Table of Contents
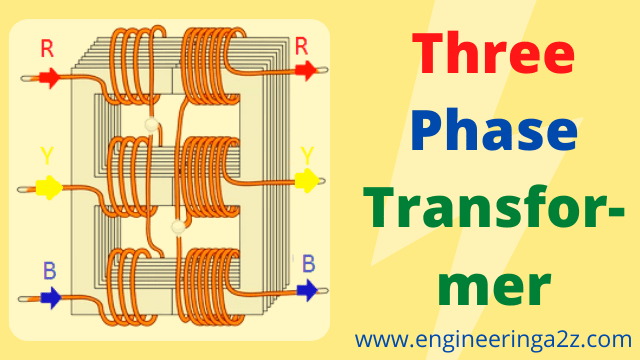
Three Phase Transformer
A three-phase transformer can be built by having its three primary and three secondary windings on a common magnetic core. The basic principle of a 3-phase transformer. The three single-phase core type transformers, each having their primary and secondary windings on only one leg, have their unwound legs combined to provide a return path to the magnetic flux. Their primaries and secondaries can be connected in a star or delta.
Construction of Three Phase Transformer
A three-phase transformer has three primary windings and three secondary windings on a common magnetic core. The core and the windings are enclosed in a tank filled with dielectric oil. The terminals of the primary and secondary windings are enclosed in a tank filled with the ends of the bushings. The bushings provide the necessary insulation to the conductor. The bushings are supported on the tank cover.
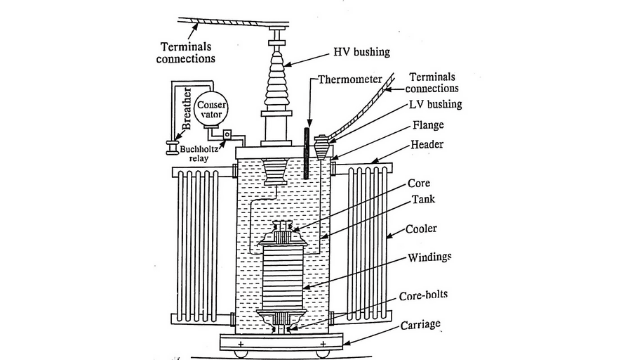
Accessories of Transformer
The various accessories used in the transformer are :
1. Conservator Tank
It is a large, cylindrical tank which is connected by pipe to the transformer. The conservator tank is filled with transformer oil up to a certain level. The remaining portion of the tank is filled with air. Conservator oil is in communication with tank oil. The expansion and contraction of the transformer tank oil is accommodated by the air cushion in the conservator. The direct contact of external air with oil is avoided.
2. High Voltage Bushings
The function of high voltage bushings is to provide insulating support to a conductor passing through earthen tank. A bushing is necessary when a conductor is taken out through a metallic tank, at earth potential. It can be used up to 20 kV.
Oil filled bushing is used for 33 kV applications. For 132 kV and above, oil impregnated paper condensor bushings are used.
3. Breather
The breather is filled with silica gel. The function of silica gel is to absorb moisture. It is fitted between the air space of the conservatory and the outside vent. The breathing of transformers during load takes place through breathers. When the load increases, the oil expands and the air from the conservator is expelled.
Dry silica gel is of pale pink colour. It turns blue when it absorbs moisture. The wet silica gel can be re-used after drying.
4. Buchholz Relay
For a protection of transformer Buchholz relay in transformer is mounted on the connecting pipes between the main tank & the conservative tank. It consists of two element. The upper element consist of a float & the lower element consist of a baffle & mercury switch.
Buchholz relay is mainly used with the transformer having capacity of 500 KVA.
Buchholz relay is to detect internal fault of the transformer.
5. Tap Changers
Tap changer is fitted with the transformer for adjusting the secondary voltage. The adjustments in secondary voltage can be made by OFF circuit tap changer. Such adjustments are for seasonal load variations. The tap is changed only after opening the circuit breaker on the supply side. Baily or short time voltage adjustment is made by means of ON load current. The modern practice is to install the type changer within the transformer tank.
Working of Three Phase Transformer
A three phase transformer’s basic working principle is similar to that of a single phase transformer. It is based upon Faraday law of electromagnetic induction for mutual induction. “when the AC supply is given to the primary winding with the voltage V and alternating flux ϕ is set up in the core of the transformer, which links with the secondary winding and as a result of it an EMF is induced in it called mutually induced EMF.
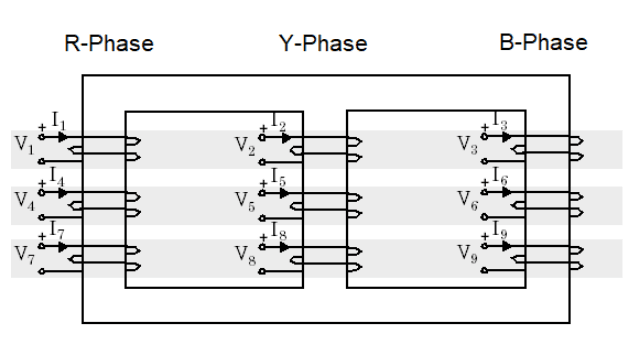
The direction of these induced EMF is opposite to the applied voltage V this is because of the Lenz’s law Physically there is no electrical connection between the two windings but they are magnetically connected therefore the electrical power is transferred from the primary circuit to the secondary circuit through mutual inductance. The induced EMF in the primary and secondary winding depends upon the rate of change of flux linkage i.e. Ndϕ/dt.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the tests conducted on transformer?
There are following main tests performed on a transformer :
1. Turns Ratio Testing.
2. Insulation Resistance Testing.
3. Power Factor Testing.
4. Resistance Testing.How many types of three phase transformer?
Three-phase transformers are transformers that are used to change the voltages of three-phase electrical systems. There are several configurations to choose from, including
Star-Star,
Delta-Delta,
Star-Delta, and
Delta-Star.Why is impedance important in transformer?
The term “impedance” refers to the amount of resistance a device has. The maximum short circuit current a transformer can give is influenced by its impedance; the greater the impedance, the lower the maximum short circuit current.






Comments (4)
It’s perfect time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy.
I have read this publish and if I could I wish
to suggest you few fascinating things or tips. Maybe you can write next
articles referring to this article. I wish to learn more issues about it!
You ought to be a part of a contest for one of the greatest sites on the
internet. I am going to highly recommend this site!
Excellent web site. Lots of useful inmfo here. I’m sendimg it to
a few buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And naturally, thank you
in your effort!
Thank you for your comment 😊