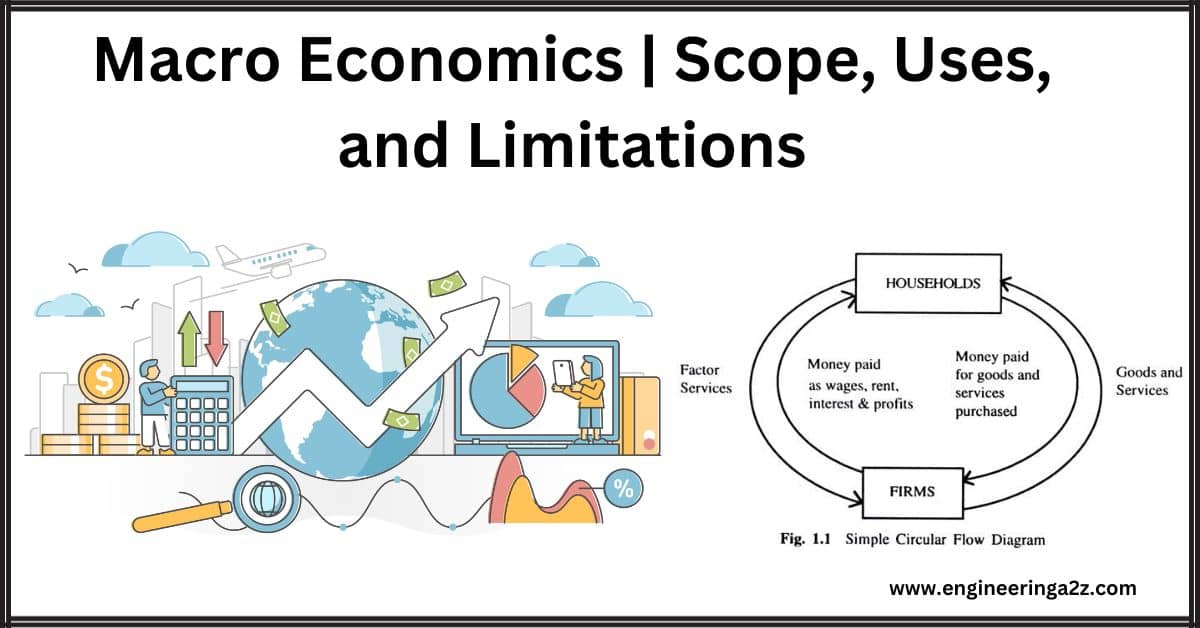
Macro Economics | Scope, Uses, and Limitations
'Macro' as used in the English language originates in the Greek word Makros, meaning large.…
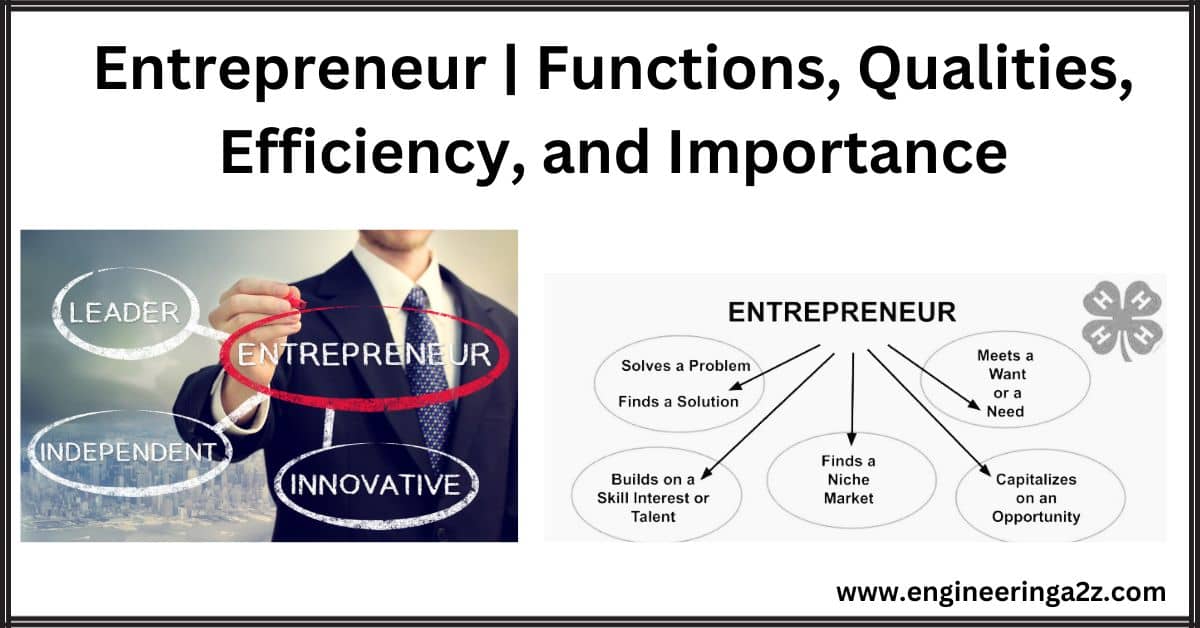
Entrepreneur | Functions, Qualities, Efficiency, and Importance
Entrepreneur In the modern age, the significance of the entrepreneur as a factor of production…
