Table of Contents
It is a glass house that is used for growing delicate plants, especially during winter. It has a higher temperature inside than outside. In a greenhouse, the glass panel allows the light in but does not allow heat to escape. Thus the greenhouse warms up, very much like inside a car that has been parked in the sun for a few hours.
Greenhouse effect
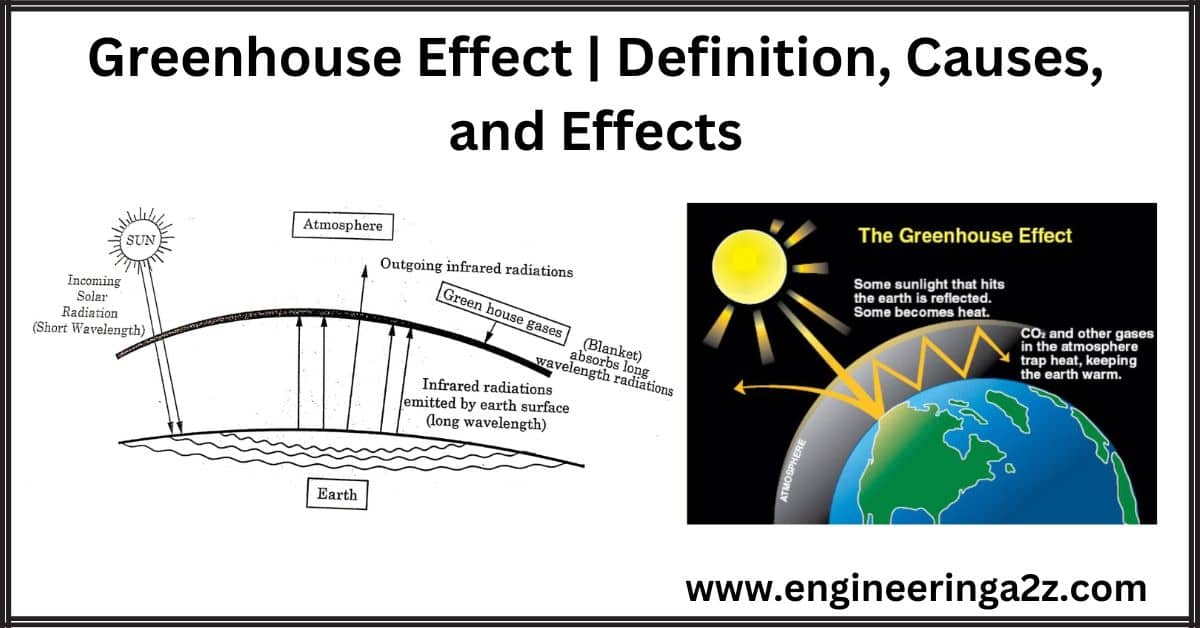
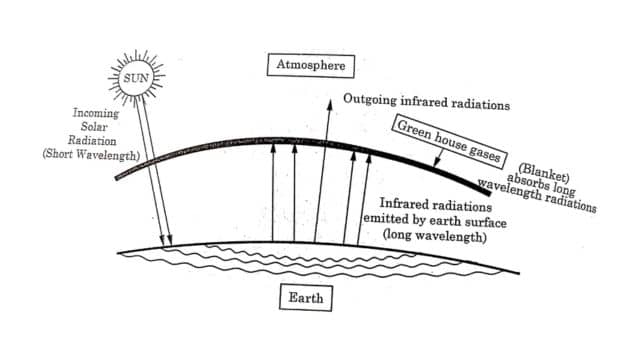
The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon that is responsible for the heating of the Earth’s surface and atmosphere. In the context of the environment, the greenhouse effect refers to ‘selective energy absorption by some atmospheric gases, which allow short wavelength energy to pass through but absorbs longer wavelengths and reflect heat back to earth.
You would be surprised to know that without the greenhouse effect, the average temperature at the earth’s surface would have been chilly -18°C rather than the present average temperature of 15°C.
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiations from the sun are absorbed by the not reflected back into space.
Here’s a simplified explanation of the greenhouse effect:
1) Sunlight: Solar radiation from the sun passes through the earth’s atmosphere and reaches the earth’s surface.
2) Absorption & Reflection: Some of the incoming solar radiation is reflected back into space by clouds, the atmosphere, and the earth’s surface. However, a significant portion of the radiation is absorbed by the earth’s surface.
3) Heat Emission: The absorbed solar radiation is re-emitted from the earth’s surface as thermal radiation(infrared radiation).
4) Greenhouse Gases: Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), Methane (CH4), Nitrous Oxide( N2O), and others absorb a portion of the outgoing thermal radiation emitted by the earth’s surface.
