Table of Contents
Introduction
Electrical cables are like electric highways that carry power or signals from one place to another. They’re used for sending things like voice messages, computer data, and images through electrical signals. When we talk about electric wires, we usually mean a single, solid metal conductor, with or without insulation. On the other hand, electric cables can be either a bunch of insulated conductors or a stranded conductor. There’s also a special type called fiber-optic cables, which use flexible glass and plastic fibers to convert electrical signals into light pulses for transmitting audio, video, and computer data.
What is an Electrical Cable?
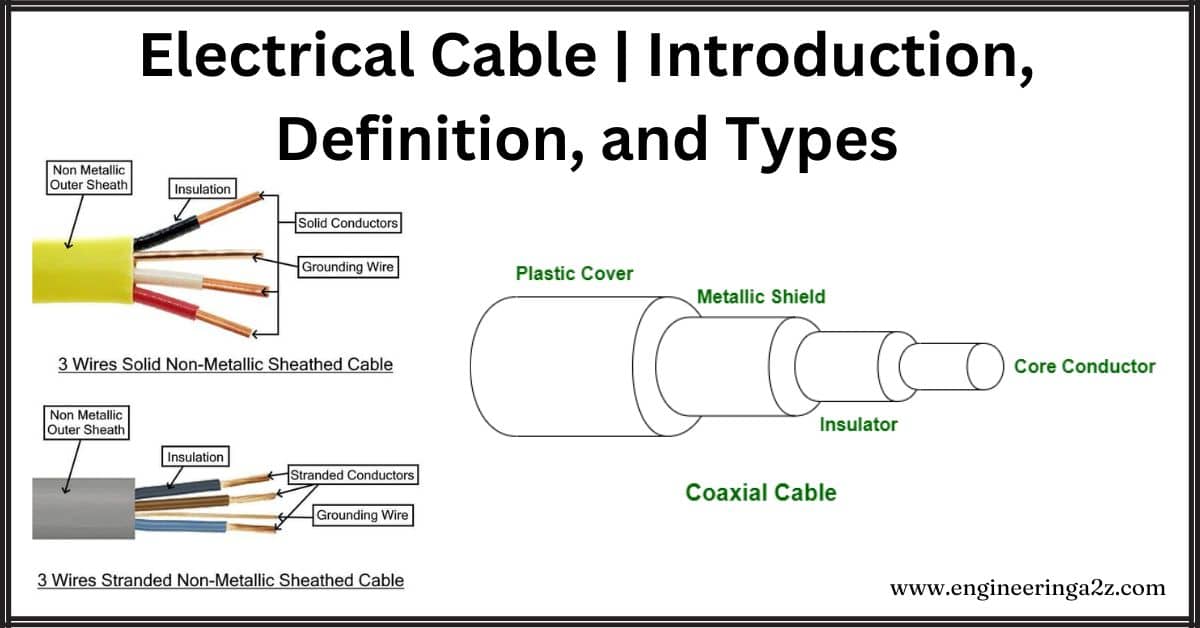
An electrical power cable is like a special wire used to carry strong electric power from one place to another, especially when using overhead lines is impossible. This cable has three main parts: the conductor, which carries the electric current; the dielectric, which protects against voltage and keeps the live conductor separate from other things; and the sheath, which keeps out moisture and shields the cable from things like chemicals, fire, and other external factors. So, in simple terms, it’s a strong and protected cable for moving electricity safely.
Components of an Electrical Cable
The electric cable is composed of three major components:
- Conductors:
- These are the wires that carry electricity.
- They’re made from metals like Copper or Aluminum, which are really good at letting electricity pass through.
- Think of them as the highway for electricity.
- Insulators:
- Imagine the conductors as cars on the highway. We need something to keep them in their lanes and prevent them from bumping into each other.
- Insulators are like dividers on the road. They keep the electricity flowing smoothly and prevent it from going where it shouldn’t.
- They used materials like paper or rubber in the past, but now they use special plastics like Polyethylene or Butyl Rubber.
- Sheath:
- This is like a protective jacket for the whole cable.
- It shields the cable from things like moisture, chemicals, or even fire.
