Table of Contents
Solar Cookers
Solar cookers are devices that use sunlight to cook food. They come in different types, but they all have something that helps capture more sunlight and keep the heat inside. Inside the cooker, there is a space like an oven where you can put the food to cook. Solar cookers can reach temperatures between 90 and 150 degrees Celsius, and some can even go up to 230 degrees Celsius. With these temperatures, you can cook almost any food as long as the sun shines.
Read Also
What is Solar Cell or Photovoltaic Cell
Working principle of Solar Cookers
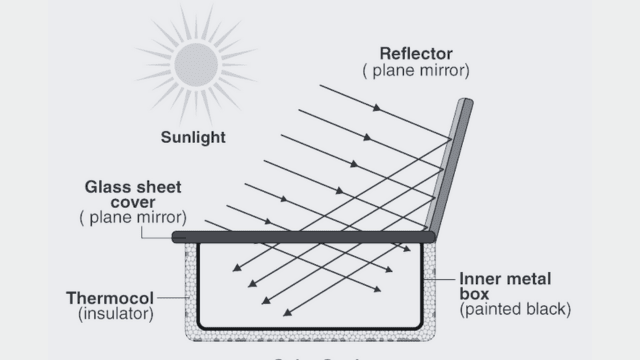
Concentrating sunlight: A special mirror surface is used to reflect and focus sunlight onto a small cooking area. This helps to intensify the heat and create higher temperatures for cooking. While sunlight can be concentrated to extremely high levels that can melt salt and metal, household solar cookers are designed to achieve temperatures ranging from 65 to 400 degrees Celsius.
Converting light energy to heat energy: The concentrated sunlight is directed towards a cooking pan or receiver. When the sunlight interacts with the receiver material, it is converted into heat energy through a process called conduction. To maximize this conversion, materials that can conduct and retain heat effectively are used. The pots and pans used in solar cookers should be matte black in color as it helps them absorb as much sunlight as possible.
Construction of Solar Cookers
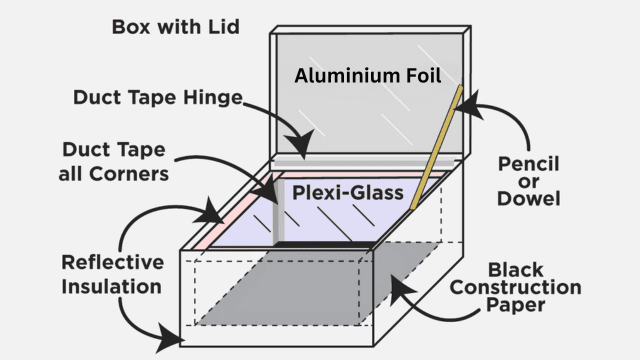
Here are the simplified steps for constructing a solar cooker:
- Create a box shape using an aluminum sheet, following the size of a wooden box.
- Paint the inside of the aluminum box black to help absorb sunlight.
- Insert the aluminum box into the wooden box.
- Attach a mirror to the lid and secure the lid to the wooden box using hinges.
- Place a glass sheet on top of the box to trap heat inside.
- Paint the cooking containers and tools black from the outside.
- Fill the painted containers with food and put them inside the box.
With these steps, the glass sheet helps retain heat inside the box, while the mirror focuses sunlight, heating the box. Now, your solar cooker is ready to prepare meals.
Types of Solar Cookers
The different types of solar cookers are :
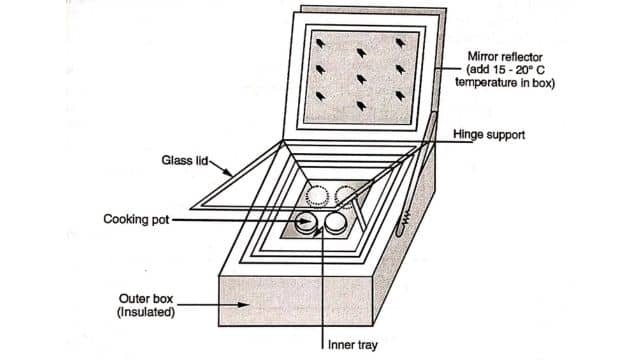
(a) Box Type: Fig. shows the box-type cooker. The solar cooker is a rectangular box measuring 50 x 50 x 12 cm. It has insulation made of glass wool on the sides and bottom to prevent heat from escaping. A reflector also helps increase the temperature inside the box by about 15-20 degrees Celsius. The glass also helps maintain a steady temperature of around 160 degrees Celsius inside the cooker.
