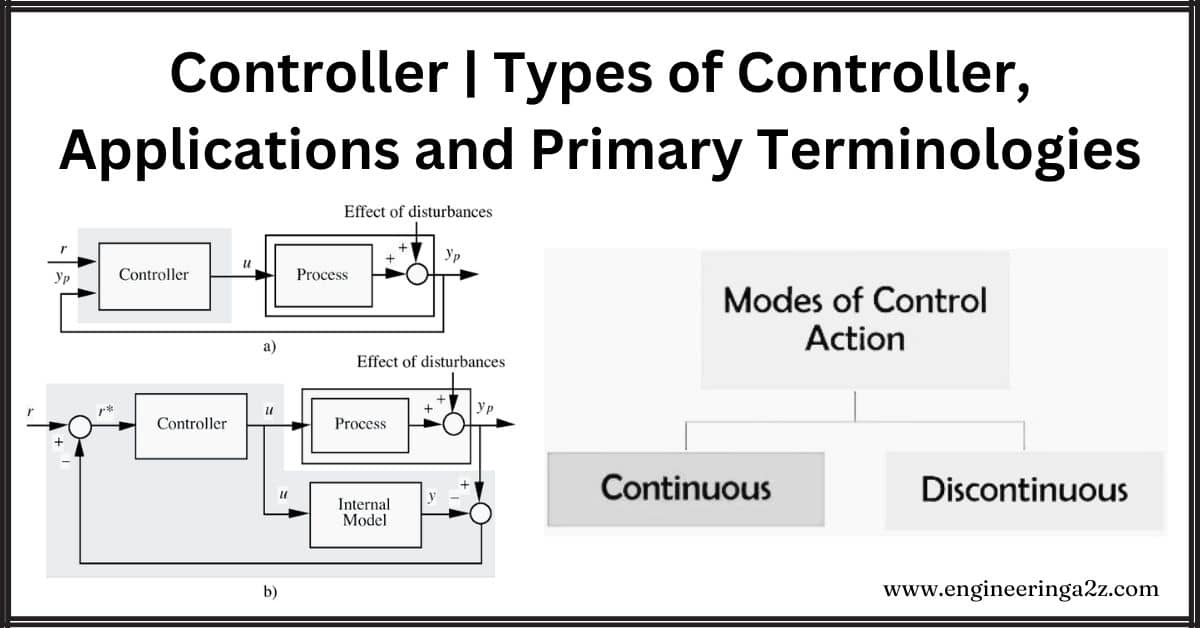
Controller | Types of Controller, Applications, and Primary Terminologies
What is a Controller? Controllers are like the brains of a control system, working to…
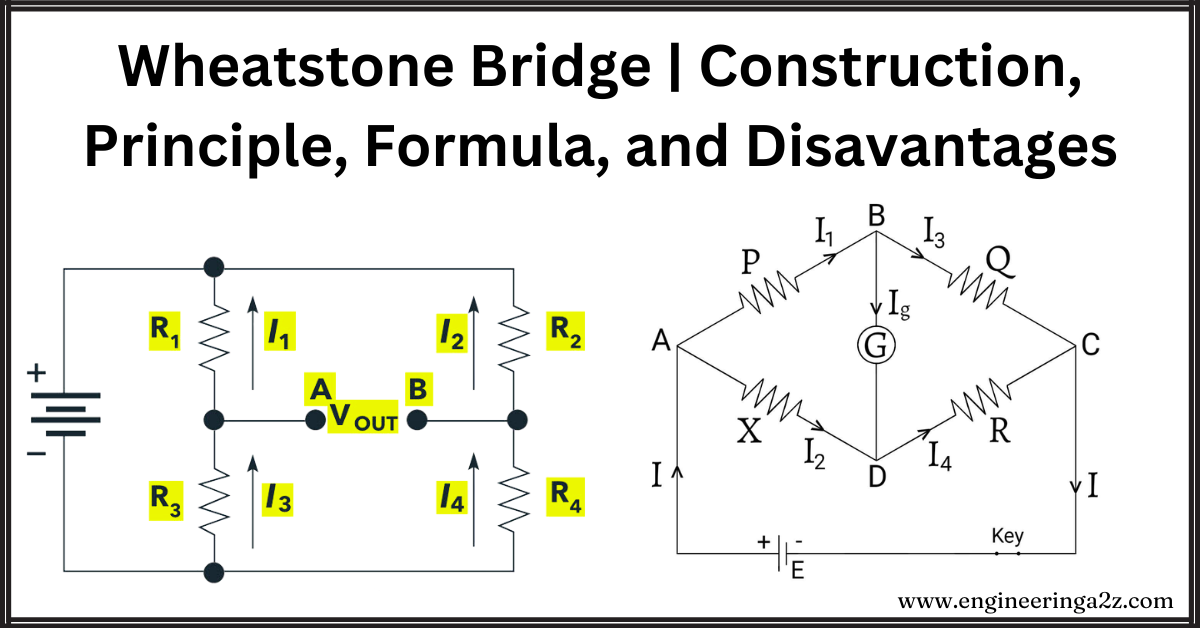
Wheatstone Bridge | Construction, Principle, Formula, and Disadvantages