Division of Labour | Main Forms, Advantages, and Favourable Conditions
Introduction Adam Smith came up with the idea that people should do what they're best…
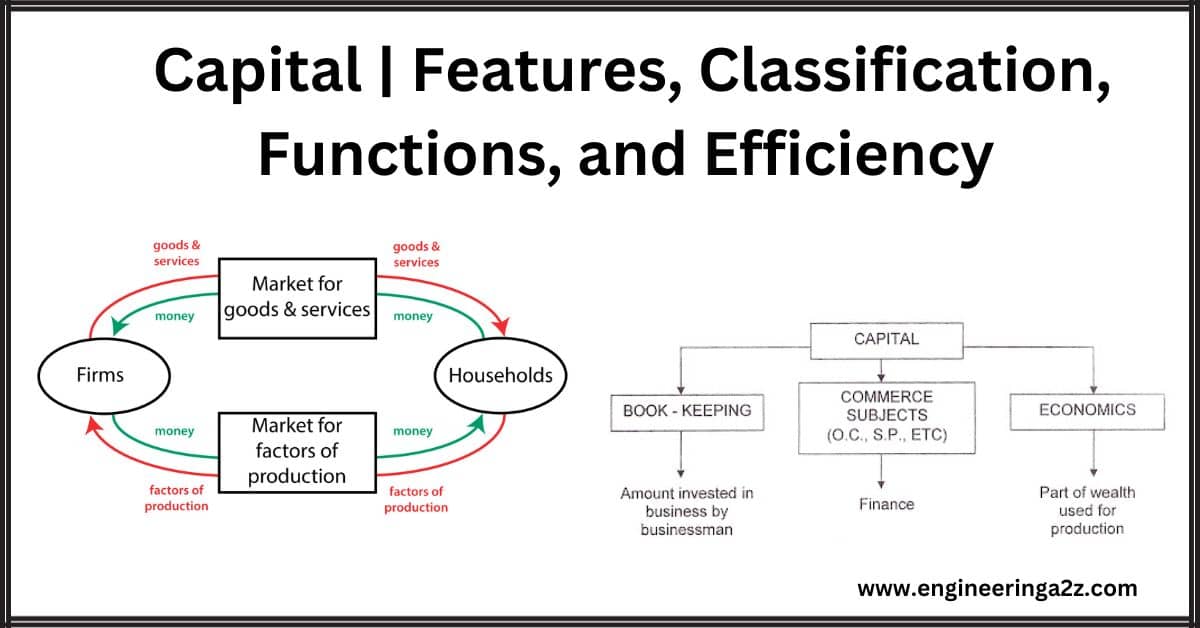
Capital | Features, Classification, Functions, and Efficiency
Capital Capital is a crucial factor in production. In everyday language, we often use terms…
Financial management | Types, Objectives, Functions and Career
