Table of Contents
Introduction
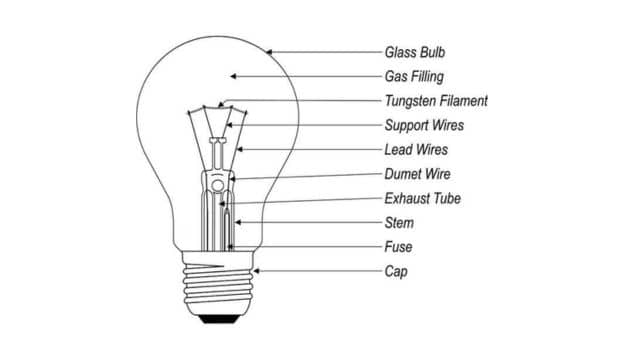
Heat is produced when an electric current is passed through a wire, which raises its temperature. At low temperatures, only heat (I.R. radiations) is produced. At high temperatures, light (UV radiation) is also produced. The wire used is called Filament. For making a filament, the wire material should have the following properties:
- High melting point.
- Low-temperature coefficient of resistance.
- Ductility, i.e., the capability to give out thin wires.
- Mechanical strength to bear the process of coiling. Generally, carbon, tantalum, and tungsten are the materials used to make filaments.
Incandescent lamps can be:
- Vacuum lamp
- Gas-filled lamp
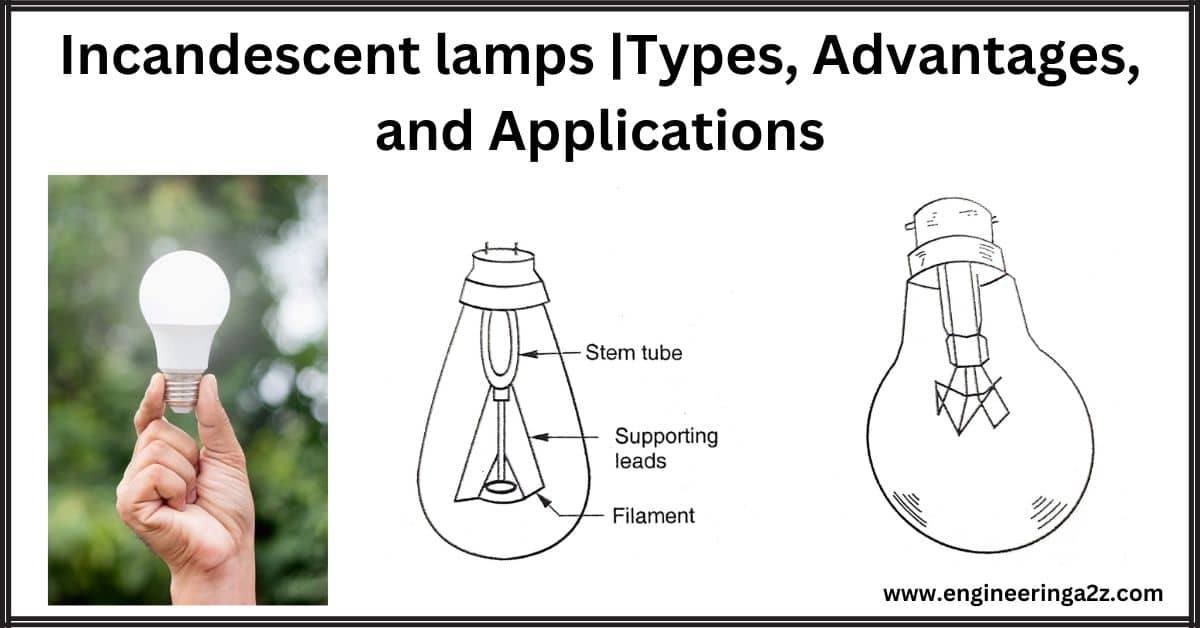
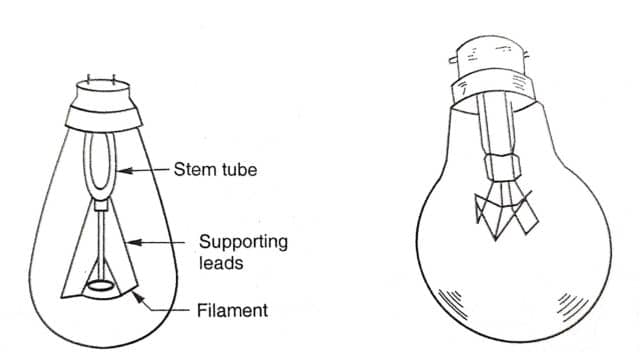
1. Vacuum lamp
In such lamps, the filament is enclosed in a totally evacuated glass-sealed cover. This prevents oxidation of the filament material. However, evacuation results in vapourization of the filament material, which reduces its life.
