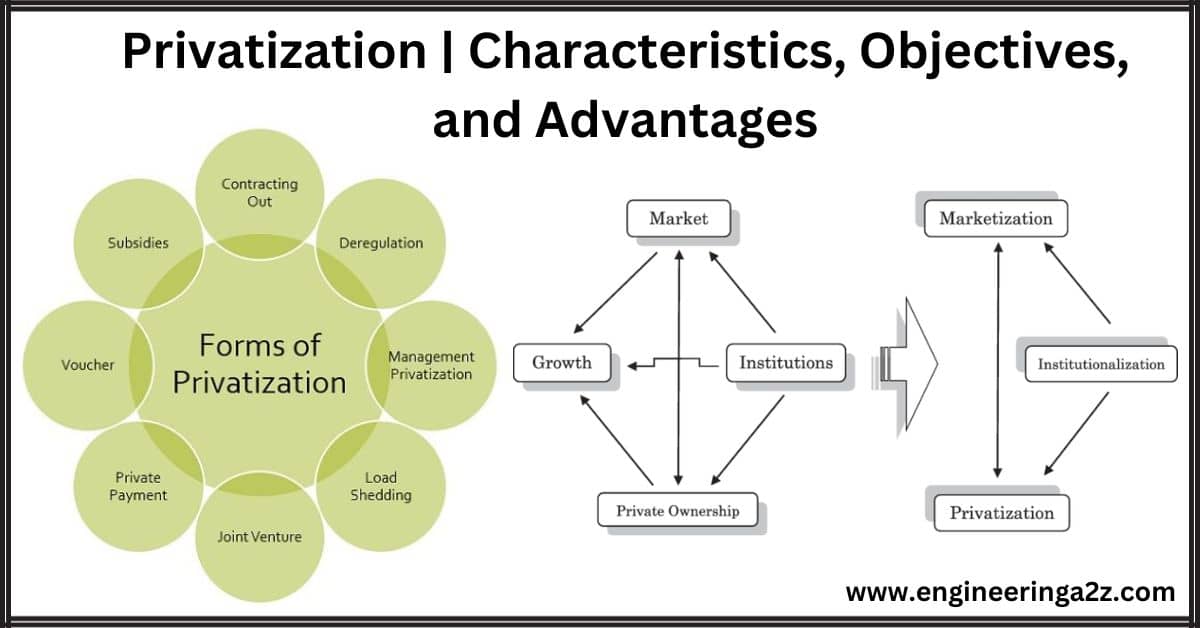
Privatization | Characteristics, Objectives, and Advantages
Privatization means different things, but it usually involves moving something from government control to private…
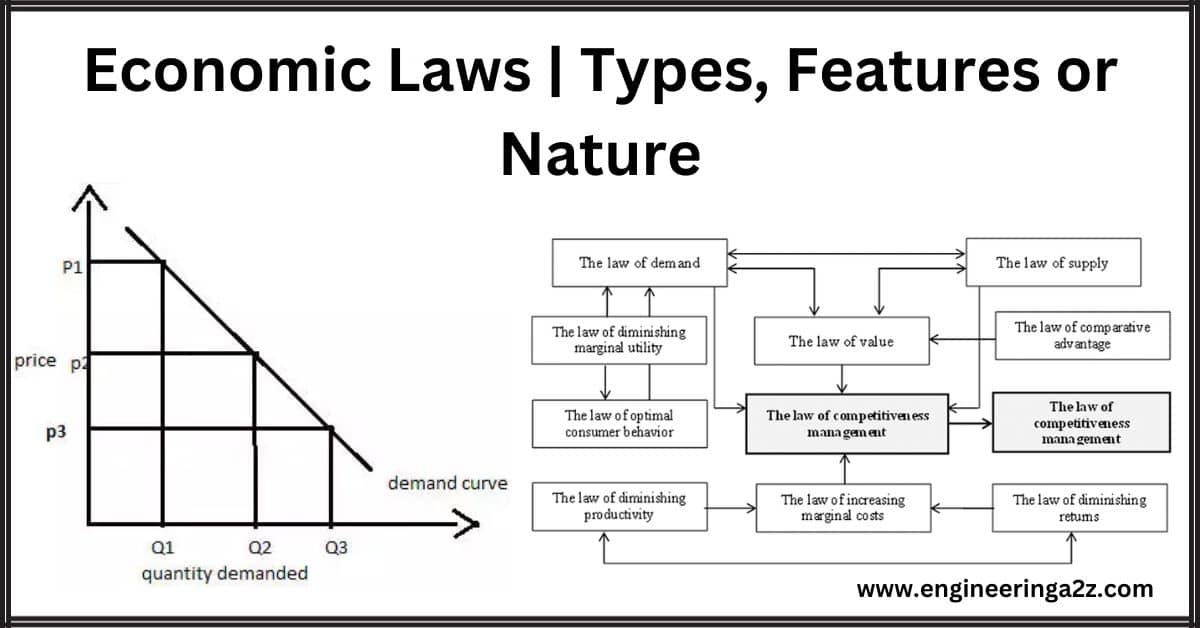
Economic Laws | Types, Features or Nature
Introduction Like all other sciences, economics collects facts and undertakes systematic study. The facts are…
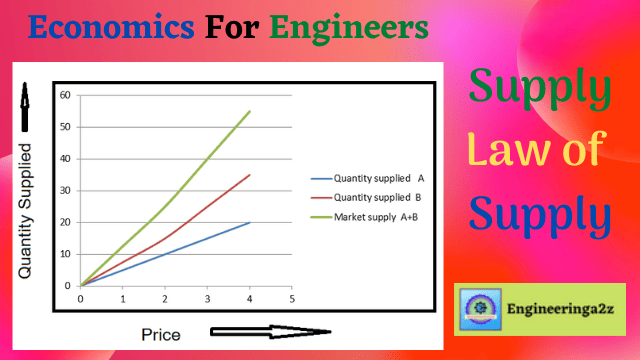
Supply : Law of Supply
What is Supply? Supply is a quantity of a commodity that a producer is willing…












Comments