Table of Contents
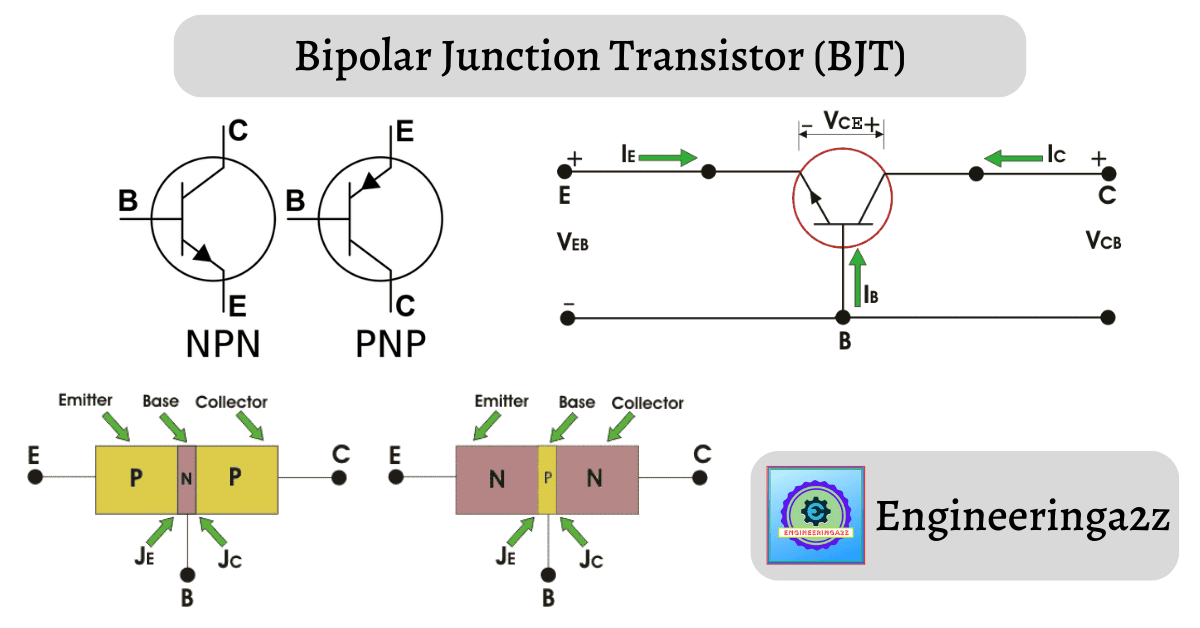
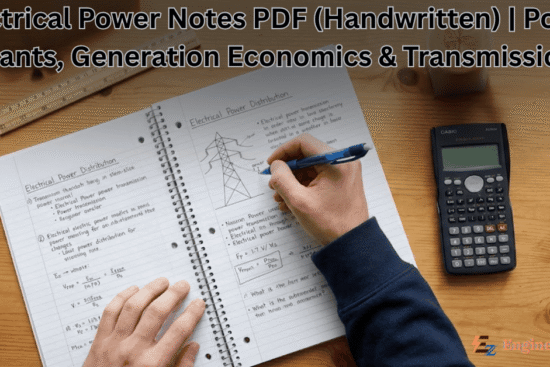
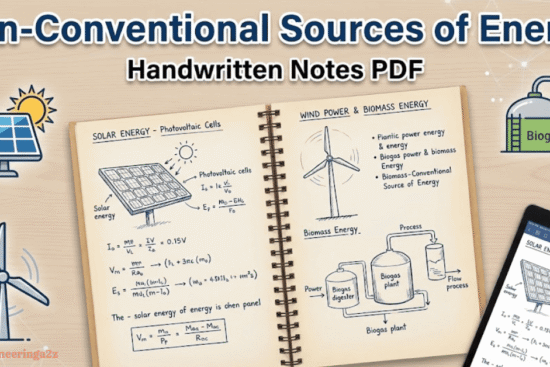
Bipolar Junction Transistor
A bipolar junction transistor is a three-terminal semiconductor device consists of two P-N junctions which are able to amplify a signal. It is a current-controlled device. The three terminals of BJT are the base, the collector and the emitter. A BJT is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and holes as charge carriers.

