Table of Contents
Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB)
In industrial, commercial, and domestic buildings sometimes leakage to earth occurs. This leakage may cause electric shock or fire. Hence, leakage into the planet is hazardous and needs protection. An earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installation with high earth impedance to prevent shock.
Read Also
MCB : Miniature Circuit Breaker | Engineeringa2z
Types Of ELCB
There are two types of Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers (ELCB)
- Voltage Operated ELCB
- Current Operated ELCB
- Voltage Operated ELCB: A Voltage Operated ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) is an electrical safety device that monitors voltage imbalances in a circuit. It trips the circuit when it detects leakage current, protecting against electrical shocks and fire hazards caused by faulty wiring or insulation breakdown.
- Current Operated ELCB: A Current Operated ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker) is an electrical safety device that monitors the current flowing through a circuit. It detects leakage currents by comparing the incoming and outgoing currents and trips the circuit to prevent electrical shocks and fire hazards caused by faults or ground faults.
Construction And Internal Circuit Details Of ELCB
The enclosures of the ELCB are molded from high-quality insulating material. The materials are fire retardant, anti-tracking, non-hygroscopic, impact resistant, and can withstand high temperatures. The body contains spring loaded mounting arrangement on the din-channel which ensures snap fitting ELCB into position. However, these also have the facility to screw on directly to any surface with the help of two screens. A 2-pole ELCB is used for a 1-phase supply and a 4-pole ELCB is used for a 3-phase, 4-wire supply.
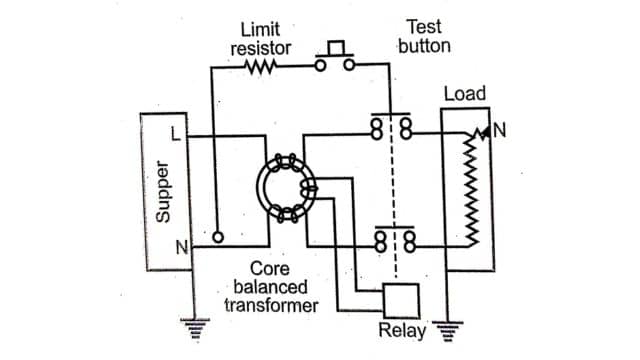
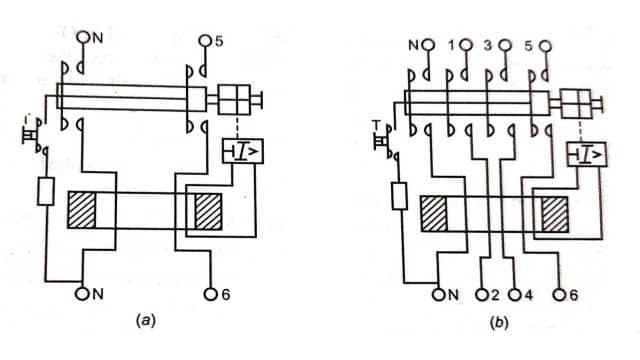
The internal wiring diagram of a 2-pole ELCB is shown in Fig above, an ELCB contains a core-balanced transformer (ferrite ring on which one or two turns of phase and neutral wire and a few turns of operating coil of the relay are wound) and a relay. A test button is placed between phase and neutral in series with a limiting resistor. The terminal designation and connection diagram for a 2-pole and 4-pole ELCB are shown in Fig.(a) and Fig.(b) respectively.
Working Principle Of ELCB
ELCBs (Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers) operate based on the principle of current imbalance detection. They monitor the difference between the current flowing in the live and neutral wires of an electrical circuit. When a fault or leakage current occurs, causing an imbalance, the ELCB senses it and quickly trips the circuit by opening its contacts. This action interrupts the power supply and protects against electric shocks and fire hazards caused by faulty insulation or ground faults.
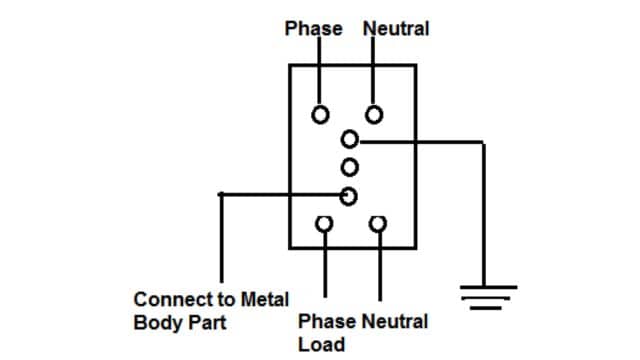
Under normal conditions, the magnitude of currents flowing through the phase wire and neutral are the same and the core of the core-balanced transformer does not carry flux (i.e. two windings neutralizes the flux). Thus, no e.m.f. is induced in the operating coil of the relay wound on the same core. When an earth fault occurs, the current in phase wire becomes more than in neutral wire. This unbalancing sets up flux in the core of the core-balanced transformer that in turn induces an e.m.f. in the operating coil of the relay. So, the relay is energized and the plunger of the ELCB protects the load by going to the off position or disconnecting the load from the supply.
Thus, ELCB protects the system against leakage. A test knob is provided for periodic checking of the mechanism and function of ELCB.
Advantages Of ELCB
- Fault Insensitivity: The ELCB is not highly sensitive to faults, meaning it requires a substantial voltage gradient in the soil to trip and provide protection.
- Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency: The ELCB is an affordable and efficient solution for electrical safety, offering reliable protection against electrical hazards while being cost-effective in terms of installation and maintenance.
- Protection against Electric Shocks: The primary purpose of the ELCB is to safeguard both humans and animals from the risks of electric shocks, ensuring their safety in the event of a fault or leakage current.
- Operation Principle: In this setup, when the ELCB is installed with two connections to the ground, a high-current lightning strike close to the ground creates a voltage gradient in the soil. The ELCB is designed to sense this voltage and promptly trip the circuit, ensuring safety measures are activated.
- Reworded: The ELCB’s fault sensitivity is moderate, offering a reliable level of protection. It is a cost-efficient and effective device that safeguards against electrical shocks, specifically by detecting the voltage gradient caused by lightning strikes near the ground, leading to a timely trip for enhanced safety.
Disadvantages Of ELCB
- Limited fault protection.
- Susceptible to false tripping.
- Complex installation requirements.
Application Of ELCB
- Residential buildings
- Commercial establishments
- Industrial facilities
- Hospitals and healthcare facilities
- Educational institutions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is ELCB?
ELCB stands for Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker. It is a safety device used to protect electrical circuits and equipment from electrical faults and electric shock. An ELCB automatically cuts off the power supply to a circuit if it detects leakage of current to the earth.
What are the types of ELCB?
There are two types of ELCB:
(i) Voltage-operated ELCB
(ii) Current operated ELCBWhat is a circuit breaker?
A circuit breaker is an electrical device designed to operate automatically during a short circuit or overload.
Related Posts
- Difference Between HVDC and HVAC
- Different Types of Faults in Overhead Transmission Lines
- Circuit Breaker | Types of Circuit Breaker
- Tariff: Definition, Types, Objectives & Characteristics of Tariff
- AC and DC System : What is AC and DC Transmission System
- Buchholz Relay | Construction and Working Principle












Leave a Reply