Table of Contents
Introduction
Digital Control System (DCS) also known as Distributed Control system is the brain of the control system. DCS refers to a control system usually of a manufacturing system, process or any kind of dynamic system, in which the controller elements are not central in location (like the brain) but are distributed throughout the system with each component sub-system controlled by one or more controllers. The entire system of controller is connected by networks for communication and monitoring.
Distributed Control System
Distributed Control System (DCS) is a computerized control system for a process or plant that consists of a large number of control loops, I’m which autonomous controller are distributed throughout the system but there is central operator supervisory control. DCS is a system of sensors, controller and associated computers that are distributed throughout a plant. DCS can be used to enhance reliability and reduce installation costs.
Subsystems of Distributed Control System
Distributed Control System are organized into five subsystems:
- Process interface, which is responsible for the collection of process data from measurement instruments and the issuing of signals to actuating devices such as pumps, motors and valves.
- Process control, which is responsible for translating the information collected from the process interface subsystem and determining the signals to be sent to the process interface subsystem based on pre-programmed algorithms and rules sets in its memory.
- Process operation, which is responsible for communicating with operation personnel at all levels including operator displays, alarms, trends of process variable and activities, summary reports, and operational instruction and guidance. It also tracks process operation and product batch lots.
- Application engines, which are the repository for all of the programs and packages for the system from control, display and report configuration tools to program language compilers and program libraries to specialized packages to repositories for archived process information.
- Communications subsystems, which enable information flow between the various DCS subsystems as well as to other computerized systems.
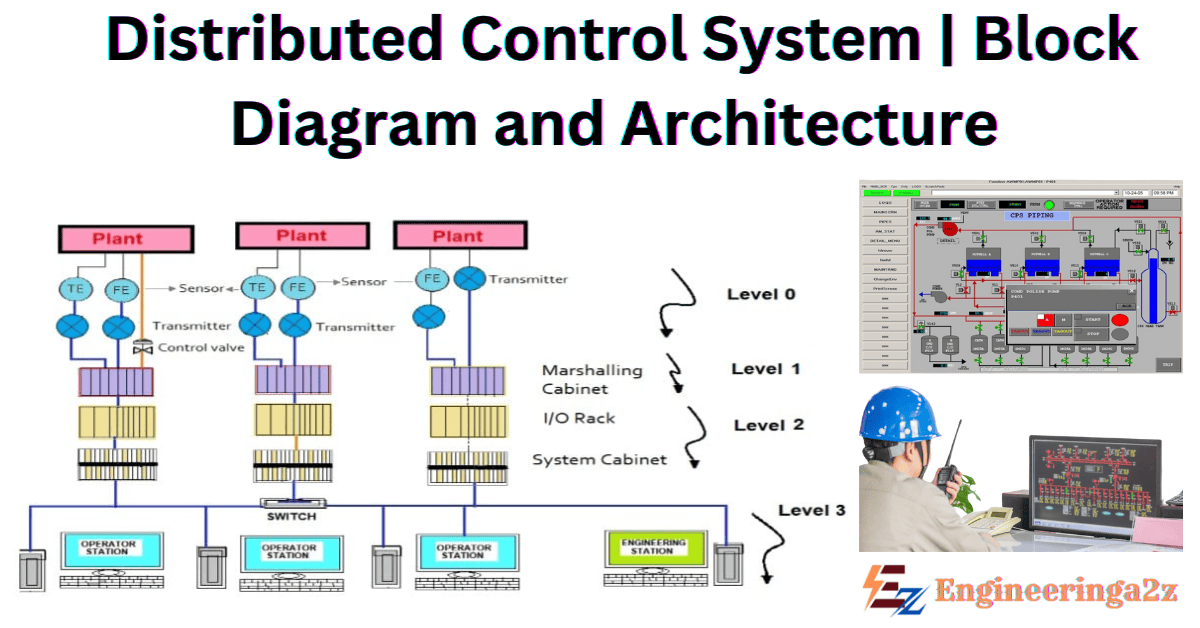
Block Diagram of DCS
As DCS contains the distribution of the control processing around nodes in the system, the complete system is reliable and mitigate a single processor failure. It will affect one section of the plant process, if a processor fails and the whole process will be affected when the central computer fails. This distribution of computing power to the (field Input/Output) field connection racks also ensures fast controller processing times by removing possible network and central processing delays.
The below diagram showcase the functional manufacturing levels using computerized control.