During winter, you may need to adjust the position of the mirror to make sure it captures enough sunlight. It’s important to note that cooking takes longer in winter compared to summer. The best time for cooking is between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m. when the sun is strongest.
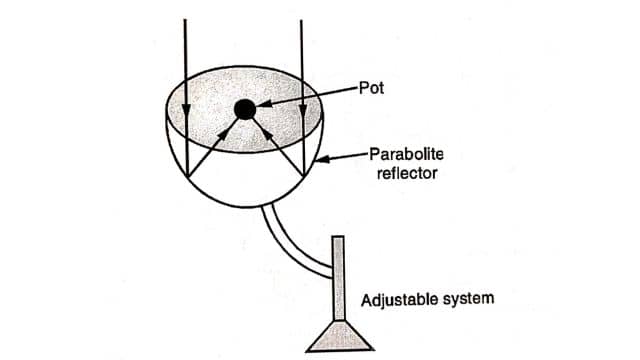
(b) Focusing Type or Indirect Type: Fig. shows the focusing type cooker as a paraboloid. The glass surface or aluminum foil is used as a reflector coating from the inside. The cooking pot is placed at the focus of the paraboloid, where reflected rays get focused to heat the pot. The temperature of the pot achieved is more than 200° C. The system is adjustable to track the sun.
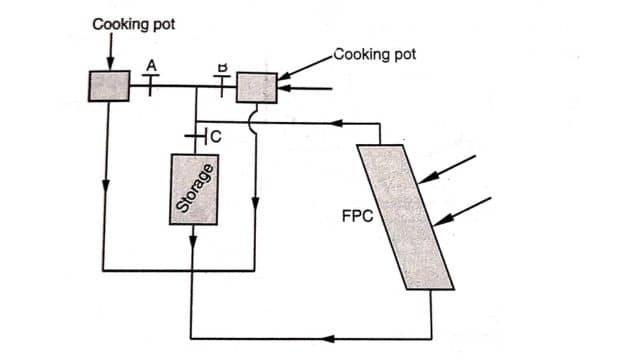
(c) Collector Type (Community Cooker): These solar cookers are designed to cook food not only during the day but also at night. They have a special feature called a collector and storage system. During the day, the collector captures extra heat energy and stores it for later use. This stored energy can be used to cook food at night. The figure illustrates how this device works. It has three modes of operation: day cooking, day non-cooking period, and night cooking. These modes are controlled by opening and closing different passages using a control valve.
Advantages of Solar Cookers
- The fuel is the free source of the sun.
- There are fewer thermal losses.
- Nutrition value is maintained.
- The heat required to change the chemical and physical structure is less than sensible heating in the conventional method.
Disadvantages of Solar Cookers
- People cook in the traditional way.
- Cooking is only done during daylight hours.
- People rely on sunlight for cooking.
- There is no control over the cooking temperature.
- It can be expensive to cook using this method.
Applications of Solar Cookers
Here are some applications of solar cookers:
- Outdoor cooking: Solar cookers are commonly used for outdoor activities such as camping, picnics, and barbecues. They provide a convenient and eco-friendly way to prepare meals in open spaces without the need for traditional fuel sources.
- Developing regions: In areas with limited access to electricity or cooking fuels, solar cookers offer a sustainable solution for cooking food. They help reduce reliance on firewood, charcoal, or fossil fuels, leading to environmental benefits and improved air quality.
- Disaster relief: Solar cookers are often used in emergency situations or disaster-stricken areas where conventional cooking methods may be disrupted. They provide a reliable and safe way to cook food without requiring external fuel sources.
- Food preservation: Some solar cookers can be used for food dehydration, which helps preserve fruits, vegetables, and herbs by removing moisture. This method can extend the shelf life of perishable food items without the need for electricity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a Solar cooker?
A solar cooker is a device that uses sunlight to cook or heat food and liquids.
What is the use of solar cookers?
Solar cookers are often used in cooking demonstrations, fairs, and exhibitions to showcase the capabilities of solar energy for cooking purposes. They serve as a practical and engaging way to raise awareness about renewable energy technologies.
How many components are there in a box-type solar cooker?
A black box, glass cover, plane mirror reflector, and cooking containers are the main components of a box-type solar cooker.
Read Also:
- DIAC | Construction | Working and V-I Characteristics
- Stand Alone PV System | Schematics and its Components
- Energy Management | Need and Environmental Aspects
- High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission
- Three Phase Transformer | Construction & Working











Leave a Reply