Paper Mill | Process, Requirements, and it’s Types
Paper Mill Pulp making and Paper making are the two main processes in a paper…
Stepper Motors | Types, Parameters, and Characteristics
Stepper Motor Stepper motors convert electrical pulses received by their excitation (control) windings into discrete…
Switched-Reluctance Motor Drives | Principle and Modes of Operation
The Switched-Reluctance Motor Drives system combines a simple motor construction and an economic power converter…
Pyrolysis | Basic Principles, Types and Uses
Introduction Pyrolysis is a process that breaks down organic material at temperatures between 400 °C…
Waste to Energy | Methods, Economic Impact and Future Trends
Introduction Waste-to-energy (WtE) or energy-from-waste (EfW) is a way to produce electricity and heat from…
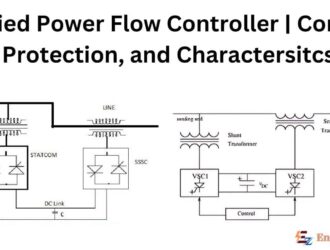
Unified Power Flow Controller | Control, Protection, and Charactersitcs
UPFC The Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) proposed by Gyugyi is the most versatile FACTS…
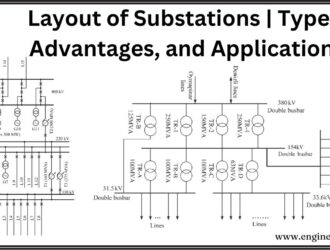
Layout of Substations | Types, Advantages and Applications
Introduction A substation is a crucial part of an electrical supply system that helps transfer…
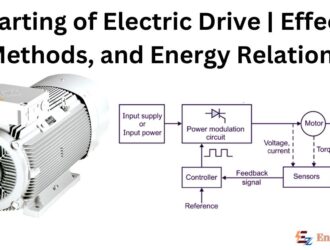
Starting of Electric Drive | Effect, Methods, and Energy Relations
Introduction The most important processes associated with a controlled electrical drive are: (i) Starting (ii)…
STATCOM | Static Synchronous Compensator
Introduction Static Synchronous Compensator was developed as an advanced static VAR compensator where a voltage…












Comments