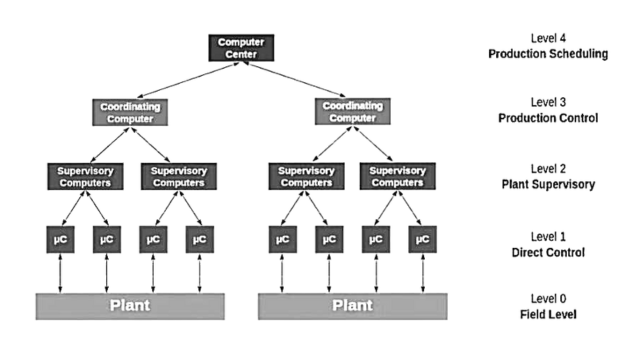
Referring to the diagram:
Level 0 : It consists of the field devices such as temperature sensors, flow, and final control elements such as control valves.
Level 1 : It consists of the industrialized Input/ Output (I/O) modules, and their associated distributed electronics processor.
Level 2 : It is included with supervisory computers that helps together information from processor nodes on the system, and provide Operator control screens.
Level 3 : It is the production control level, which does not directly control the process but is concerned with monitoring production and monitoring targets.
Level 4 : It is the production scheduling level.
On the other hand, Level 1 and Level 2 are the functional levels of a traditional DCS, in which all equipment are part of integrated systems from a single manufacturer. Level 3 and 4 do not strictly process control in the traditional sense, but where production control and scheduling takes place.
Architecture of Distributed Control Systems
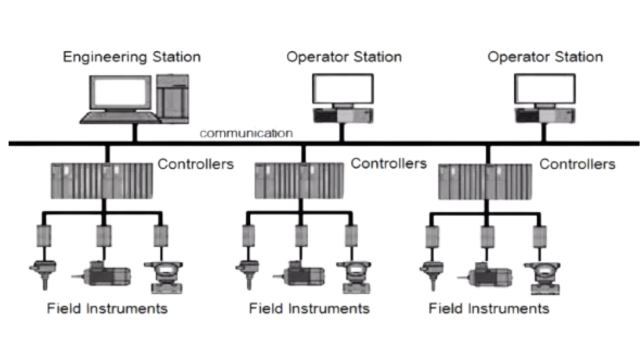
The architecture design of a DCS includes the following:
- Controller: Local processors that perform control tasks, receiving input signals from sensors and sending output signals to actuators.
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): A user interface that allows operators to monitor and control the system, typically through computers or touchscreens.
- Input/output (I/O) modules: Interface devices that connect field instruments (like sensors and actuators) to the controller.
- Field Devices: Instruments such as sensors and actuators located throughout the plant that measure or control physical variables like temperature, pressure and flow.
- Communication Network: This system brings data from station to station and is important in the distributed control system. Typical network protocols used include Ethernet, Profibus and DeviceNet.
- Engineering Workstation: A computer used to configure, monitor and maintain the DCS.
Characteristics of DCS
The characteristics of the distributed control system are:
- Various control functions can be distributed into small sets of subsystems that the semi-autonomous. These are connected with high speed communication bus and their function us data presentation, data acquisition, process control etc.
- Automation of manufacturing process by integrating advanced control strategies
- Arranging the things as a system.
- System protection.
Advantages of DCS
The advantages of the distributed control system are:
- Its reducing engineering time.
- Control function is distributed among multiple CPUs (Field Control Stations). Hence failure of one FCS does not affect the entire plant.
- It requires minimal troubleshooting and maintenance becomes very easy.
- Generation and modification of the interlocks are very flexible and simple.
- Information regarding the process is presented to the user in various formats.
Applications of DCS
The processors where the DCS is employed are:
- Chemical plants, Nuclear power plants and Petrochemical, Refineries
- Environmental control systems
- Water management systems
- Water treatment Systems and sewage plants
- Food and food processing
- Metal and mines
- Automobile manufacturing
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is DCS?
Distributed Control System (DCS) is a computerized control system for a process or plant that consists of a large number of control loops, I’m which autonomous controller are distributed throughout the system but there is central Operator supervisory control.
-
What are the components of a DCS?
The primary components of a DCS includes are:
1. Controllers
2. Input/Output (I/O) modules
3. Communication Networks
4. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI)
5. Engineering workstation
6. Field devices -
Who invented DCS?
The First Distributed Control System was made by Honeywell in 1969.
-
What is DCS full form?
The full form of DCS is the Distributed Control System.
Related Posts
- Difference Between HVDC and HVAC
- Different Types of Faults in Overhead Transmission Lines
- Circuit Breaker | Types of Circuit Breaker
- Tariff: Definition, Types, Objectives & Characteristics of Tariff
- AC and DC System : What is AC and DC Transmission System
- Buchholz Relay | Construction and Working Principle














Leave a Reply