Table of Contents
DIAC
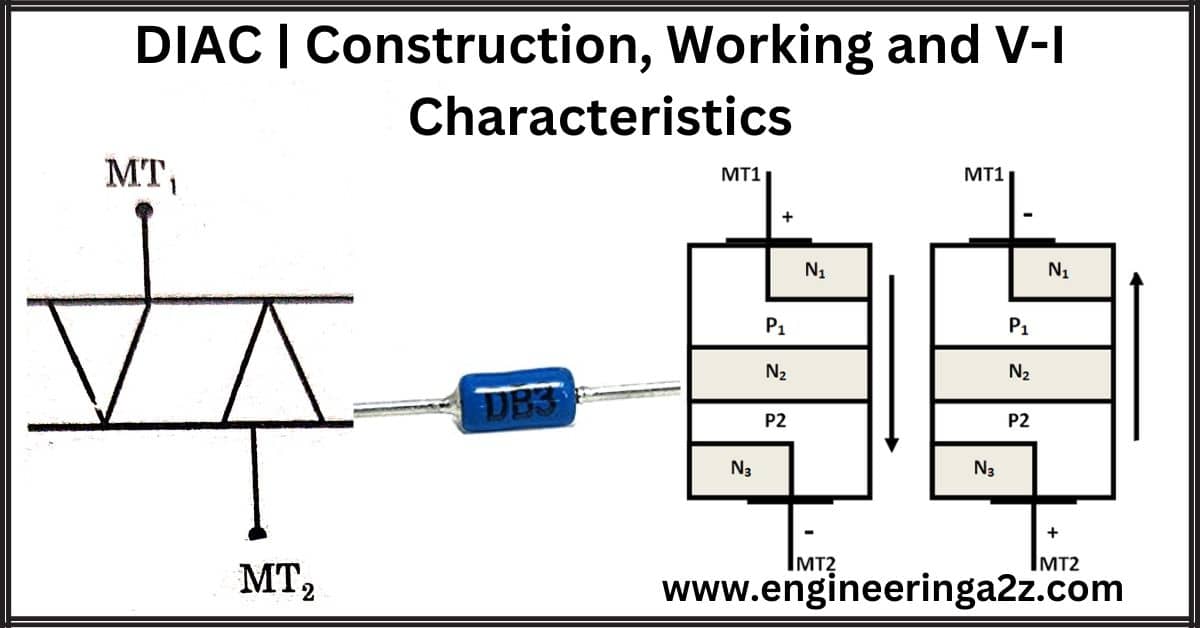
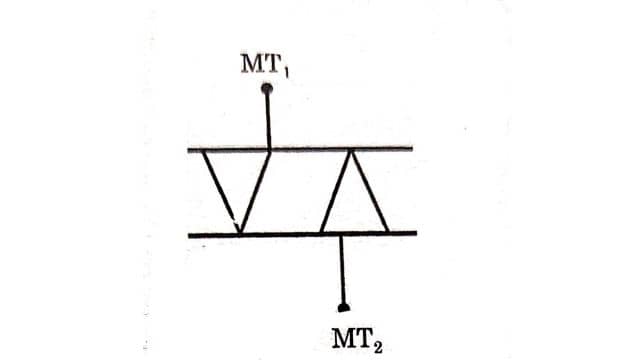
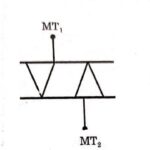
DIAC can be abbreviated as Diode for alternating current. A DIAC is a bidirectional device that can be conducts in either a positive or negative direction. Basically, DIAC is the triggering device that can be used for triggering the TRIAC as well as SCR. The term DIAC is obtained from capital letters of Diode that work on AC. It is also called bilateral trigger diode. The symbol of DIAC is shown in the figure below.
Construction of DIAC
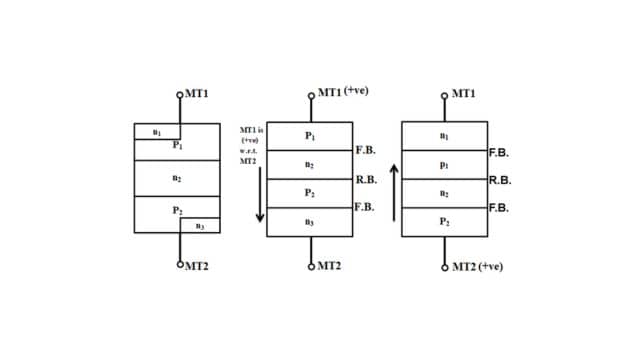
The constructional arrangement of DIAC with all its layers and junction are shown in Figure.