Causes of Greenhouse Effect
The major causes of the greenhouse effect are:
1. Burning of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are a crucial part of our lives. We use them a lot for transportation and generating electricity. When we burn fossil fuels, they release a gas called carbon dioxide. As the population grows, we’re using more and more fossil fuels, which means we’re releasing more greenhouse gases into the air. These gases are causing the Earth’s temperature to rise and changing our climate. It’s not good for our environment, and it’s happening because we’re burning too many fossil fuels.
2. Deforestation
Plants and trees are really important because they take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen, which is what we need to breathe. But when we cut down a lot of trees, it leads to a big increase in greenhouse gases. These gases make the Earth’s temperature go up, causing global warming. It’s happening because there are fewer trees to soak up the carbon dioxide and release oxygen. So, cutting down too many trees is bad for the environment and makes the Earth hotter.
3. Farming
One of the factors in the atmosphere’s greenhouse effect is the nitrous oxide used in fertilizers.
4. Industrial Waste and Landfills
Harmful gases are produced by factories and industries and released into the atmosphere. Methane and carbon dioxide are also released by landfills, which increases the amount of greenhouse gases.
Mechanism of the Greenhouse Effect
There are four different layers of atmosphere-Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, and Thermosphere. In the lowermost layer (troposphere) there is a layer of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas and in the next upper layer (stratosphere) there is a layer of ozone gas.
When the sunlight consists of ultraviolet rays, visible and infrared rays fall on the top of the atmosphere, then first of all the harmful ultraviolet rays are absorbed by the ozone layer which is present in the stratosphere. The visible and infrared rays pass through the layer of CO2 and fall on the surface of the earth. The infrared rays are of short wavelength and they pass through layers of CO2 easily.
When these rays strike the earth’s surface, they become hot and the earth’s surface starts emitting long wavelength rays. These rays cannot pass through the CO2 blanket easily and CO2 traps all the hot rays (long wavelength rays) and the atmosphere of the earth gets heated up.
Effects of Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that helps regulate the Earth’s temperature. However, human activities like burning fossil fuels and cutting down forests have made this effect stronger. Here are some effects of this stronger greenhouse effect:
1. Global Warming
The primary consequence of the greenhouse effect is global warming. The increased concentration of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), traps more heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. This leads to a gradual increase in the average global temperature, causing climate change and its associated impacts.
2. Climate Change
The changes in temperature affect the environment, like rainfall patterns and ecosystems. This can harm agriculture, water resources, and animals that depend on certain habitats.
3. Depletion of Ozone Layer
The ozone layer is like a shield that protects the Earth from harmful rays from the sun called ultraviolet (UV) rays. It’s located high up in the sky in a part called the stratosphere. But when the ozone layer gets thinner or damaged, more UV rays can reach the Earth’s surface, which can be harmful to our skin and can also cause big changes in the climate.
The main reason this happens is because of certain gases that are made by nature and by humans. These gases include things like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4).
4. Ocean Acidification
More carbon dioxide in the air gets absorbed by the oceans, making them more acidic. This harms marine life, especially creatures with shells like coral reefs and shellfish.
5. Health Effects
Climate change can harm human health. It can cause more heat-related illnesses, spread diseases carried by insects, and worsen air quality, leading to breathing problems.
6. Social and Economic Impacts
Climate change can have economic effects, like lower crop yields and higher food prices. It can also hit vulnerable communities harder, making existing inequalities worse.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Define greenhouse?
It is a glass house that is used for growing delicate plants, especially during winter. It has a higher temperature inside than outside. In a greenhouse, the glass panel allows the light in but does not allow heat to escape.
Define the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon that is responsible for the heating of the Earth’s surface and atmosphere.
Define greenhouse gases?
The gases which trap the infrared radiation to produce the greenhouse effect are called greenhouse gases. In other words, the atmospheric gases which are permeable (allow to pass through) to short-wave solar radiations, but are strong absorbers of long-wave radiations emitted from the earth’s surface are called greenhouse gases.
List the greenhouse gases?
The following are the greenhouse gases present in the troposphere (i.e. the lowermost layer of the atmosphere):
(i) Carbon dioxide (CO2)
(ii) Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
(iii) Ozone (O3)
(iv) Methane
(v) Nitrous oxide (N20)
(vi) Water vapors (H2O)
Read Also:
- Characteristics and Advantages of A.C. Over D.C. and Vice Versa
- Difference Between A.C. and D.C.
- TRIAC | Construction, Working, and V-I Characteristics
- Advantages | Disadvantages and Applications of Electric Power
- DC Generator | Construction and Working Principle






Leave a Reply