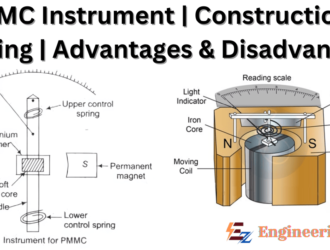
Permanent Magnet Moving Coil | Construction and Working
Introduction PMMC stands for Permanent Magnet Moving Coil. These instruments are used to measure DC (Direct Current) quantities…
Ultrasonic Flow Meter | Principle Operation, Working, and Installation
Introduction An Ultrasonic Flow Meter measures the flow of liquid without touching it, using sound…
Vortex Flow Meter | Design, Working Principle, Accuracy and Rangeability
Vortex Flow Meter Vortex Flow Meter is a device used to measure the flow of…
Electronic Flow Meter | Working Principle, Types, and Advantages
An electronic flow meter measures the flow of liquids and gases in industries. Common types…
Electromagnetic Flow Meter | Construction, Working Principle, and Limitations
Introduction A magnetic flow meter, also known as a mag meter or electromagnetic flow meter,…
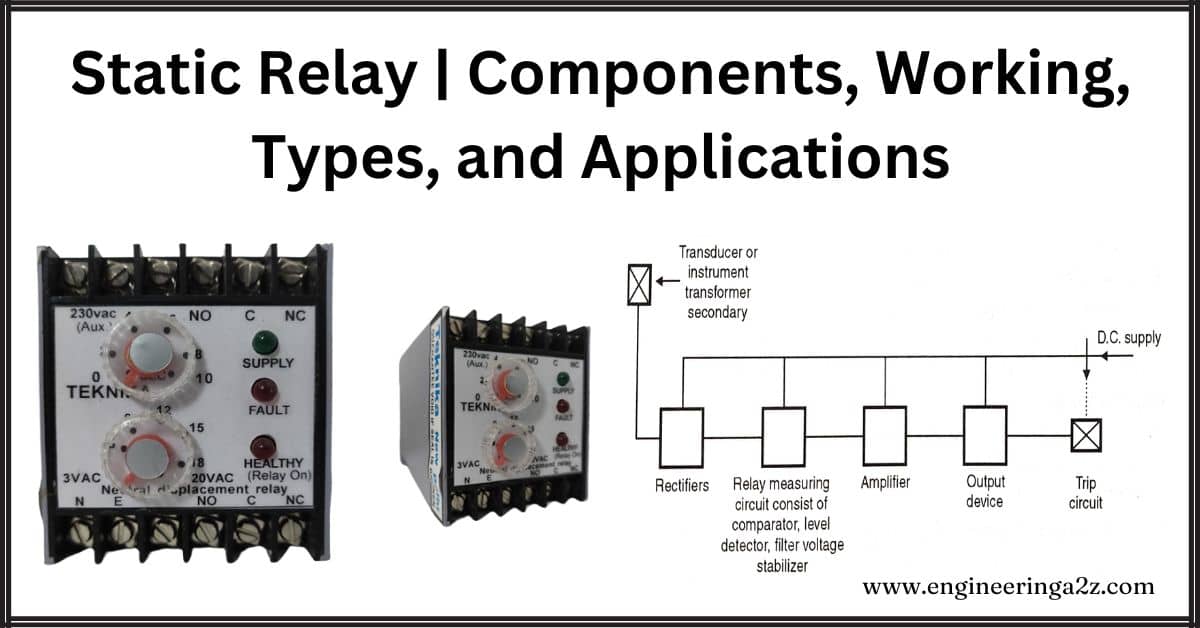
Static Relay | Components, Working, Types, and Applications
Introduction The solid-state relay, also known as a static relay, was introduced back in 1960.…
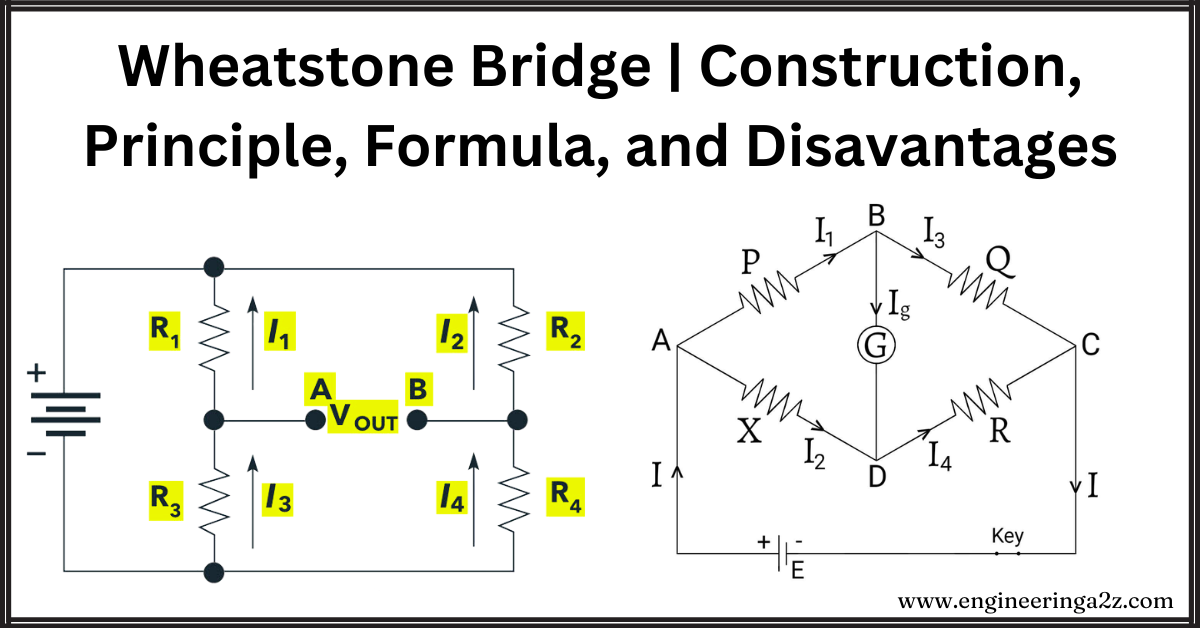
Wheatstone Bridge | Construction, Principle, Formula and Disadvantages
Introduction The Wheatstone Bridge is a gadget invented in 1842 by scientist Wheatstone to figure…