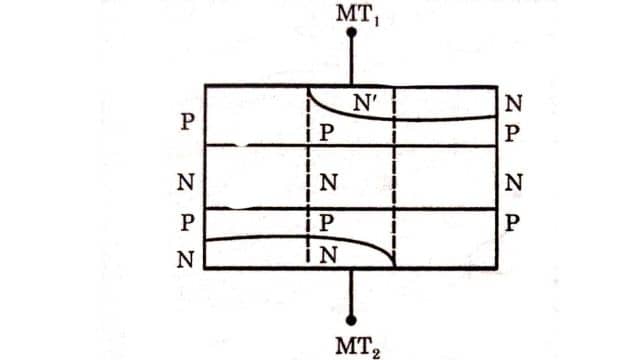
DIAC is four layers, PNPN and PNPN’ & having two terminals MT1 and MT2 The DIAC is the parallel inverse combination of semiconductor layers that permits triggering in both directions.
Working principle of DIAC
The two modes of operation of a DIAC are explained below.
(a) When MT1 is Positive w.r.t MT2: When MT is positive w.r.t MT1, the layers PNPN start conducting. This conduction is achieved when the voltage of the MT1, terminal is more than the breakdown voltage (Vio) as shown in the V-I characteristics of DIAC. Once the conduction starts, the current through DIAC becomes very large.
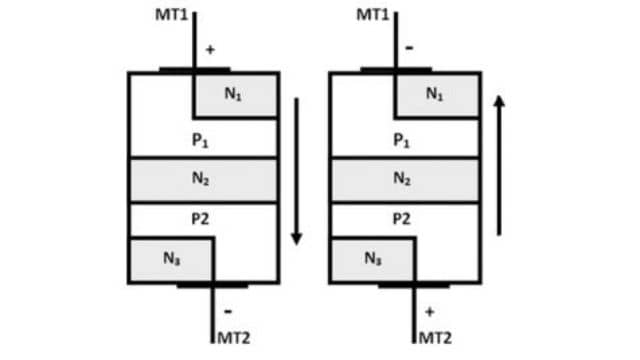
(b) When MT2 is Positive w.r.t MT1: When MT2 is +ve w.r.t. MT1, the layer PNPN’ starts conducting. This conduction is achieved when the voltage of MT2 is more than the breakdown voltage of MT2, which is more than the breakdown voltage (VB02) as shown in the V-I characteristics of DIAC.
V-I Characteristics of DIAC
The V-I characteristics of DIAC are shown in Figure. When MT1 is +ve very small current will flow until the voltage of MT1 and MT2 reach the breakdown voltage. At this point, avalanche breakdown will occur and the current becomes very large. This current can be limited by external resistance in the circuit. As the current increase, the voltage across the DIAC decreases. Thus DIAC exhibits negative resistance characteristics.
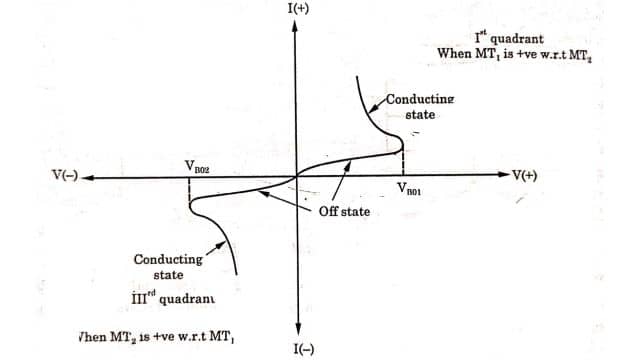
When the MT2 is positive w.r.t MT1, the DIAC will conduct the current but in the opposite direction. The behavior in both directions is similar because the voltage drop is the same in both directions.
Applications of DIAC
- DIAC is used to turn on the TRIAC.
- It can used in an oscillator circuits.
- It is low power triggering device.
- It provides the positive or negative gate signal to the TRIAC for turn on.
- Therefore combinations of DIAC TRIAC are used in various control circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a heat sink?
Thyristors require a heat sink to transfer the heat energy from the case of the thyristor to the surroundings.
What is a DIAC used for?
DIAC is primarily used as trigger devices in phase-triggering and variable power control applications because a disc helps provide a sharper and more instant trigger pulse (as opposed to a steadily rising ramp voltage) which is used to turn “ON” the main switching device.
Is DIAC a 3 layer?

Yes , DIAC is a three-layer, two-junction semiconductor device that has two leads. A DIAC is also referred to as a bi-directional diode thyristor because it can conduct current in either direction. The DIAC is a diode that conducts electrical current only after its break over-voltage, VBO, has been reached momentarily.
What is TRIAC device?
The Triac is a five layer, three terminal power semiconductor device, which has a pair of phase controlled SCRs connected in parallel manner on the same chip. TRAIC, Here TRI
indicates that the device is three terminals and AC means that the device controls alternate current or can conduct current in either direction, Hence it is a bidirectional device .
Read Also:
- Difference Between A.C. and D.C.
- Relay | Construction and Working
- Difference Between Filament Lamps and Fluorescent Tubes
- Megger | Construction & Working | Engineeringa2z
- Advantages | Disadvantages and Applications of Electric Power







Leave a Reply