Definition Financial management is like being the money boss of a business. Whether it's a…
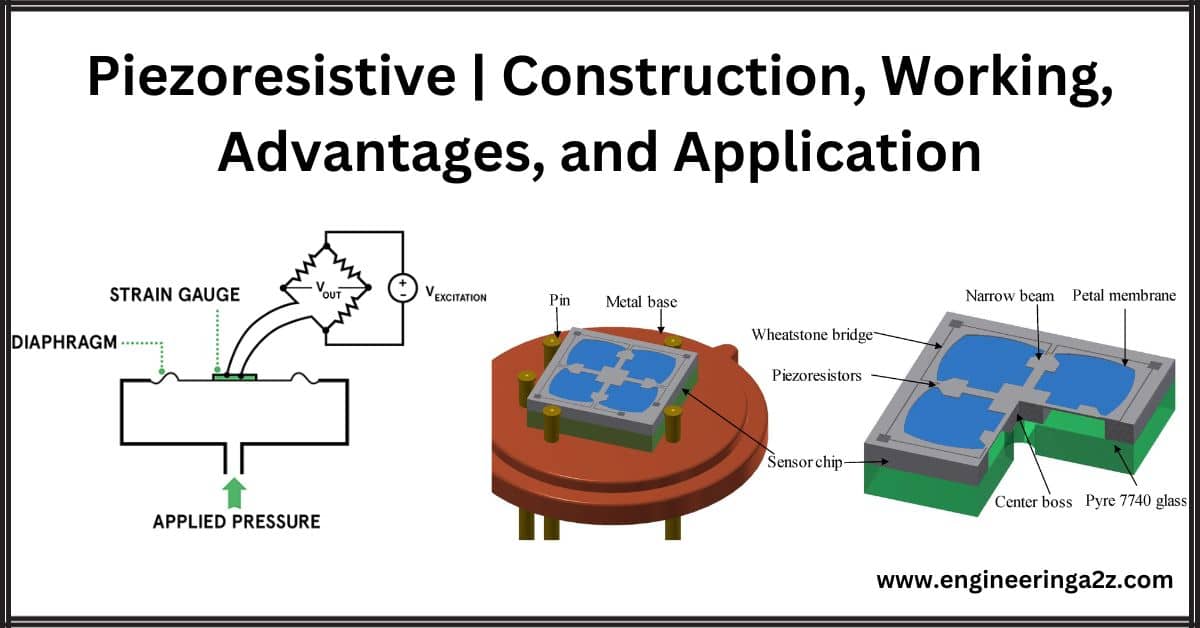
Piezoresistive | Construction, Working, Advantages, and Application
Piezoresistive Piezoresistive materials are substances that exhibit changes in electrical resistance when subjected to mechanical…
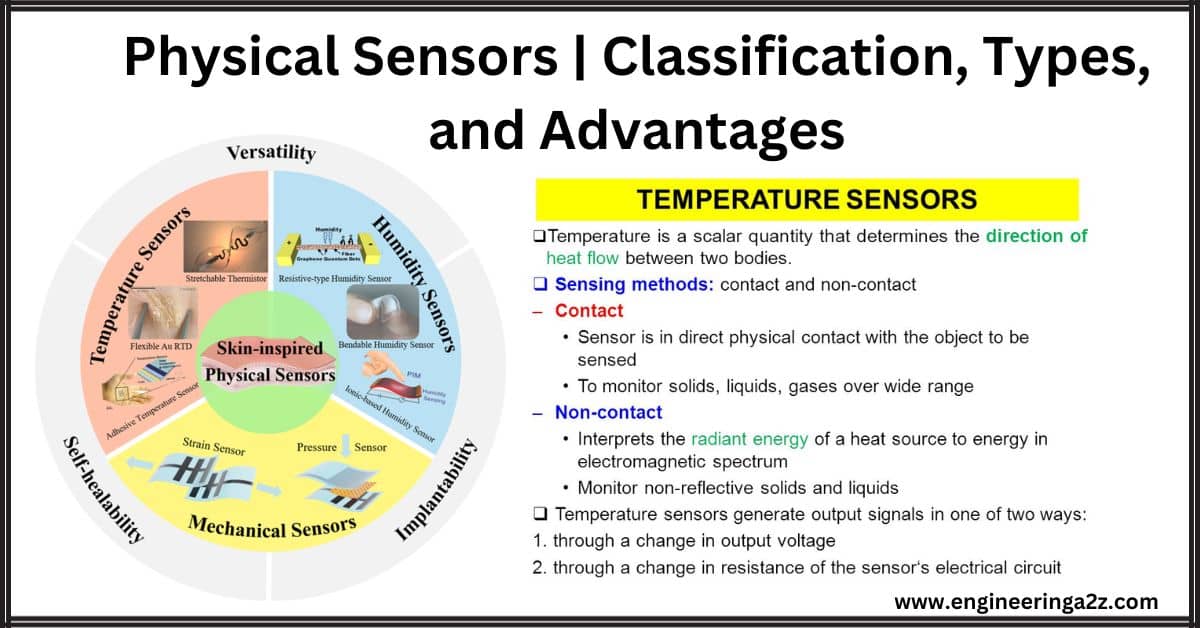
