
Table of Contents
Introduction of Globalisation
Globalisation simply means that combining the economy of the country with the world economy. Globalisation embodies combination of the international markets for goods, services, technology, finance and labour.
In current economy literature the term Globalisation is used to mean a more liberal “Outward Oriented Policy” .which includes eliminating anti export bias, lowering of very high import tariff, planning lesser reliance on quantitative restriction on imports.
However it can be said that the outward looking policy does not mean the government would completely abandon all forms of control and place the entire economy at the mercy of multinationals. The main aim of the policy of globalisation would be to remove certain imbalance and restrictions which hamper the free flow of trade.
Economics For Engineers Book PDF
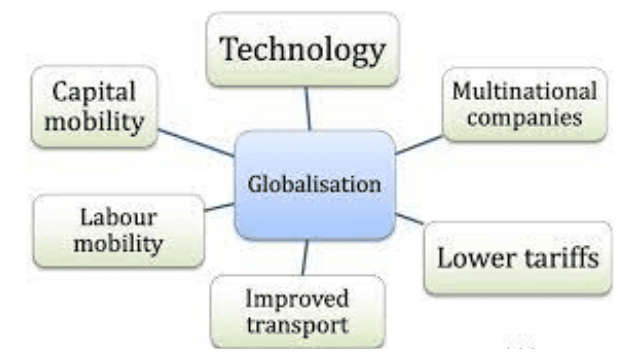
Globalisation of Indian Economy
In order to put the country out of economic crises, govt. of India in 1991 sought financial need from the International Monetary Fund and World Bank. These two international institution imposed on India for implementation of stabilisation and Structural Adjustment Programme to secure the said assistance.
It was to fulfil these conditions that India introduce New Economic Policy in 1991. The process of Globalisation in India was the outcome of this policy. The two part of condition laid down by the International institution were:-
Stabilisation :- It means that situation of the economy wherein inflation and balance of payments deficit are kept under control. To achieve this objective it is essential to scale down Fiscal deficit and rate of money supply.
Structural Adjustment Programme :-It refers to the structural adjustment of economy on the basis of policy of liberalisation. It has two aspects:- 1. Internal :-In domestic sector liberal policy be adopted for adjustment of invested, production, prices etc. Government controls should be minimized in this regard and ultimately the same be removed. 2. External:- Govt. controls over the flow of foreign goods, services, capital, technology investment etc. should be reduced to minimum. It implies liberalization of foreign economic policy or globalisation of the economy.
Impact of Globalisation in India
On consumers
- Greater choice
- Enjoy improved quality and lower prices of several products
- Higher standard of living than was possible earlier.
On producers and workers
- MNCs investment increased due to which jobs created, increased raw material supply from local companies.
Top Indian companies, benefits from increased competition
- Invested in newer technology and production method.
- Raised their production standards.
- Successful collaborations with foreign companies.
- Large Indian companies to emerge as multinational themselves.
Created new opportunities
- New opportunities for companies providing services, particularly those involving (IT)
Challenges due to globalisation for small producers and workers
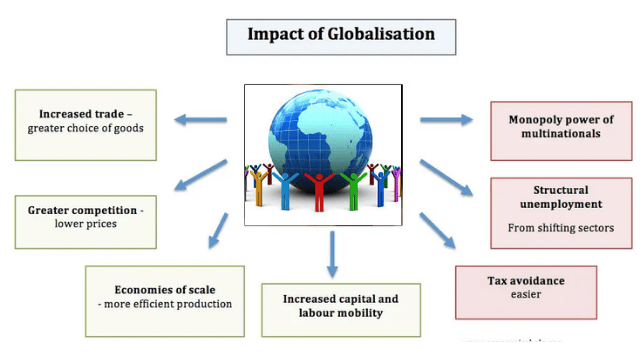
Advantages of Globalisation
- The globalisation create ample jobs opportunities as more and more companies extend their presence to different parts of the world.
- Globalisation gives educational aspirants from developing and underdeveloped countries more quality learning opportunities. It leads not only to the pursuit of the best higher education but also to cultural and language exchanges.
- Due to globalisation , it has been observed that there is a considerable reduction of poverty world wide.
- Globalisation also enhances a faster flow of information and quick transportation of goods and services. Moreover one can order any item from anywhere merely sitting at home.
- Globalisation usually restructures production and trade pattern favouring labour intensive goods and labour intensive techniques as well as expansion of trade in services.
- With the help of globalisation there will be flow technology, education, medicines etc that help in developing of country in faster rate.
Disadvantages of Globalisation
- Globalisation paves the way for redistribution of economic power at the world level leading to domination by economically powerful nations over the poor nations.
- Globalisation turned out to be a significant threat to the cottage and small scale industries as they have to complete with the product of MNCs.
- Globalisation usually results greater increase in imports than increase in exports leading to growing trade deficit and balance of payments problems.
- Although globalisation promotes the idea that technological change and increase in productivity would lead to more jobs and higher wages but during the last few years. Such technological changes occurring in some developing countries have resulted more loss of jobs than they have created leading to fall in employment growth rates.
- Globalisation is also blamed to have paved the way from human trafficking, labour exploitation and spread of infection diseases too.
- In addition to all these if any economic disaster hit the country and if they subsequently suffer from economic depression, its ripples ore felt deeply in other countries as well.






Leave a Reply