- Picture it as a raincoat for the cable. The most common material for this protective layer is PVC, which helps keep the cable safe from the environment.
Types of Electrical Cable
Different types of cables are used for different purposes all around. Each cable has its own job based on its type. Electrical cables typically have aluminium or copper wires covered with a protective coating made of synthetic materials. In simpler terms, cables come in various kinds, and they do specific jobs, like carrying electricity, and they’re made with materials that keep everything safe.
Cables are classified into 5 types depending upon their purpose as follows:
1. Ribbon Electric Cables
A bunch of separate insulated wires are lined up next to each other. These wires help send lots of different information at the same time. For instance, it’s the kind of cable that links the computer’s brain (CPU) to the motherboard. We often use it to connect different devices in a network.
2. Shielded Cables
It’s a cable with one or two insulated wires, wrapped in a woven shield or aluminum foil. This helps the cable transmit signals better and prevents disruptions from power fluctuations and outside interference, especially in radios. These cables carry strong electric currents and have a shield for protection.
3. Twisted Pair Cables
It’s a cable with two or more copper wires inside that are twisted together and have different colors. We often see these in telephone cables. The more wires there are, the better the cable can resist outside interference.
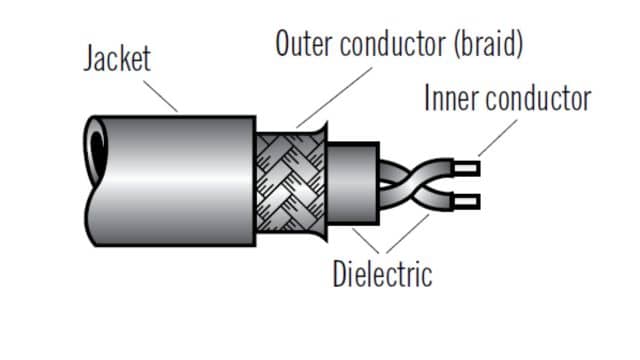
4. Coaxial Cables
It’s a cable with a solid copper or steel core covered in copper and then wrapped in metal braid and tape. An outer covering protects the whole thing. We use these cables for connecting computers and for audio-video setups.
5. Optics Cable
These cables carry light signals from one place to another. We know them as optical fibers, and they’re used in many different ways for various things.
Applications of Electrical Cable
Electrical cables are used in various ways:
- Power Transmission: Cables carry electricity from power plants to homes and businesses, ensuring a constant supply of power.
- Building Wiring: Inside buildings, cables distribute electricity to lights, outlets, and appliances, enabling them to function.
- Communication: Some cables transmit signals for internet, telephone, and television, connecting people globally.
- Industrial Machinery: Cables power and control machinery in industries, facilitating manufacturing processes.
- Transportation: In vehicles, cables play a role in powering engines, lights, and various electronic systems.
- Renewable Energy: Cables are crucial in connecting renewable energy sources, like solar panels and wind turbines, to the electrical grid.
- Data Centers: Cables enable the transfer of vast amounts of data within data centers, supporting digital services and storage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the definition of cable?
A cable is a bundle of thick wires covered in rubber or plastic. It’s used to carry electricity or electronic signals, like the ones you see overhead.
What are the 3 main parts of a cable?
A power cable has three parts: conductor (carries current), dielectric (insulates and withstands voltage), and sheath (protects). The conductor carries electricity, insulation keeps it safe, and a sheath shields it.
What is cable size?
Choosing the right cable size is straightforward. It depends on the cable length from the power source to the appliance and the current it carries. Longer cables or higher currents need larger cables to prevent voltage loss.
What is cable power?
“Cable power” could refer to the ability of Cable, a fictional character in comics, to possess telepathic and telekinetic powers, manipulating minds and objects. In a different context, “cable power” may relate to electrical power transmitted through cables in real-world applications.
Read Also:
- Transmission Line | Introduction, Classification, and Modelling
- Substation | Classification of Substations
- 10 Difference Between Indoor and Outdoor Substations
- Modern Grid | Characteristics and Functions
- High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) Transmission






Leave a Reply