Table of Contents
Introduction
Improving Coverage and Capacity in Cellular System was the first cellular mobile telephone network in the 1960s that was proposed by Bell System. The cellular mobile telephone network covers large geographic areas. The modern telephone cellular networks use low-power transmitters and normally give service to smaller geographical areas. Cell splitting and cell sectoring are the two methods to increase the capacity of a cellular system.
Different Techniques of Cellular System
The different techniques to increase capacity in cellular systems are :
- Cell Splitting
- Cell Sectoring
- Segmentation and Dualization or Repeater for Range Extension
1. Cell Splitting
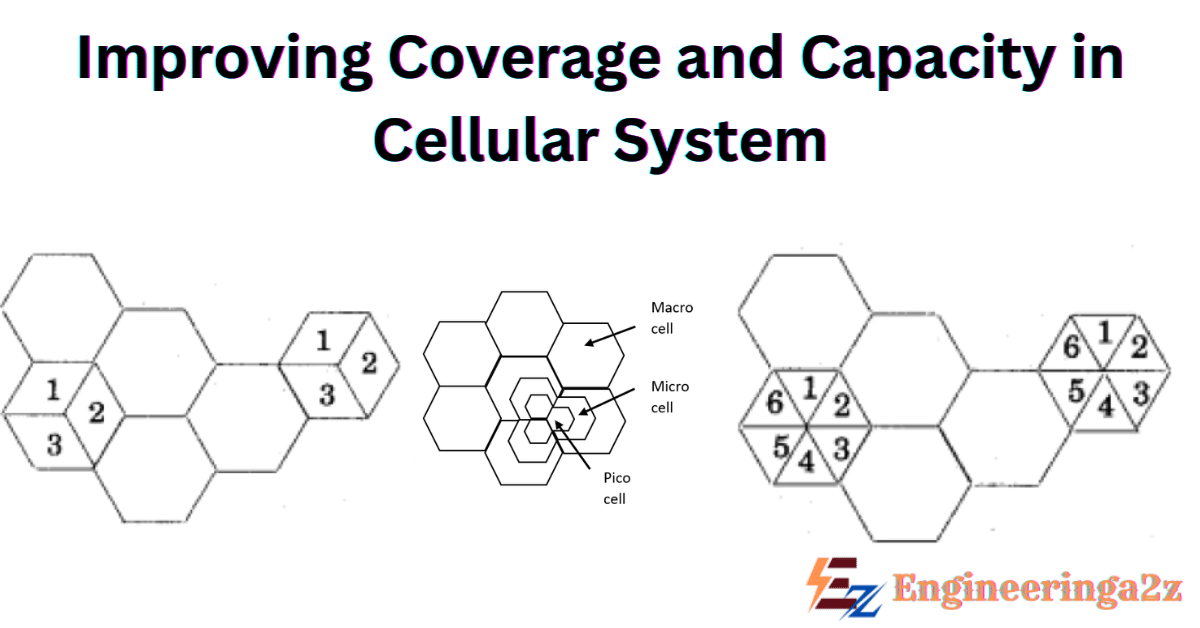
Cell Splitting is a technique in which the geographic area is divided into several smaller cells. Cell Splitting increases the channel capacity and also improves the reliability and availability of a cellular network. In cell splitting, each cell size is resized. By using cell splitting, largely congested cells get subdivided into smaller cells to release the congestion, each smaller cell has its own base station and group of frequency channels.
Methods of Cell Splitting
There are generally two ways of splitting :
- When the original cell site is not used.
- When the original cell site is used.
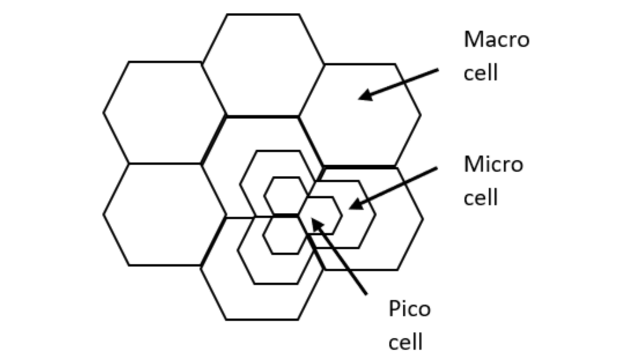
1. When the original cell site is not used
When the cell site splitting takes place in such a way that the original cell base station has been removed and the microcells cover the original cell area.
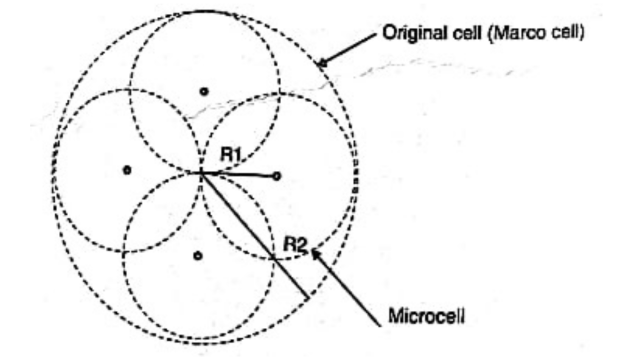
2. When the original cell site is used
When the cell site splitting takes place in such a way that the original cell base station remains unaffected and the original base station antenna works as the base station antenna of the microcell. Various microcells cover the rest of the original cell area.

