Table of Contents
Wireless Network Technology
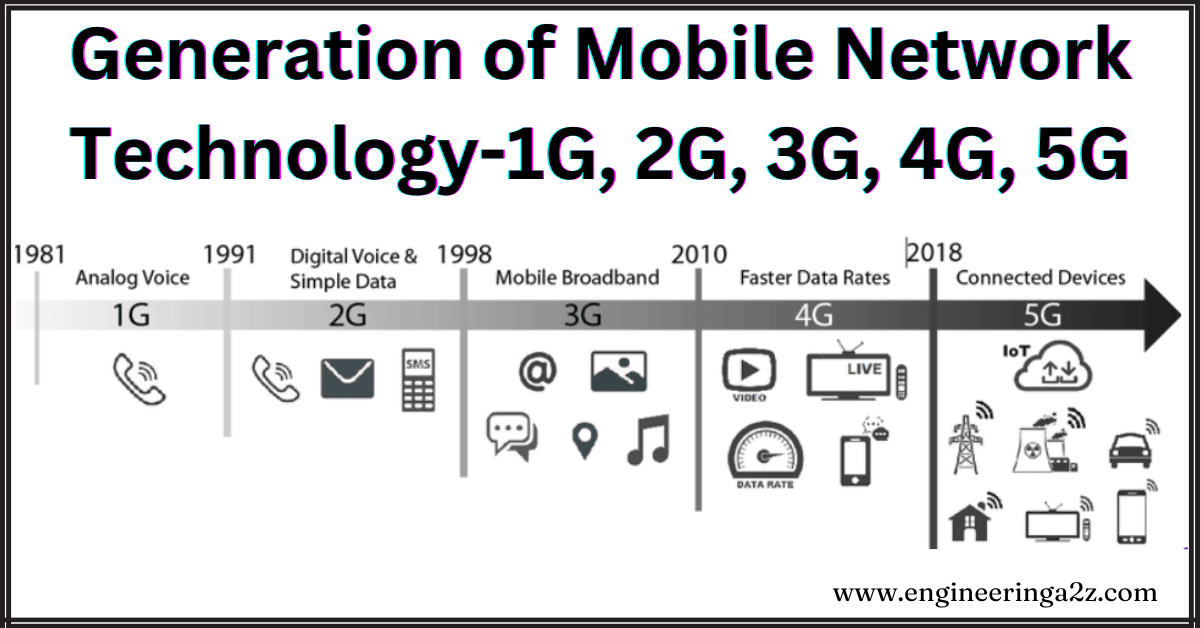
Wireless network technology allow devices to connect to the internet and communicate without physical cables. It has evolved over generations, each bringing faster speeds and better connectivity.
First Generation (1 G) Technology
It is the first generation of mobile network technology. where analog signal used to transmit data. It was introduced in US in early 1980 and designed for voice communication. 1 G technology allowed wireless telephone calls to be made without the need for a fixed landline connection. It used the frequency modulation (FM) radio signals and supported voice-only calls. It has two important developments
- Invention of microprocessor
- Digitization of control link between mobile phone and the cell site
Characteristics of 1 G Technology
- Maximum speed up to 2.4 kbps
- Poor voice quality
- Poor battery life
- little data security
Second Generation (2 G) Technology
It is the second generation of mobile network technology. it effectively took cell phones from analog to digital communications. Their first major upgrade when their technology went from 1 G to 2 G.it was launched in Finland in 1991 and used GSM (Global system for mobile) networks. 2 G introduced call and text , analog with data services such as SMS, MMS, which allowed users to send text messages to other users. GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) was also introduced in 2 G, which allowed users to access the internet and send emails.
Characteristics of 2 G Technology
- Maximum speed up to 64 kbps.
- Slow data transmission
- Better quality than 1 G
- Text and multimedia manage easy.
Third Generation (3 G) Technology
It is the third generation of mobile network technology. The introduced of 3 G networks in 1998. Its began with the start new millennium and offered major advancement with faster data transmission speed. such as for video calling and mobile internet access. This technology was the first to allow users to access the internet at high speed, allowing for better web browsing and file transfers. 3 G also provided better security as compared to 2 G.