Physical Sensors | Classification, Types, and Advantages
Introduction Physical sensors are devices that detect and respond to physical input from the environment.…
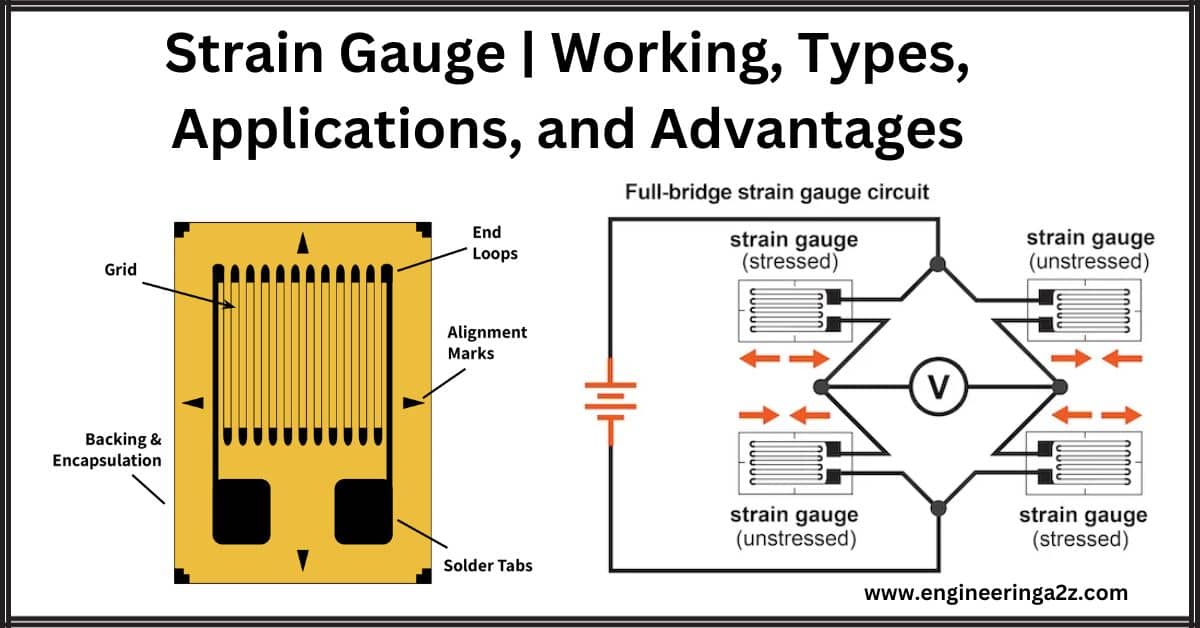
Strain Gauge | Working | Types | Applications and Advantages
Introduction A strain gauge is like a smart sensor that senses changes in resistance when…
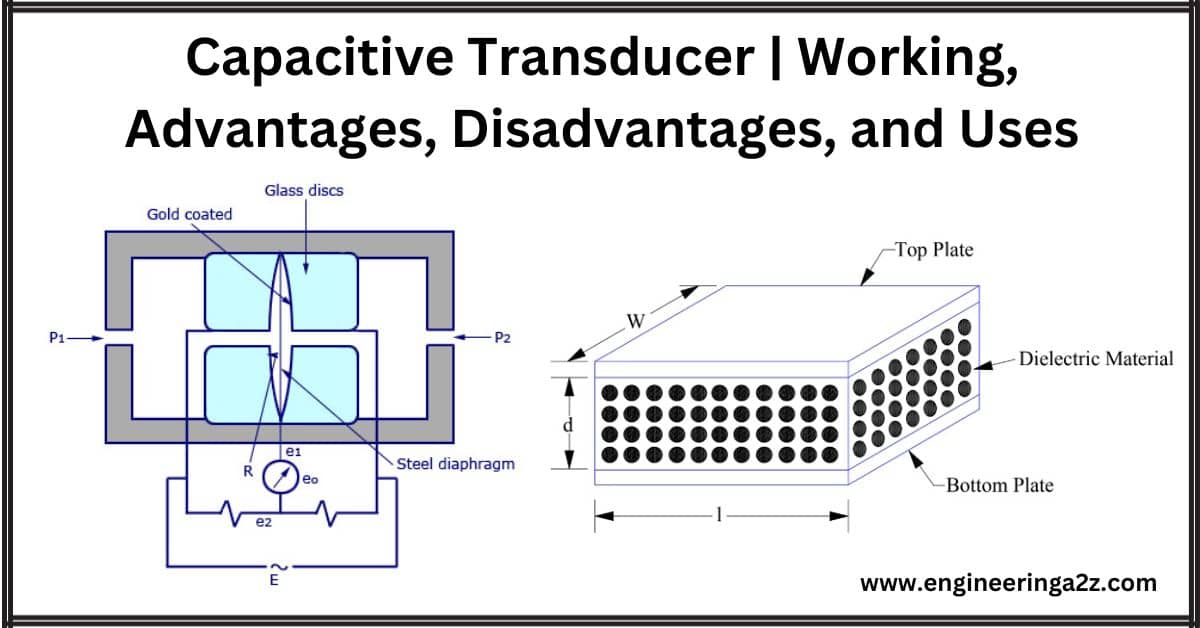