Introduction The Wheatstone Bridge is a gadget invented in 1842 by scientist Wheatstone to figure…
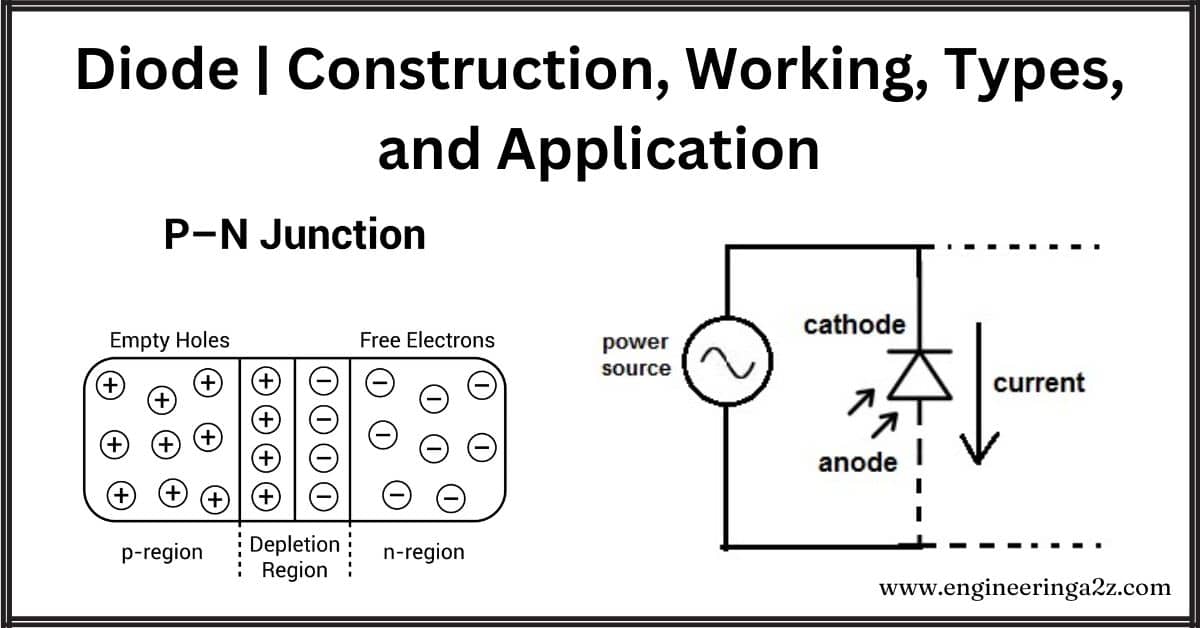
Diode | Construction, Working, Types, and Application
Introduction A diode is a small device with two ends, and it mostly allows electricity…
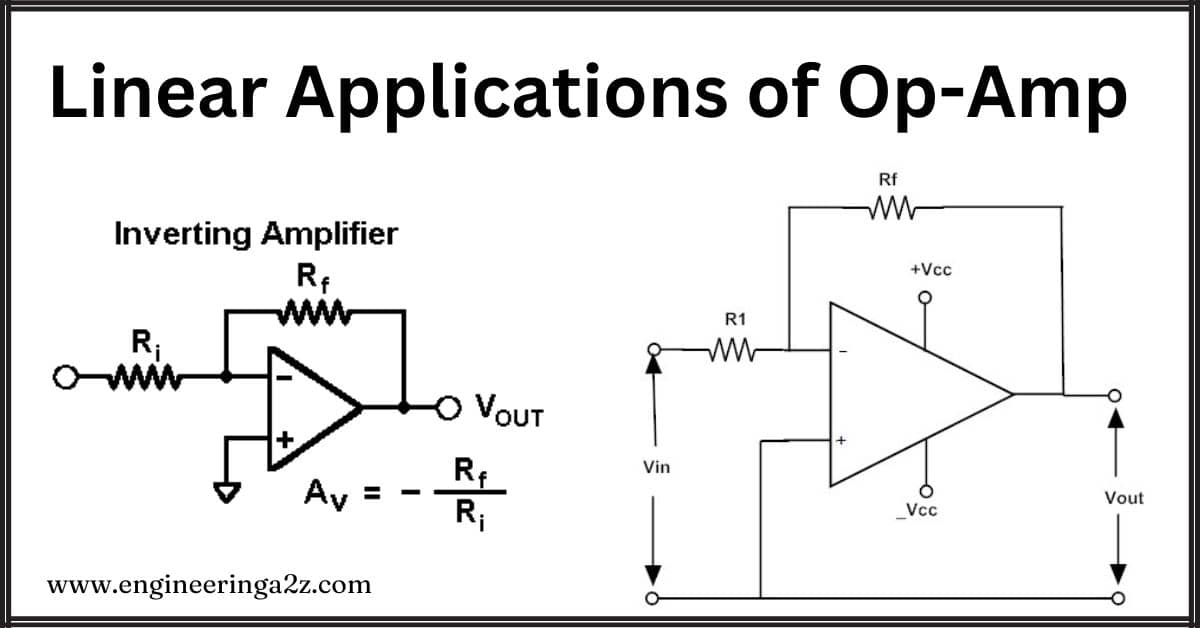
Linear Applications of Op-Amp
