Table of Contents
What is MCB?
MCB stands for Miniature Circuit Breaker. It’s the most recent development in low-voltage circuit breaker technology. In both home and industrial applications, it can be used instead of fuses. In an abnormal condition, the MCB disconnects the circuit from the power source, and all that is required to restore the circuit is to simply turn on. A fuse, on the other hand, requires the replacement of the fuse element, which takes time, as does reconnecting the circuit.
Types of MCB
1. B-Type MCB
For the protection of resistive loads such as lamps, heaters, and other electrical appliances.
2. C-Type MCB
In this type of MCB, we protected Inductive loads, such as motors and air conditioners.
3. D-Type MCB
For the protection of cables and high-starting-current inductive loads such as transformers.
Working of MCB
Its design is based on current technological limitations. It has a current-carrying conductor in it. Contacts, a flexible cord, a current-carrying bimetal strip, chutes, and a tripping mechanism Thermal magnetic technology is used in MCBs. A temperature-sensitive device and a current-sensitive electro-magnetic device are used to give protection. Mechanically, both components activate the mechanism. The bimetal bends and triggers the tripping mechanism to trip the MCB when excess current runs across it owing to temperature generated by heating.
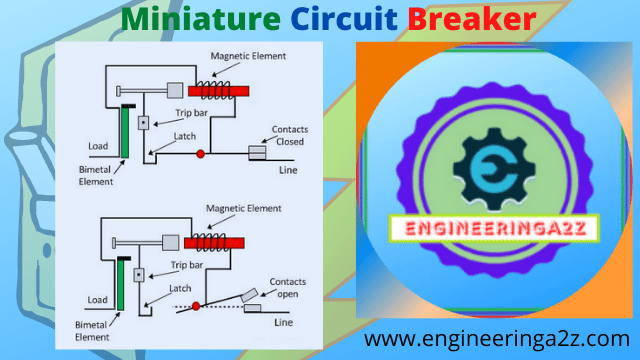
The arc chute separates the arc during tripping. As a result of the lengthening and cooling effects, the arc is quenched. The tripping mechanism isn’t intended to turn on the MCB automatically. While supplying the circuit, it necessitates human operation. An MCB has pure silver contacts. This has a number of benefits, including an extended contact life. Because of the low resistance, power loss is minimal. During the closure process, contacts have no bounce. These can withstand fault currents of up to ten kiloamperes. A schematic view of an MCB is shown in Figure .An operating handle is used to trip and reset the MCB usually.
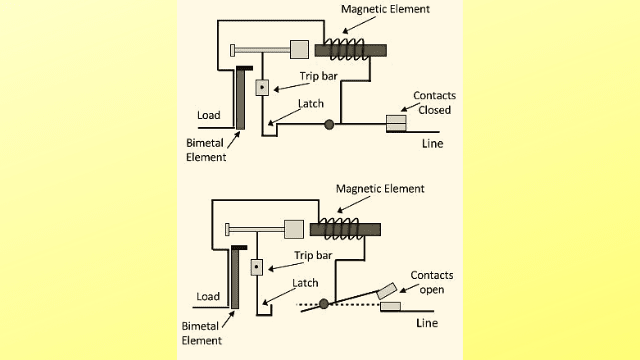
It also shows the status of the circuit breaker when operated manually. The majority of MCBs are intended to trip even while the handle is held or locked in the ON position. This is also known as a “free” or “positive” trip operation. During operation, the actuator mechanism pushes the contacts together or apart. The MCB’s main contact allows current to flow when they are in contact and breaks the current when they are apart.
The following are the important features of MCB
- Their normal rating is 1-5 – 125 A, according to the loads to be supplied.
- They are intended for domestic applications.
- They are free from nuisance, tripping caused by vibrations.
- Their breaking capacity is as per the requirements (below 10 kA on average)
Advantages of MCB
- MCBs are more current-sensitive than fuses.
- It works quickly to prevent short circuits.
- It responds quickly to overloading and under voltage situations.
- It is reusable, resulting in lower maintenance and replacement costs.
- Restarting the supply is quite simple.
Disadvantages of MCB
- The MCB is more costly than the fuse.
- The MCB distribution board is more expensive than a rewireable fuse board.
- The risk of a circuit overloading due to an unskilled operator has been avoided.
Application of MCB
- It is used in homes.
- It is used in industries, like electrical panels etc
- It is used in ground fault trip mechanisms.
- It is used in lightings
- It is used industries applications.
- It is used with heaters.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQs)
Is it possible to use a MCB as the primary switch?
MCB may perform better than normal switches, but they are not switches. They can’t be used interchangeably. As a result, it is not advisable to use a circuit breaker as a switch.
What is the purpose of using MCB?
In an abnormal condition, the miniature circuit breaker disconnects the circuit from the power source, and all that is required to restore the circuit is to simply turn on. A fuse, on the other hand, requires the replacement of the fuse element, which takes time, as does reconnecting the circuit.







Comments (3)
Hmm it appears like your website ate my first comment (it
was super long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I
submitted and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog.
I as well am an aspiring blog blogger but I’m still new to
everything. Do you have any tips and hints for
beginner blog writers? I’d definitely appreciate it.
My partner and I absolutely love your blog and find almost all of your post’s to be just what
I’m looking for. Does one offer guest writers to write content for you personally?
I wouldn’t mind writing a post or elaborating on a number
of the subjects you write regarding here. Again, awesome weblog!
Excellent article. Keep writing such kind of information on your blog.
Im really impressed by your site.
Hello there, You’ve performed a fantastic job.
I will definitely digg it and individually recommend to my friends.
I am sure they’ll be benefited from this site.