Capacitive Transducer | Working | Advantages | Disadvantages and Uses
Introduction A capacitive transducer is a device used to measure displacement and pressure. It relies…
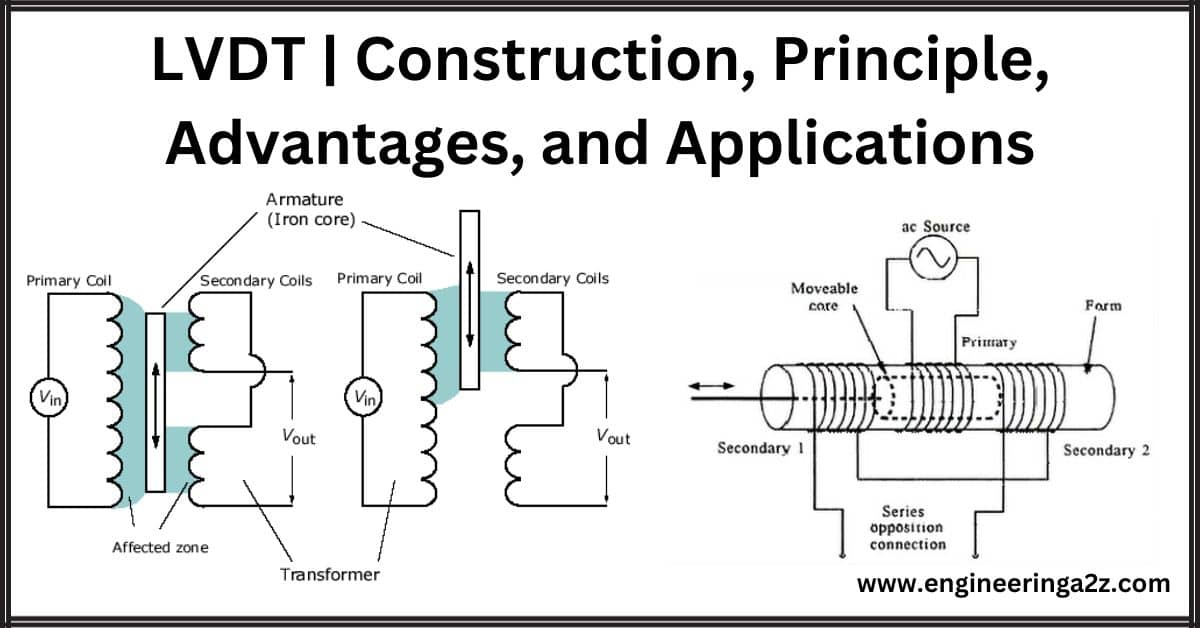
LVDT | Construction | Principle | Advantages and Applications
Introduction The term LVDT stands for Linear Variable Differential Transformer. It is the most widely…






Comments