Types of BJT
- NPN Transistor
- PNP Transistor
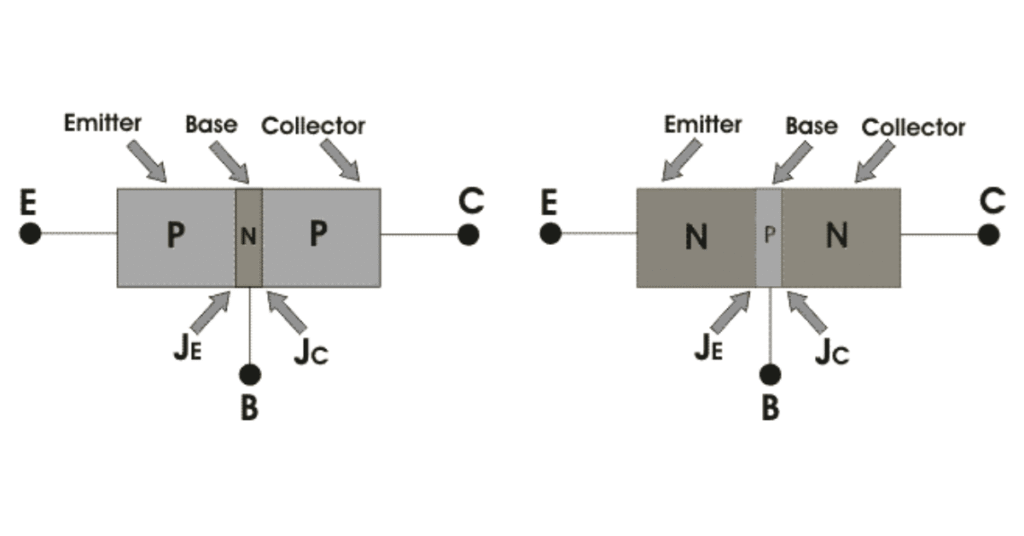
From the above figures, we can see that every BJT has three parts named emitter, base and collector. JE and JC represent the junction of emitter and junction of collector respectively.
1. NPN Transistor
In an NPN transistor one P-type semiconductor resides between two N-type semiconductors.
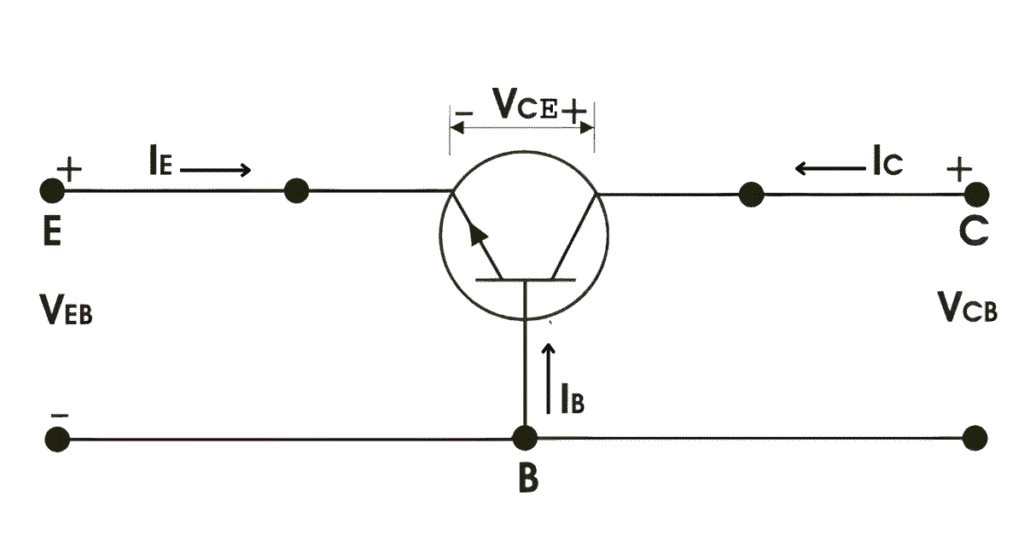
Now IE, IC is emitter current and collector current respectively and VEB and VCB is emitter-base voltage and collector-base voltage respectively.