Characteristics of 3 G Technology
- Maximum speed of 144 kbps to 2 Mbps
- Running web based application like multimedia e-mail etc.
- Fast and easy transfer of audio and video files.
- High speed web browsing.
Fourth Generation (4 G) Technology
It is the fourth generation of mobile network technology. which was released in 2008, is 4 G. It represents a significant advancement over previous generation (1 g,2 g,.. 3g) and It support or provided high data transmission speed, low latency and is suitable for HD video calling, fast download and upload, live streaming, cloud gaming etc.
Characteristics of 4 G Technology
- Highest data speed rates of 100 mbps to 1 Gpbs without interruption at any location
- provided high speed at low cost
- Global mobility, service portability etc.
- IP telephony
Fifth Generation (5 G) Technology
It is the Fifth latest generation of mobile network technology. This technology 100 times faster than 4 G technology. Its enable users to access the internet more quickly, stream video in ultra high definition etc. 5 G is designed to deliver faster data speeds, ultra low latency and support for a maximum number of connected devices simultaneously.
Characteristics of 5 G Technology
- Maximum speed up to 10 Gbps
- Faster speed than data transmission
- Capable of supporting a massive number of devices and user simultaneously
- User can enjoy high- quality streaming services without any buffering
Compare Different Generations of Wireless Network Technology
| Sr. No. | Technologies | 1G | 2G\2.5G | 3G | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Features | 1970-1980 | 1990-2004 | 2004-2010 | 2011- Now | Now |
| 2. | Data rate | 2 kbps | 14.4-64 kbps | 2 Mbps | 200 Mbps- 1 Gbps | 10 Gbps-100 Gbps |
| 3. | Famous standard | AMPS | Integrated high-quality audio ,video and data | WCDMA, CDMA | LTA, WI-MAX | Not yet defined |
| 4. | Technology behind | Analog cellular technology | Digital cellular Technology | IP technology | Undefined IP and seamless combinational of broadband LAN\ WAN\PAN\WLAN | Undefined IP and seamless combinational of broadband LAN\ WAN\PAN\WLAN |
| 5. | Service | Voice | 2 G: digital voice, SMS 2.5: voice + data | Integrated high-quality audio , video and data | Dynamic information access | Dynamic information access with AI capabilities |
| 6. | Multiplexing type of switching | FDMA circuit | TDMA, CDMA 2 G: circuit 2.5 G: circuit packet | CDMA packet | CDMA packet | CDMA packet |
| 7. | Core network | PSTN | PSTN | Packet network | Internet | Internet |
| 8. | Key- differentiate | Mobility | Secure | Better internet experience | Faster broadband internet lower latency | Better coverage, no dropped calls |
| 9. | Weakness | Poor spectral efficiency major security issue | Limited data rate difficult to support demand for Internet & e-mail | Real Information fail to match type | Battery use in required to complicated & expensive hardware | |
| 10. | Hand off | Horizontal | Horizontal | Horizontal | Horizontal & vertical | Horizontal & vertical |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the 4 G?
It is the fourth generation of mobile network technology. which was released in 2008, is 4 G. It supports and provides high data transmission speed, low latency and is suitable for HD video calling, fast download and upload, live streaming, cloud gaming etc.
What type of modulation was used in (1G to 5G ) network?
1 G networks used analog modulation, Frequency Modulation(FM)
2 G networks used Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK ), Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) 3 G networks used Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) 4 G networks used Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for downlink, Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) for Uplink 5 G networks used Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) for both downlink and uplinkWhat advancement does 5G Technology bring compared to 4G?
5G technology brings advancement such as ultra-fast speeds, ultra-low latency and support for a maximum number of connected devices simultaneously.
Related Posts
- Waveguide | Types, Characteristics, Parameters, and Advantages
- USART (8251) : Universal Synchronous And Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter
- UPS | Types | Comparison Between Online and Offline UPS
- Two Cavity Klystron Amplifier | Working, Operation and Performance
- TRIAC | Construction, Working and V-I Characteristics
- Travelling Wave Tube | Construction, Working and Applications











Leave a Reply