Leadership | Qualities, Function and Styles
Leadership Leadership has been defined by Davis as follows: Leadership is the ability to persuade…
Paper Mill | Process, Requirements, and it’s Types
Paper Mill Pulp making and Paper making are the two main processes in a paper…
Travelling Wave Tube | Construction, Working and Applications
Travelling Wave Tube A travelling wave tube is a specialized vacuum tube that is used…
Stepper Motors | Types, Parameters, and Characteristics
Stepper Motor Stepper motors convert electrical pulses received by their excitation (control) windings into discrete…
Switched-Reluctance Motor Drives | Principle and Modes of Operation
The Switched-Reluctance Motor Drives system combines a simple motor construction and an economic power converter…
Pyrolysis | Basic Principles, Types and Uses
Introduction Pyrolysis is a process that breaks down organic material at temperatures between 400 °C…
Waste to Energy | Methods, Economic Impact and Future Trends
Introduction Waste-to-energy (WtE) or energy-from-waste (EfW) is a way to produce electricity and heat from…
Distributed Control System | Block Diagram and Architecture
Introduction Digital Control System (DCS) also known as Distributed Control system is the brain of…
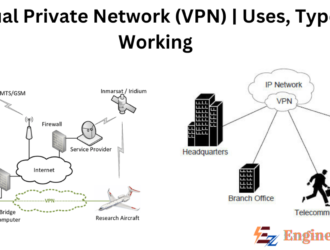
Virtual Private Network (VPN) | Types, Working and Uses
Virtual Private Network A Virtual Private Network (VPN), which illustrates virtual confidential organization, lays out…















Comments