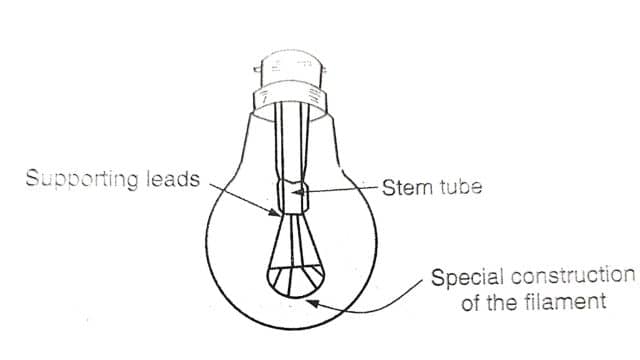
2. Gas-filled lamps
In the past, there were vacuum lamps. But when they were made with higher power, they weren’t very efficient. So, for power above 100 watts, people started making lamps with gas inside. They used a mix of 80% argon and 20% nitrogen gas. This gas doesn’t react with the part that gets hot (filament) in the lamp. They also designed the lamp in a way that the hot part doesn’t lose heat easily.
Here are some important things about these regular light bulbs:
- They use electricity efficiently.
- They don’t take up much space.
- They can be shaped in nice ways and come in different sizes.
- They don’t work as well as fluorescent lights.
- They give off yellow light, which might bother people.
- They only last about 1000 hours of use.
- They can’t handle changes in electricity well.
3. Halogen Lamps
Regular incandescent light bulbs have a problem where the filament (a thin wire inside the bulb that gets hot and produces light) starts to disappear over time, and the inside of the bulb gets dirty, which makes the bulb dimmer.
Halogen light bulbs fix this problem. They add a special kind of gas and a little bit of another substance called halogen to the bulb. When the filament gets too hot and starts to disappear, this halogen gas helps put the disappearing filament back onto the filament itself. This makes the bulb last longer and stay brighter.
Halogen bulbs are also more efficient than regular light bulbs because they have smaller glass containers filled with high-pressure gas. This makes the light brighter while using less energy.
Advantages of Halogen Lamps
The halogen lamps have the following advantages.
- They have almost double the life (2000 working hours) as compared to incandescent lamps which have a life of about 1000 working hours.
- They have better emission of color.
- No blackening of the inner surface of the lamp occurs. So efficiency is maintained the same throughout life.
- They have better efficiency than incandescent lamps. The halogen lamps have a luminous efficiency of 20 to 30 lm per watt.
- The size of the halogen lamps is less and they occupy less space.
- They are available in ratings up to 5 KW.
Halogen lamps are used in outdoor places such as car parking. Airport runaway, playground, gardens, parks, etc.
4. Metal Halide (MH) Lamps
Metal halide lamps are becoming really popular lights all around the world. These lamps have been getting better and better recently. There’s a new kind of technology called pulse start technology that’s making these lamps even more useful for different things. Because of this, there are lots of different types of these lamps that people can choose from to match what they need.
A company called Venture Lighting has made many special lamps to meet what people want. The lamps and the things that help them work (called ballasts) have been improved a lot. Also, metal halide lights themselves have some good qualities that make them grow in popularity.
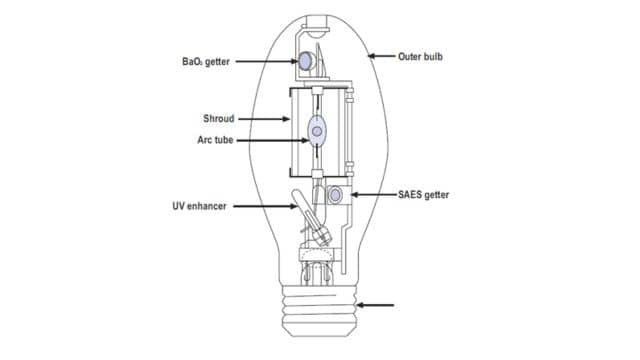
Overall, these lamps have been growing a lot because they’re getting better with new technology and designs. They can be used for many different things, and that’s why more and more people are using them.
- Versatility: Today there are almost 400 styles available. Those new lamp types have made it possible to use metal halide in almost any setting, including industrial, commercial, retail, and residential applications.
- Efficiency: Metal halide lights are really good at giving off bright and efficient white light. You can also get these lights in different colors depending on what you need. On the other hand, high-pressure sodium and mercury lights can only make a few colors of light, and those colors might not look nice or work well for many things. Because of this, more and more people are choosing metal halide lights because they are versatile and can make better light for different situations.
- Life: Metal halide lamps have exceptionally long rated lives of up to 30,000 hours.
- Color: This light source can be manufactured to produce almost any color of light desired (2700K-20000K). Special lamps of specific colors can also be produced, including, Blue, Green, Aqua, and Pink. The metal halides in the arc tubes are selected for their ability to generate individual saturated colors.
- Ecology (Pollution-free): Metal halide lighting helps with a big problem we face in our modern world: how power is made and its impact on the environment. These lights are very small but give off a lot of light, and they use less energy than other types of bright lights. If we switch to these lights, we could save about 10% of all the energy we use. This also means we would burn less stuff like coal and oil, which would make less bad stuff go into the air, like carbon dioxide and other pollutants.
Construction Metal Halide Lamps
Metal halide bulbs are very efficient and produce between 65 and 115 lumens of light output per watt of electricity used. MH bulbs produce a light that is very close to the full summer sun, with a spectrum rich in the blue end.
