Table of Contents
Low Frequency Induction Heating
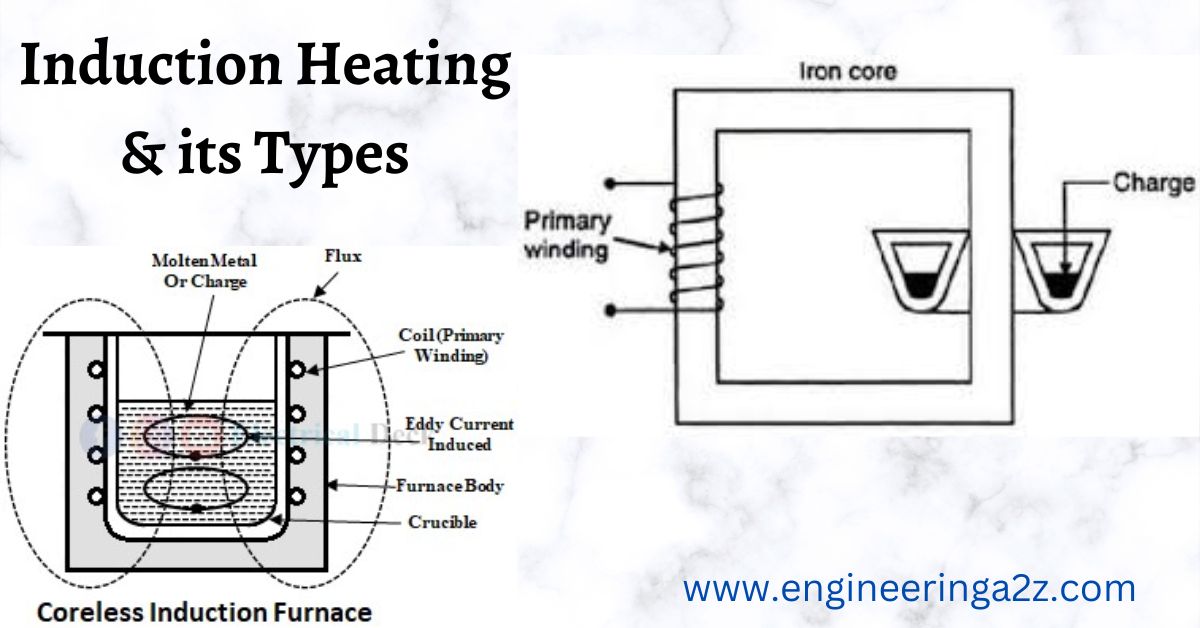
We know when a coil is wound on a magnetic core and is given supply, magnetic field is produced. If this field changes its magnitude periodically, an emf is produced, and if circuit is closed current flows. Transformer is an example of low frequency induction heating
If ac is made to flow through the coil wound on a core, the magnetic flux linking with the core changes hence an emf is induced in the core. As core provides a closed path, eddy current flows through Supply AC the core. Now if the substance to be heated is used as a core, the substance can be heated by these eddy currents and this is the principle of Induction furnaces.
Read Also
What is Electric Heating
The frequencies employed for eddy current heating are usually between 104 to 106 Hz. Typical application of this heating is in tempering and surface hardening of tool steel, as in that case, metal is required to be heated upto a small depth only.
Types of Induction Furnace
- Core type
- Coreless type.
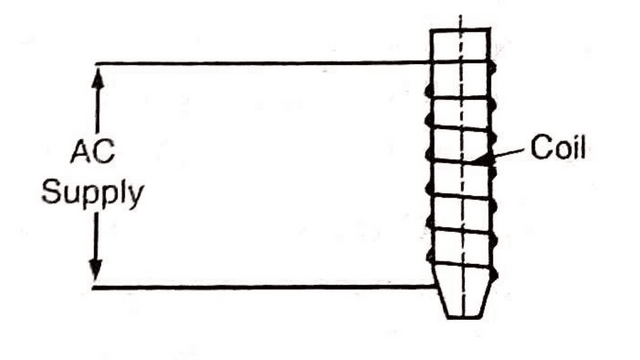
1. Core type Induction Heating
Core type induction furnace employs the principle of on which transformer works The charge acts like secondary of transformer, and consists of one turn only formed by the metal to be heated. The current of several thousand amperes flows through the charge which heats it. These furnaces operate at 25 Hz or lower frequencies.
Limitations of Core Furnaces
(a) Leakage reactance is high and PF is poor
(b) It can be used at low frequencies (< 25 Hz). So we need frequency converter to lower down the power frequency.
(c) The crucible is of odd shape and not suitable from metallurgical point of view.
Read Also
Methods of Heating
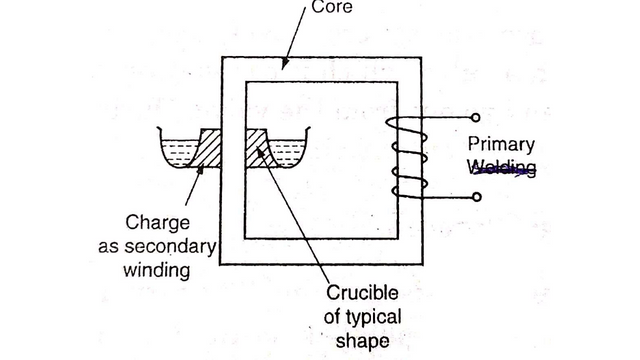
2. Coreless Furnace
This is a furnace without a cure. The flux set up in the primary winding indus eddy currents in the charge as a result the charge melts. The frequency at which furnace operates produces skin effect in the primary winding which produces heat. For cooling, the primary coils are made hollow to circulate water through them Modern furnaces operate at 500 Hz. In olden times the frequency was very high upto 3000 Hz. Since the max. power increases with frequency, there is an optimum frequency which can be used.
The high frequency power supply can be obtained by following:
- Transformers: By stepping up the voltage.
- Mercury are converters: They can give upto 600 KW and frequency of 1500 Hz.
- Motor generator set: They can give upto 2500 KW at 1200 Hz.
- Spark gap converters: Can give upto 50 KW at 500 K Hz.
- Vacuum tube converters: Can give upto 25 KW at 50 KHz.
Advantages of Coreless Furnaces:
Few advantages are listed below.
- The time taken to reach melting point by this furnace is short and oxidation is also reduced.
- A very precise control can be achieved.
- The crucible of any suitable shape can be used.
- It takes no time for warming up, and can be used instantaneously.
- There is no dirt, smoke, noise, etc.
Applications of Coreless Furnace
- The main application of coreless furnaces is in production of steel. The production is economical upto 5 ton capacities.
- Melting of non-ferrous metals such as bronze, brass, copper, etc.
- For Vacuum melting.
- Melting for precision casting.
- Electronic industry.
- In brazing, soldering, hardening and annealing, etc.






Leave a Reply