A linear amplifier like an op amp has many different applications. It can make weak…
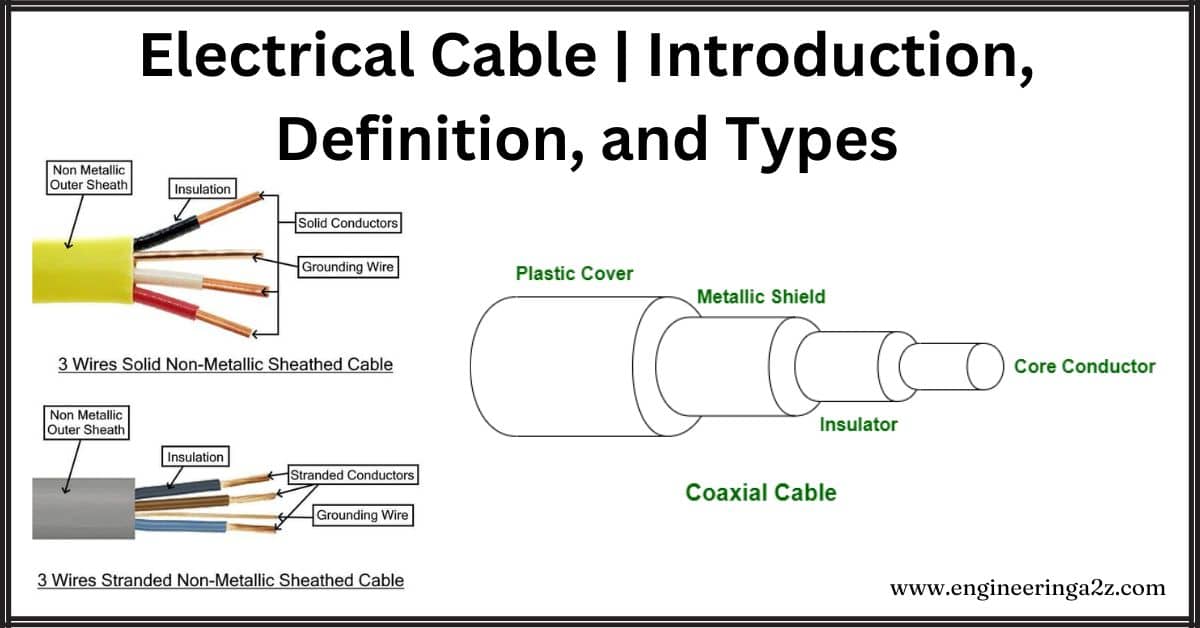
Electrical Cable | Components, Types and Application
Introduction Electrical cables are like electric highways that carry power or signals from one place…
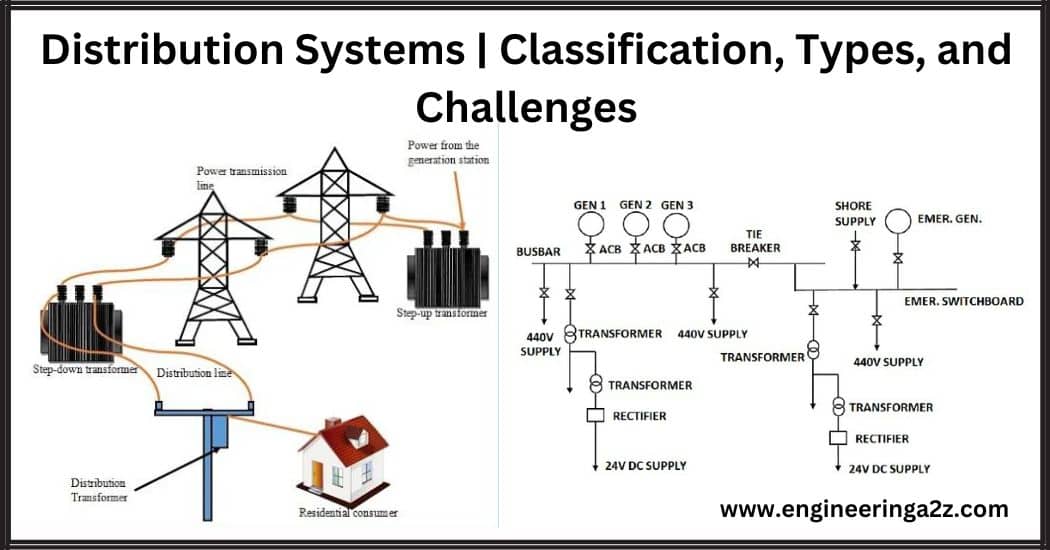
