Table of Contents
Introduction
Distribution Automation (DA) is a collection of technologies like sensors, processors, communication networks, and switches that help utilities collect, automate, analyze, and optimize data. This improves the efficiency of power distribution systems.
What is Distribution Automation?
Distribution automation (DA) uses technologies like sensors, processors, and communication networks to improve the efficiency of power distribution systems. It automates data collection, analysis, and optimization to enhance processes such as fault detection, feeder switching, and voltage control, ensuring reliable and efficient power delivery.
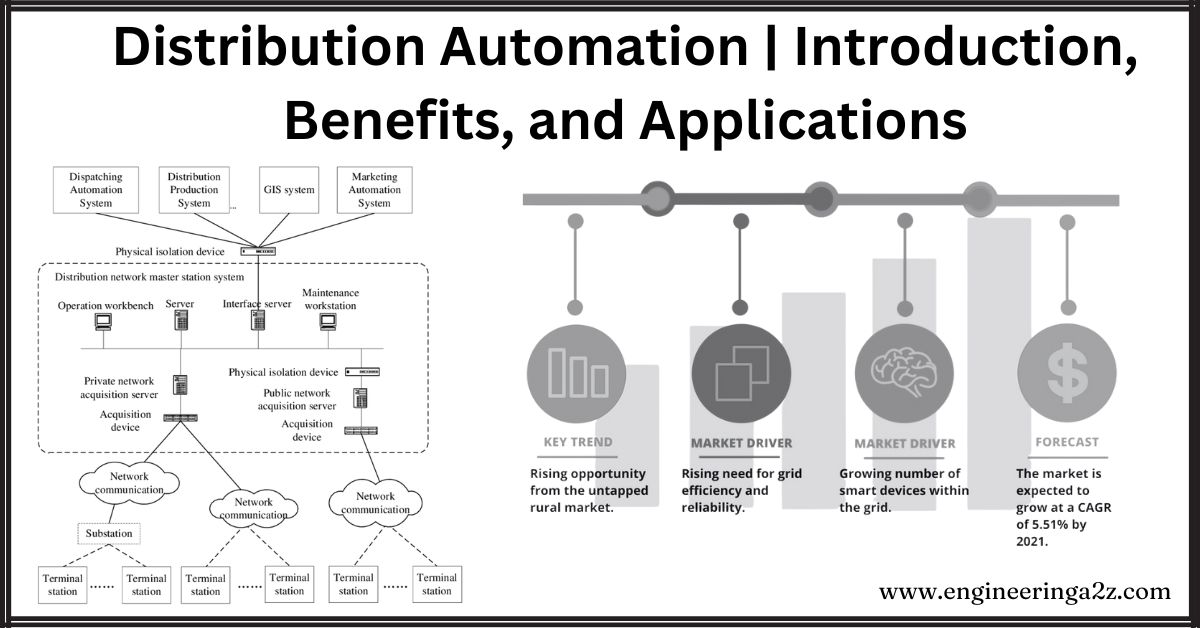
Components and Systems of Distribution Automation
DA includes various products and systems to manage distribution and substations’ electrical loads. These include:
- Asset optimization
- Automated and interconnected equipment
- Demand optimization
- Distribution optimization
- Monitoring and control software for distribution systems
- Information and communication technology networks
- Test equipment for product certification and compliance

Areas of Distribution Automation System
The area distribution automation system can be divided into two parts:
A. Distribution Substation & Feeder Automation:
- This involves integrating automation at substations and feeders to share common monitoring and control equipment.
- It includes controlling circuit breakers, load tap changers (LTCs), regulators, reclosers, sectionalizers, switches, and substation capacitor banks.
- Remote data collection is needed to effectively use these control functions.
B. Consumer Location Automation:
- This involves automation at the consumer’s location, allowing remote tasks such as reading meters, programming time-of-use (TOU) meters, connecting or disconnecting services, and controlling consumer loads.
Benefits of Distribution Automation System
The benefits of implementing a distribution automation system can be grouped into three main areas:
1. Operational & Maintenance Benefits:
- Improved reliability by reducing outage times with automatic restoration
- Better voltage control through automatic VAR control
- Reduced labor hours and manpower
- Accurate and useful data for planning and operations
- Improved fault detection and diagnostic analysis
- Better management of system and component loading
2. Financial Benefits:
- Increased revenue from quicker restoration
- Improved use of system capacity
- Keeping customers due to better quality of supply
3. Customer-Related Benefits:
- Better service reliability
- Reduced interruption costs for industrial and commercial customers
- Better quality of power supply
Stakeholders in Distribution Automation
The distribution automation can be categorized into three stakeholders: utilities, customers, and society. While societal benefits are often harder to quantify, they are equally critical in evaluating the overall advantages of a specific function, as they encompass broader impacts on community well-being, environmental sustainability, and economic development. This holistic assessment ensures a comprehensive understanding of the value distribution automation brings.
Distribution Automation Applications
- Fault Detection: Quickly identifies and isolates faults in the power system.
- Feeder Switching: Automatically switches power routes to maintain supply during faults.
- Outage Management: Reduces downtime by quickly restoring power.
- Voltage Control: Maintains stable voltage levels in the network.
- Reactive Power Management: Balances power to improve efficiency.
- Preventative Maintenance: Monitors equipment to prevent failures.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Supports the connection of renewable energy sources to the grid.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is meant by distribution automation?
Distribution automation (DA) uses technology to automate and optimize power distribution, improving efficiency, reliability, and fault management.
What are the 4 types of automation?
The four types of automation are:
1. Fixed Automation: High-volume production with fixed processes.
2. Programmable Automation: Flexible for batch production.
3. Flexible Automation: Quickly adaptable for different products.
4. Integrated Automation: Entirely automated manufacturing processes.Where is automation used?
Automation is used in manufacturing, transportation, utilities, healthcare, financial services, agriculture, and home automation to improve efficiency, accuracy, safety, and reduce labor costs.
Related Posts
- Difference Between HVDC and HVAC
- Different Types of Faults in Overhead Transmission Lines
- Circuit Breaker | Types of Circuit Breaker
- Tariff: Definition, Types, Objectives & Characteristics of Tariff
- AC and DC System : What is AC and DC Transmission System
- Buchholz Relay | Construction and Working Principle












Leave a Reply