According to the convention if for the emitter, base and collector current IE, IB and IC current goes into the transistor the sign of current is taken as positive and if current goes out the transistor the sign of current is taken as negative.
2. PNP Transistor
In an PNP transistor one N-type semiconductor resides between two P-type semiconductors.
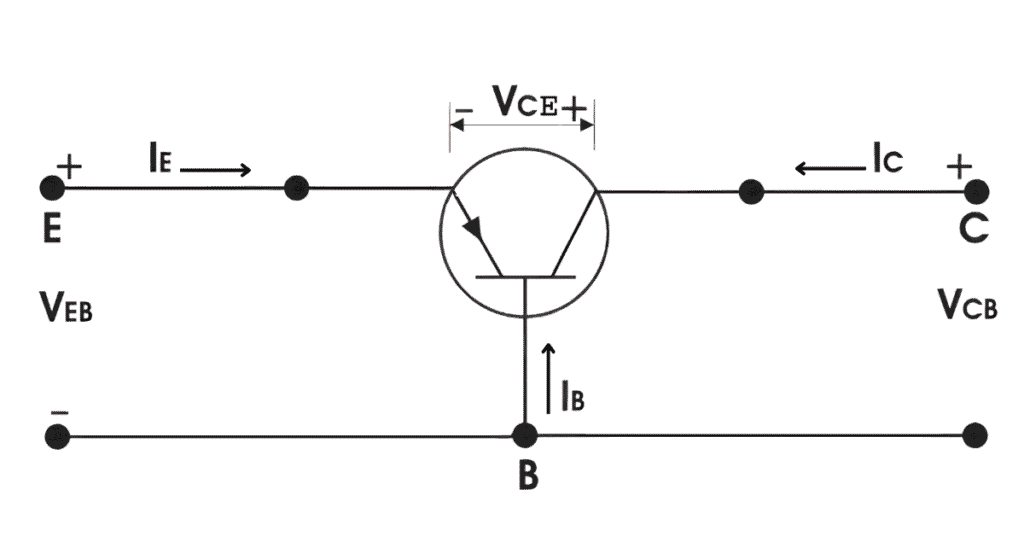
For PNP transistor, current enters into the transistor through emitter terminal. Like any bipolar junction transistor, the emitter-base junction is forward biased and the collector-base junction is reverse biased.
Working of BJT
Consider an NPN transistor, the BE junction is forward biased and CB junction is reverse biased. The width of the depletion region at the junction CB is higher as compared with BE junction.
When the BE junction is forward biased it decreases the barrier potential, hence the electrons starts flowing from the emitter to the base. As the base is thin and lightly doped it consists of very few holes so some of the electrons from the emitter recombine with the holes present in the base region and flow out the base terminal.
Similarly, when you consider the PNP transistor, is same as of the NPN transistor, the only difference in that the majority charge carriers are holes instead of electrons.
Advantages of BJT
- It has a better voltage gain.
- It has high current density.
- It shows better performance at high frequency.
- The BJT has a large gain bandwidth.
- There is a low forward voltage drop.
- It can be operated in low or high power applications.
Disadvantages of BJT
- It more noise produced.
- It has a low thermal stability.
- The switching frequency of a BJT is low.
- The BJT is more an effect of radiation.
Related Posts
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT): Types, Working, Construction, Advantages
- MOSFET | Working Principle | V-I Characteristics & Applications
- Full Wave Rectifier | Definition, Types and Working
- Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (CRO) Construction and Working Principle
- Solar Cell or Photovoltaic Cell Construction and Working
- B.Tech – Electrical Engineering Previous Year Question Papers Download














Comments (1)
So easy language