Distribution Systems | Classification and Challenges
Introduction The distribution systems is like the delivery system for electricity in a local area.…
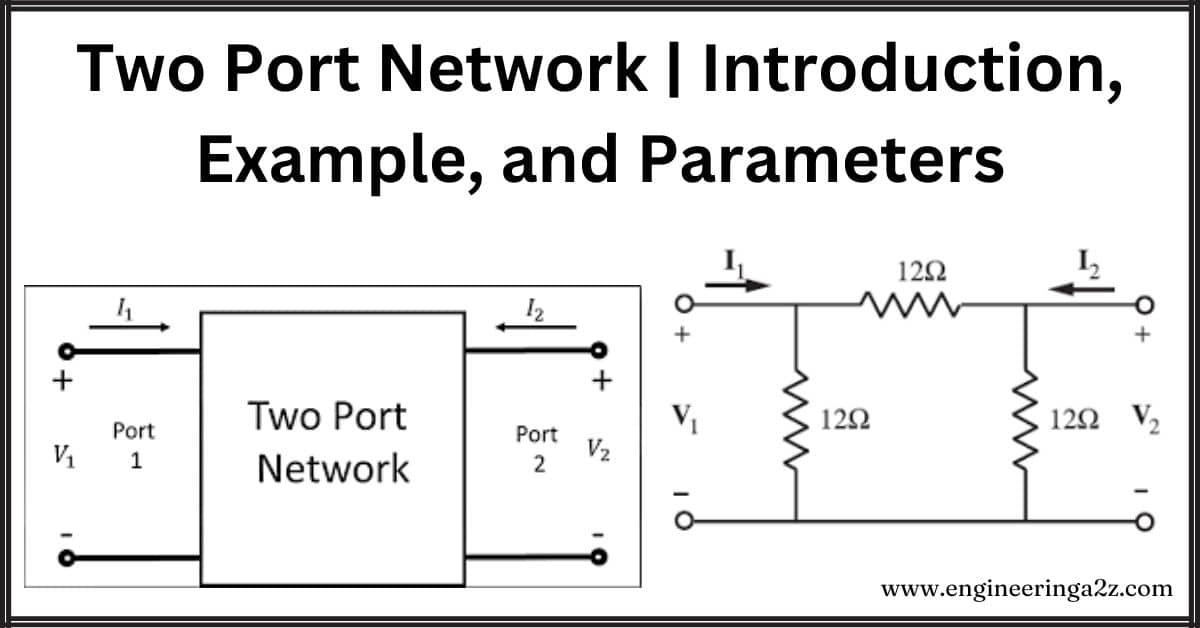
Two Port Network | Introduction, Example, and Parameters
Introduction Two-port networks simplify complex electrical circuits. They represent components like transmission lines and transformers,…