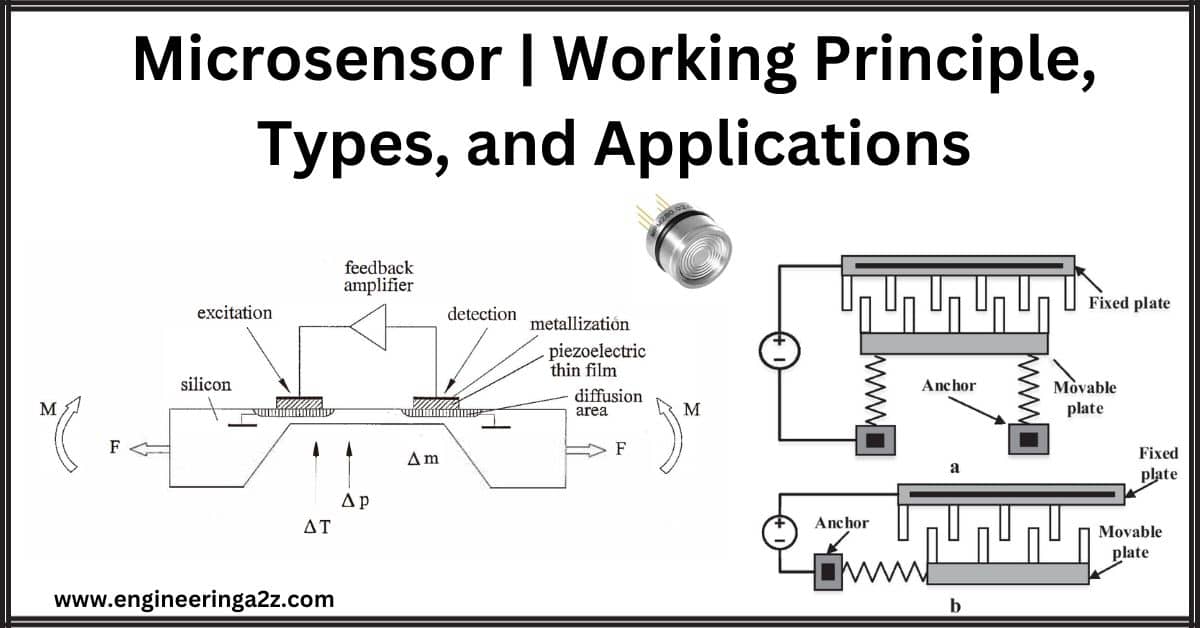
Microsensor | Working Principle, Types, and Applications
Introduction A microsensor is a minuscule device built to sense and measure specific physical properties…
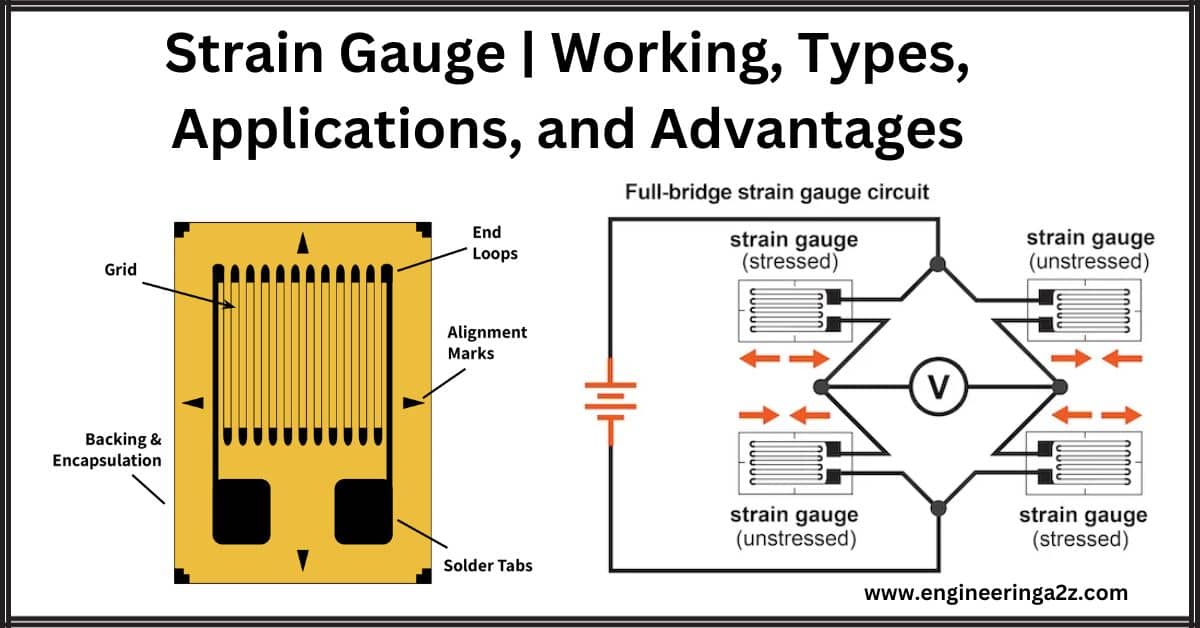
Strain Gauge | Working | Types | Applications and Advantages
Introduction A strain gauge is like a smart sensor that senses changes in resistance when…
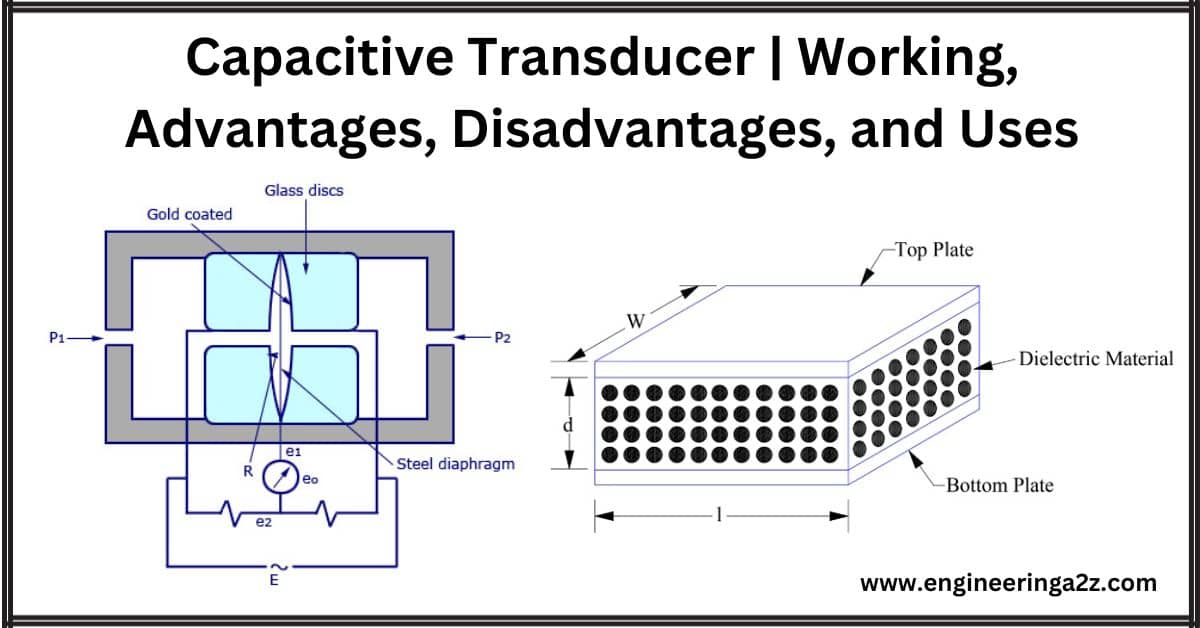
Capacitive Transducer | Working | Advantages | Disadvantages and Uses
Introduction A capacitive transducer is a device used to measure displacement and pressure. It relies…












Comments