Metal halide bulbs create light by passing electricity through a clear inner arc tube that is enclosed in the vacuum of an outer clear glass tube. This inner arc tube contains mercury and other metals in iodide form. When electricity is applied to these metal iodides they give off very intense light and heat. The outer casing can be either clear or phosphorus-coated.
Size and Life of Metal Halide Lamps
MH bulbs come in sizes from 70 to 1500 watts with the 250 W, 400 W, and the 1000 W being the most popular sizes. All the bulbs need to run with a ballast (basically a transformer to step up the voltage to the proper amount), that are designed to run a specific size bulb.
The bulbs themselves need to be burned in a specific position. They come in three types: Vertical (marked BU or BD). Horizontal (marked HOR) and Universal (marked U). The universal bulbs can be burned in any position, but they are more efficient when burned vertically.
The bulbs also come in a variety of styles, among them are regular MH bulbs and Super Bulbs (which produce 10% – 12% more light but use the same amount of electricity). The super bulbs cost slightly more, but they are more efficient, making them a good choice in the long run.
Metal halide bulbs (except the 1000 W Super Bulb) should be replaced about every 9500 10000 hours or aprox. 18 months (assuming an 18 hour/day cycle). The 100 W super bulbs do not last as long as any of the others and should be replaced every 6500 hours, which is about 12 months if you run the bulb 18 hours a day.
Advantages of Incandescent Lamps
- Warm and Natural Light: Incandescent lamps produce a warm and cozy light that closely resembles natural sunlight. This type of lighting is often preferred for creating a comfortable and inviting atmosphere in residential and hospitality settings.
- Color Rendering: Incandescent lamps have a high color rendering index (CRI), which means they can accurately render colors. This is particularly important in settings like art galleries, photography studios, and makeup areas, where accurate color perception is essential.
- Dimmability: Incandescent lamps are easily dimmable without the need for additional equipment or circuitry. They can be smoothly adjusted to achieve different levels of brightness, making them suitable for setting various moods and ambiance.
- Instant Illumination: Incandescent lamps provide full brightness as soon as they are turned on. There’s no warm-up time or delay in achieving the desired illumination level, which can be advantageous in situations where immediate light is required.
- Affordability: Incandescent lamps typically have a lower upfront cost compared to some other lighting options, such as LED bulbs. This can make them an attractive choice for individuals on a tight budget or for temporary lighting solutions.
Disadvantages of Incandescent Lamps
- Incandescent lamps are highly inefficient in converting electrical energy into visible light. They produce a significant amount of heat, and only a small fraction of the energy consumed is actually emitted as visible light. This inefficiency results in higher electricity bills and increased energy consumption compared to more energy-efficient lighting options like LEDs or CFLs.
- Incandescent lamps have a relatively short lifespan compared to other lighting technologies. They typically last for about 1,000 to 2,000 hours, which is significantly shorter than the lifespan of LED bulbs (tens of thousands of hours) or CFLs (around 8,000 to 10,000 hours). This means that incandescent lamps need to be replaced more frequently, adding to the overall cost of lighting.
Applications Of Incandescent Lamps
- Outdoor Lighting: Incandescent lamps have been used for outdoor lighting purposes such as garden lights, patio lighting, and decorative lighting in outdoor spaces.
- Display Lighting: Incandescent lamps have been used to illuminate retail displays, museum exhibits, and other showcases due to their ability to render colors accurately and highlight the details of displayed items.
- Mood Lighting: The warm and dimmable nature of incandescent lamps has made them suitable for creating mood lighting in restaurants, cafes, and other hospitality settings.
- Stage Lighting: Incandescent lamps have been used in theatrical and stage lighting applications, especially for certain lighting effects that require a specific color temperature or warmth.
- Portable Lighting: Incandescent lamps have been used in portable lighting solutions like handheld lanterns and battery-operated lamps for camping or emergency situations.
- Decorative Lighting: Incandescent lamps have been incorporated into decorative fixtures and lighting designs to enhance the visual appeal of indoor and outdoor spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is used in incandescent?
In regular incandescent light bulbs, a material called tungsten is used. Tungsten is chosen because it can handle really high temperatures without melting. The part that gets super hot in the bulb is called the tungsten filament. This filament can get as hot as 4,500 degrees Fahrenheit! The bulb around it is made of glass and helps to keep oxygen from reaching the hot filament.
What are 2 examples of incandescent sources?
. Incandescent light bulbs, the coil in an electric stove, and even candles all produce light by heating up to very high temperatures. This heat causes them to glow and emit visible light, which is why they’re considered incandescent sources of light.
What is Incandescent Lamps?
Incandescent lamps are light bulbs that produce light by heating a tungsten filament until it glows. They’re less efficient compared to modern alternatives like LEDs and CFLs.
Read Also:
- Difference Between Filament Lamps and Fluorescent Tubes
- Quality Systems | Types, Benefits, and Need For Standardization
- Arc Extinction | Principle, Methods, and Applications
- Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) | Types, Working Principle, And Construction
- Overvoltage Protection | Internal and External Causes Of Overvoltage







Leave a Reply