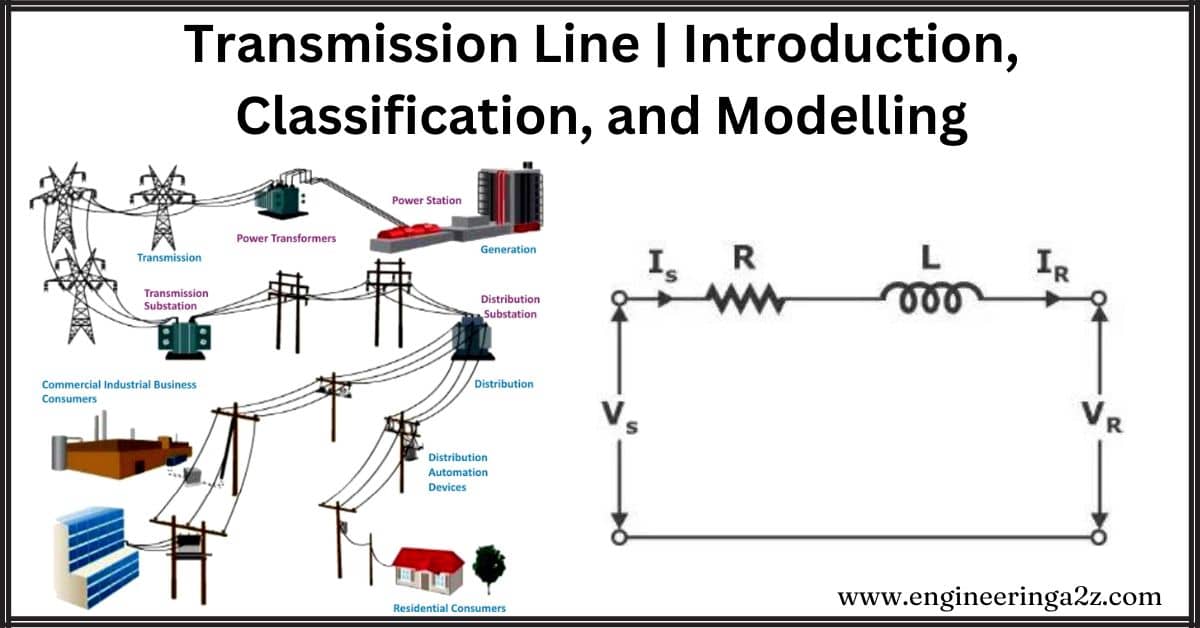
Transmission Line | Introduction, Classification, and Modelling
Introduction A transmission line is like a power highway for electricity to travel from a…
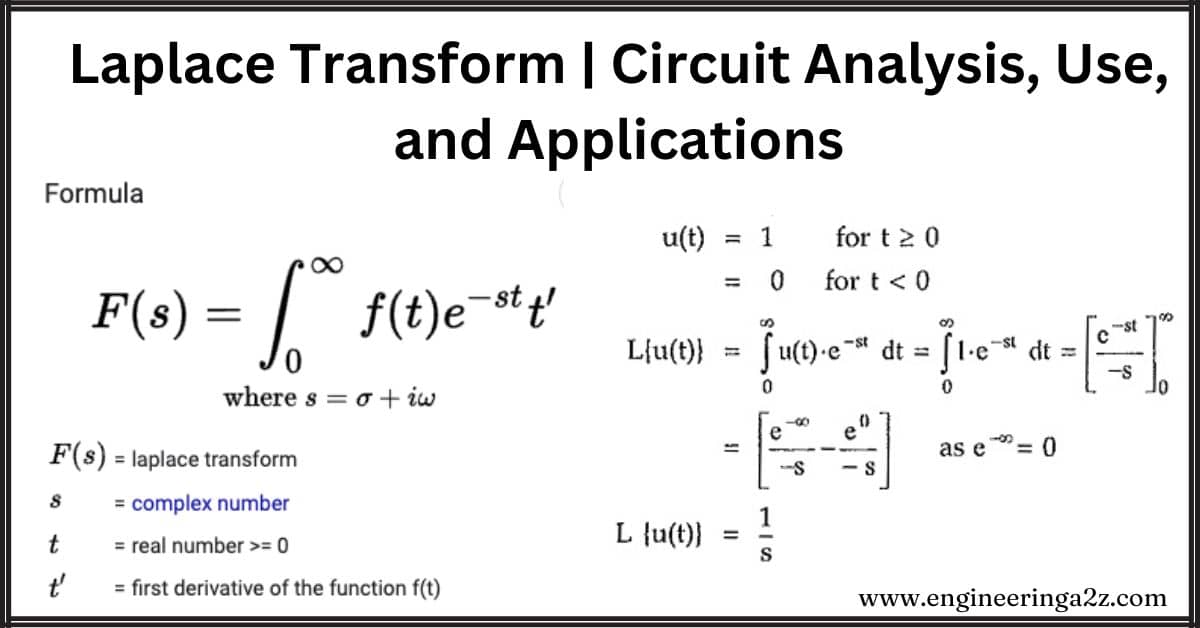
Laplace Transform | Circuit Analysis, Use, and Applications
