Table of Contents
Dielectric Heating
In dielectric heating the energy of high-frequency electromagnetic field is being transferred to thermal energy. It happens due to the effect of alternating electromagnetic field to the polar molecules of the material.
Read Also
What is Electric Heating
Working of Dielectric Heating
In dielectric heating the energy of high-frequency electromagnetic field is being transferred to thermal energy. Thermal energy is generated due to the effect of alternating electromagnetic field to the polar molecules of the material.
The molecular dipoles changes regularly because of current field orientation up to billion times per second. During this phenomenon following effects occur
(a) The intermolecular friction surpassing the molecular attraction forces and
(b) The hysteresis occurring between the fields and induced electric feedback caused by inertia depending on electric charge, mass and shape of the molecules.
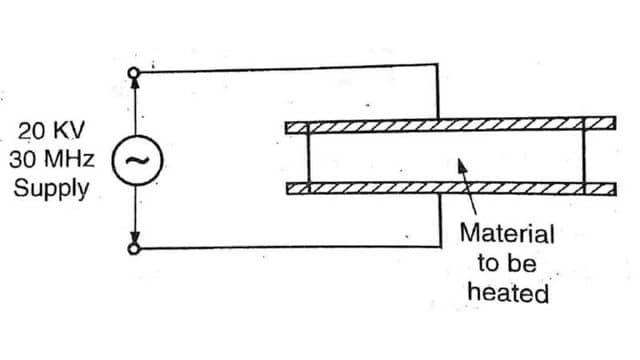
Dielectric heating does not apply to gasses. The dielectric heating is also known as High Frequency capacitor heating. It is used for non metal and dielectric materials like wood. Cloth, paper, plastic etc. The frequency applied is in MHz and voltage near 20 KV. Heating takes place in the material itself. The time of heating is lesser than the heating in furnaces. Note that there is no other method of heating insulating materials.
Read Also
Methods of Heating
When a capacitor is subjected to the sinusoidal voltage in ideal case, current leads the voltage by 90° but practically this angle is less and hence dielectric loss occurs. At small frequencies this loss is less but at MHz frequencies this loss is enough to the heat the material.
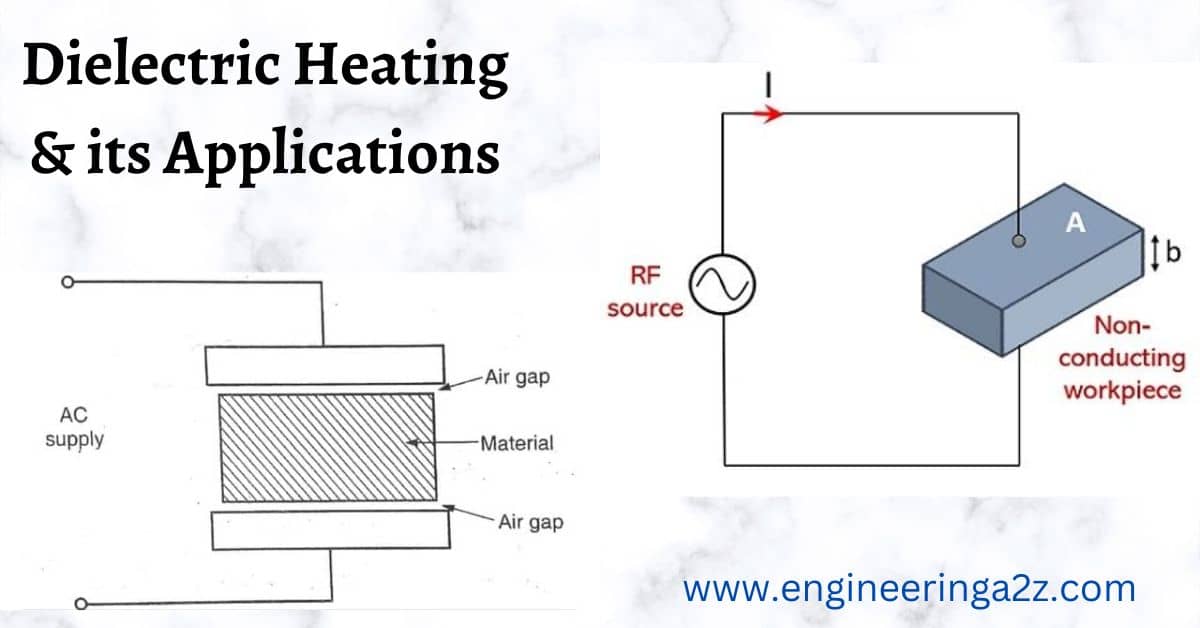
The insulating material to be heated is kept in between two conducting plates across which High Frequency voltage is applied. This forms a capacitor and the dielectric losses occuring in the insulating material heat up the material.
An important feature of this heating is that the materials with poor thermal conductivity can be heated in a very short time. The processes which would take hours with furnace heating can be carried out in minutes by dielectric heating.
The dielectric heating depends only upon the frequency and the square of voltage used. By changing either, the rate of heating can also be changed. To get more heat, use of high frequency is therefore, the only alternative.
Read Also
Induction Heating and its Types
This has been discussed below :
- For a particular frequency withstand power can be increased by increasing the voltage. But this depends upon the dielectric strength of the materials. The voltage more than the dielectric strength of the material may cause break down of the material. for example, the Breakdown voltage of mica is 80 kV per mm. A voltage more than this cannot be applied across mica. Thick dielectrics can bear more voltage and thinner dielectrics can withstand less voltage. So there is a limit for increasing voltages. Applying more than 20 kV is not advisable.
- Consideration of voltage gradient is also to be kept in mind. The heat produced in any part of the dielectric, is proportional to the square of the voltage gradient. If the gradient is not constant, heating will not be uniform.
So an air gap is provided between the material and the electrode to over come the problem.
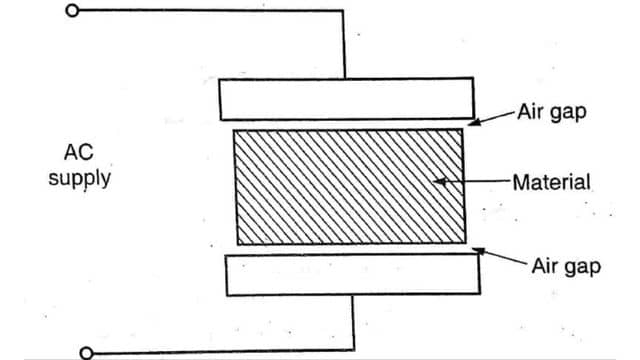
The air gap is a must in the following cases
- When the material moves on a conveyor.
- When different regions of materials are to be heated at different rates.
- When the shape of the material is not regular.
For this, electrodes used are of slightly large in size that the material.
Advantages of Dielectric Heating
- Heating is very quick
- The efficiency is higher
- Heating is uniform
- Being free from smoke, dust, process is very clean.
- There are no flue gases, no risk of pollution.
- Heat is produced due to dielectric loss occurs in the material itself.
Applications of Dielectric Heating
Few application of dielectric heating are :
- Raw plastic is heated by dielectric heating.
- Glueing of wood is done by dielectric heating for making panels. It takes 30 sec. where as conventional method takes one day.
- Dielectric heating in used for electronic sewing of plastic film garments such as rain coat.
- Dielectric heating is used for drying process in textile industry.
- In food processing, the dielectric heating is used for cooking foods, dehydrating fruits etc.
- For evaporating.
- As a source of ionized matter in plasma generator.
- For melting.






Comments (3)
Very Nice
Great content
Great content