It has been observed that
New cell radius = old cell radius/2
i.e. R1 = R2/2 and
New cell area = old cell area/4
Let each new cell carry the same maximum traffic load of the old cell; then, in theory,
New traffic load/Unit area = 4* (traffic load / unit area)
Techniques of Cell Splitting
There are two kinds of cell-splitting techniques :
- Permanent Cell Splitting
- Dynamic Cell Splitting
1. Permanent Cell Splitting
The important features of permanent cell splitting are as follows:
- The location of each new split cell, number of channels, transmitted power, spectrum allocation, and traffic load consideration will be planned in advance.
- Frequency assignment should follow the rules and regulations based on the frequency-reuse distance ratio.
- Appropriate algorithms should be designed for the handoff procedure.
- When the installation is ready the actual service cut-over is set at the lowest traffic point, usually at midnight on a weekend.
2. Dynamic Cell Splitting
This technique is also known as temporary cell splitting or adaptive traffic cell splitting.
The following are the main features :
- The dynamic cell splitting technique is based on utilizing the allocated spectrum efficiency in real-time.
- This technique does not require the creation of new-based terminal stations.
- With the help of directional antennas, the exiting cell base station is reconfigured to increase the capacity of the system.
2. Cell Sectoring
- Another method of increasing the channel capacity of a cellular telephone network is to reduce the D/R ratio by keeping the radius of the cell constant.
- It is important to minimize the interference without reducing the transmitting power of the base station.
- Such smaller areas are referred to as “Sectors”.
- Techniques in which the co-channel interference can be minimized and at the same time the capacity of the network can be increased by using directional antennas is known as “Cell Sectoring”.
- A cell is divided either into three 60-degree or six 120-degree sectors.
- In a three-sector configuration, three antennas would be placed in each 120-degree sector.
- The three antennas are one transmit antenna and two receive antennas.

3. Segmentation and Dualization or Repeater for Range Extension
- When more cells are needed in the frequency reuse distance, the segmentation and dualization techniques are united together.
- The segmentation technique divides the group of frequency channels into smaller groups of frequency channels.
- These smaller group frequency channels are allocated to the new cells which are within the reuse distance.
- Segmentation also helps to avoid co-channel interference.
- The dualization technique avoids cell splitting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Cell Splitting?
Cell Splitting is a technique in which the geographic area is divided into several smaller cells. Cell Splitting increases the channel capacity and also improves the reliability and availability of a cellular network.
What are the two types of Cell Splitting?
There are two types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Most of the time when people refer to “Cell Division”, They mean mitosis, the process of making new body cells. Meiosis is the type of cell division that creates egg and sperm cells.
Which of these are the advantages of Cell Sectoring?
The Cell Sectoring technique is more efficient in the case of a smaller coverage area. By using cell sectoring, the capacity of the network increased.
How are Repeaters used for a range of Extensions in cellular systems?
A Repeater extends a wireless network by receiving and retransmitting signals to increase the network’s range.
Related Posts
- Travelling Wave Tube | Construction, Working and Applications
- Radar | Types of Radar, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Radar | Block Diagram, Working Principle and it’s Applications
- Multiple Access Techniques for Wireless Communication
- Internet of Things | Functional Block of IoT, Characteristics and Application
- Microphone | Types, Block Diagram, and its Working












Leave a Reply