Introduction Circuit analysis is crucial in electrical engineering for designing circuits. The Laplace transform, created…
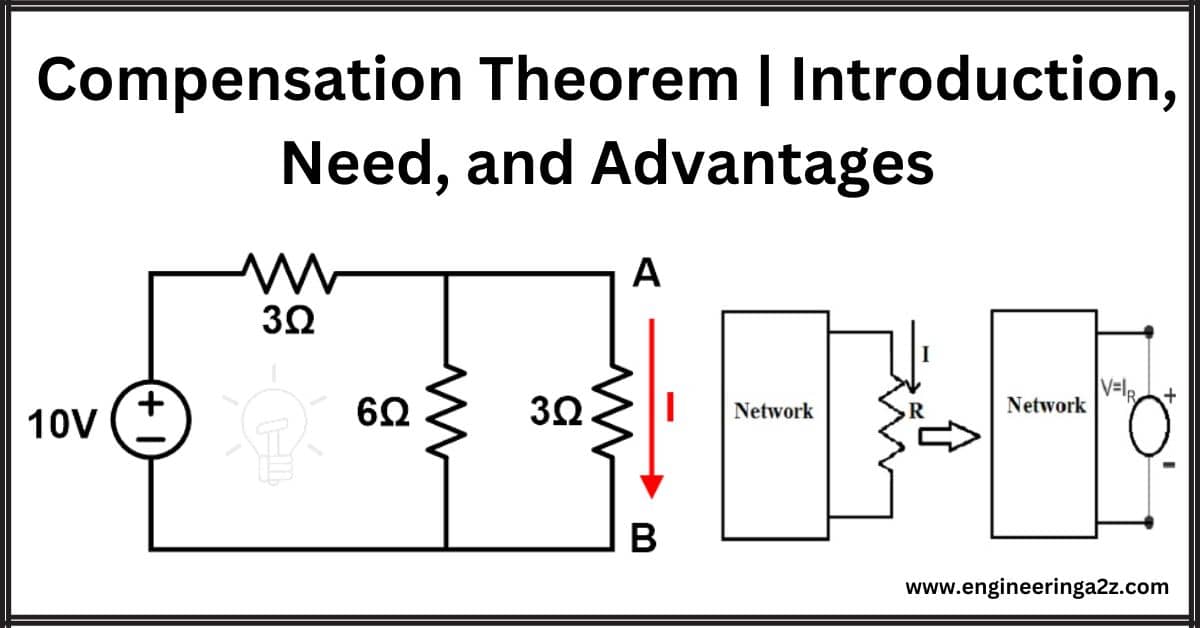
Compensation Theorem | Introduction, Need, and Advantages
Introduction To understand the compensation theorem let's, imagine you have a network or circuit with…





Comments