Table of Contents
Introduction
Pyrolysis is a process that breaks down organic material at temperatures between 400 °C and 900 °C without oxygen. This process produces various chemicals from wood, some of which can replace conventional fuels . The types and amounts of these products depend on the biomass composition and the operating conditions.
Pyrolysis
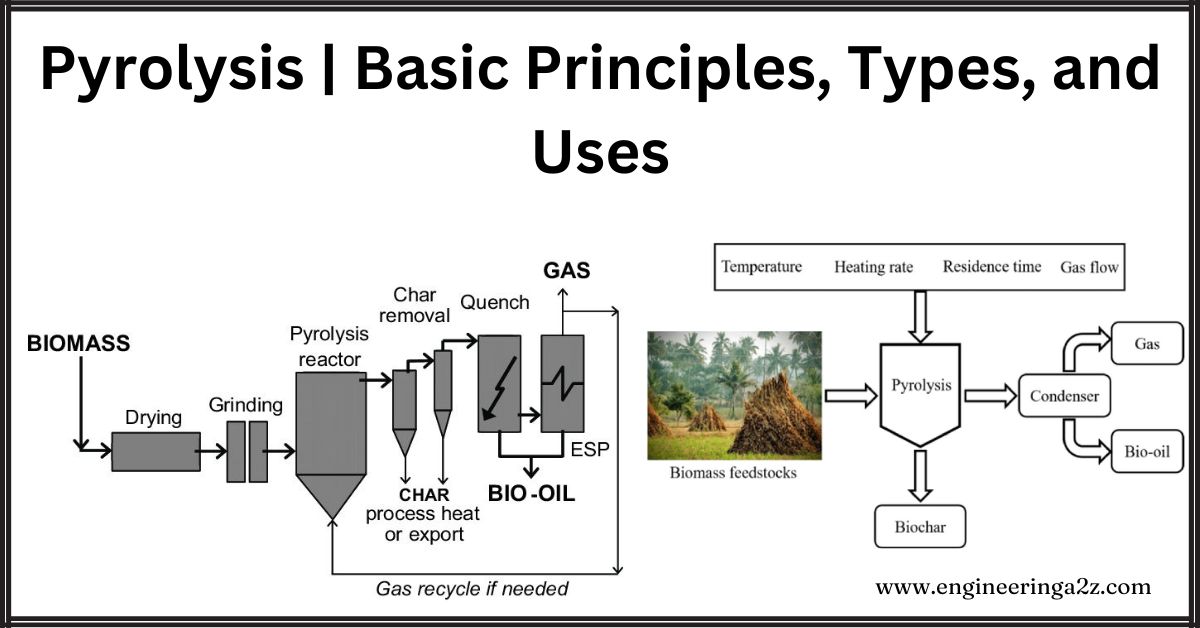
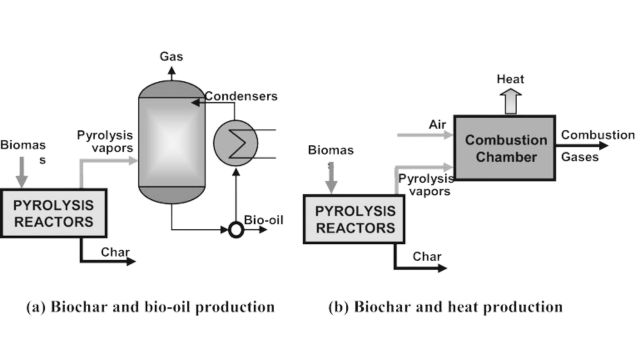
Pyrolysis is a technology that converts biomass into liquid products that can be turned into biofuels, fuel additives, and chemical replacements. It involves heating organic material, like biomass, without oxygen, usually at or above 500 °C . This high heat breaks down the biomass into three products: a liquid called bio-oil, a solid called bio-char, and gases (syngas). Bio-oil can be used as fuel, while bio-char and syngas can provide energy. With high heating rates, fast pyrolysis produces more bio-oil (60-70%) and less bio-char (15-25%) . Slow pyrolysis, with slower heating, produces more biochar . The process can be self-sustaining by burning some of the syngas and bio-oil or bio-char for energy
Basic Principles of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass involves heating it without oxygen in an inert atmosphere like argon or nitrogen. This complex chemical process breaks down biomass components like cellulose and lignin into biochar, bio-oil and gases such as methane, hydrogen, carbon monoxide and dioxide. The temperature range for decomposition is typically 350–800°C, influencing the proportions of these products along with factors like time, heating rate and moisture content. Higher temperatures yield more gases and ash, while slower heating favors biochar production . Managing moisture is critical; too much leads to liquid products and dust, requiring drying for efficient pyrolysis.
Types of Pyrolysis
There are three main types of pyrolysis :
- Slow Pyrolysis
- Fast Pyrolysis
- Flash Pyrolysis
1. Slow Pyrolysis
This chemical reaction is used to produce biochar, biogas and biooil. It involves slowly heating the material, and decomposing it at a low rate, with temperatures increasing as slowly as 10°C per minute.
2. Fast Pyrolysis
In this process, biomass is quickly heated to high temperatures without air. The temperature ranges from 300-700°C, with a heating rate of 10-200°C per second .
3. Flash Pyrolysis
In this type, quick heating occurs at very high rates, over 1000°C per second. The reaction temperatures can be as high as 900-1300°C.
Parameters of Pyrolysis
- Biomass type and preparation of feeding
- Pyrolysis temperature
- Catalyst
- Sweeping gas velocity
- Particle size
- Reactor geometry
- Heating rate
Uses of Pyrolysis
- Converts low-energy biomass into high-energy fuels.
- Processes a wide range of feedstock types .
- Produces organic materials like plastics and rubbers.
- Generates electricity.
- Prepares chemicals such as acetone and phenol through the process.
Advantage of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis turns waste into useful products like bio-oil, gas and charcoal . It reduces landfill waste, generates renewable energy and can handle various types of biomass.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What are the three stages of Pyrolysis?
The stages of pyrolysis for Liulin bituminous coal are :
1. Activation Stage (Stage-I): Occurs between 260–330°C.
2. Primary Pyrolysis Stage (Stage-IIA): Happens between 330–400°C.
3. Secondary Pyrolysis Stage (Stage-IIB): Takes place between 400–500°C.
4. Recombination Dominated Stage (Stage-III): Follows the secondary stage. -
What is the pyrolysis of plastic waste to fuel?
Pyrolysis of plastic waste to fuel is a process where plastic is heated without oxygen to break it down into liquid fuel, gases and solid residues.
-
What is the disadvantage of pyrolysis?
A disadvantage of pyrolysis is the production of tar and other byproducts that require additional treatment, along with high energy consumption and potential environmental concerns from emissions and residues .
-
What are the different types of pyrolysis equipment?
Different types of pyrolysis equipment include fixed-bed reactors, fluidized-bed reactors, rotary kiln reactors, ablative reactors and vacuum pyrolysis reactors, each designed for specific feedstocks and processing conditions .











Leave a Reply